Divisibility Math Tricks to Learn the Facts
... Take the last digit in a number. Double and subtract the last digit in your number from the rest of the digits. Repeat the process for larger numbers. Example: 357 (Double the 7 to get 14. Subtract 14 from 35 to get 21 which is divisible by 7 and we can now say that 357 is divisible by 7. ...
... Take the last digit in a number. Double and subtract the last digit in your number from the rest of the digits. Repeat the process for larger numbers. Example: 357 (Double the 7 to get 14. Subtract 14 from 35 to get 21 which is divisible by 7 and we can now say that 357 is divisible by 7. ...
Varsity Meet 4 – March 6, 2013 ANSWERS
... While not terribly useful in this case, it can be easier if the exponents are large.] 2. In total, there are 640+231+100+91+1003 = 2065 women. Therefore, our (unreduced) answer is 1003/2065, and the problem is asking us to find the greatest common divisor (gcd) of 1003 and 2065. METHOD I: The prime ...
... While not terribly useful in this case, it can be easier if the exponents are large.] 2. In total, there are 640+231+100+91+1003 = 2065 women. Therefore, our (unreduced) answer is 1003/2065, and the problem is asking us to find the greatest common divisor (gcd) of 1003 and 2065. METHOD I: The prime ...
Mathematica 2014
... So, if you have the exact securities A and B as above, and two thirds of your portfolio consists of A and the rest B, then you will get 15% return with 0% risk. Smashing. These equations will actually produce curves on a graph of return against risk, so investors can choose shares with certain level ...
... So, if you have the exact securities A and B as above, and two thirds of your portfolio consists of A and the rest B, then you will get 15% return with 0% risk. Smashing. These equations will actually produce curves on a graph of return against risk, so investors can choose shares with certain level ...
Mathematics - Sainik School Nalanda
... well as International system of numeration. (i) 435002 (ii) 1047509 (iii) 25202805 Q9 In each case, use all the digits only once to make the smallest possible 6 digit number. a) 4, 7, 1, 8, 9, 2 b) 5, 1, 2, 9, 6, 8 Q10 Write the smallest and the greatest 7 digit numbers by using the following digits ...
... well as International system of numeration. (i) 435002 (ii) 1047509 (iii) 25202805 Q9 In each case, use all the digits only once to make the smallest possible 6 digit number. a) 4, 7, 1, 8, 9, 2 b) 5, 1, 2, 9, 6, 8 Q10 Write the smallest and the greatest 7 digit numbers by using the following digits ...
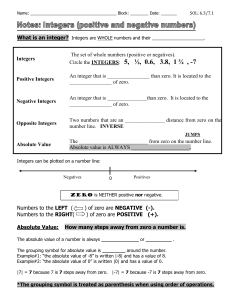
Chapter 1-1 Integers and Absolute Values
... Chapter 1-1 Integers and Absolute Values Pre-assessment: Draw a number line. Graph the following numbers: 2, 5, 0. Identifying opposite situations - Write an opposite for each word. a. win b. simple ...
... Chapter 1-1 Integers and Absolute Values Pre-assessment: Draw a number line. Graph the following numbers: 2, 5, 0. Identifying opposite situations - Write an opposite for each word. a. win b. simple ...
2.5 Floating-Point Representation
... • To resolve the problem of synonymous forms, we will establish a rule that the first digit of the significand must be 1. This results in a unique pattern for each floating-point number. – In the IEEE-754 standard, this 1 is implied meaning that a 1 is assumed after the binary point. – By using an i ...
... • To resolve the problem of synonymous forms, we will establish a rule that the first digit of the significand must be 1. This results in a unique pattern for each floating-point number. – In the IEEE-754 standard, this 1 is implied meaning that a 1 is assumed after the binary point. – By using an i ...
Mathematical Practices - Anderson School District 5
... create a story context for 4 ÷ (1/5), and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient. Use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that 4 ÷ (1/5) = 20 because 20 × (1/5) = ...
... create a story context for 4 ÷ (1/5), and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient. Use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that 4 ÷ (1/5) = 20 because 20 × (1/5) = ...