ppt
... with ~ same speed • But this creates a winding dilemma • So density waves must sweep around galaxy, which move more slowly around the galaxy than the matter inside • This crowding promotes stellar birth and recycling of ISM ...
... with ~ same speed • But this creates a winding dilemma • So density waves must sweep around galaxy, which move more slowly around the galaxy than the matter inside • This crowding promotes stellar birth and recycling of ISM ...
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Black Holes
... as plutonium-244, 244Pu, (81 million years). The short-lived isotopes are particularly interesting. If they formed in an exploding star, that explosion might have triggered the collapse of the huge interstellar cloud in which the Sun formed. ...
... as plutonium-244, 244Pu, (81 million years). The short-lived isotopes are particularly interesting. If they formed in an exploding star, that explosion might have triggered the collapse of the huge interstellar cloud in which the Sun formed. ...
Life cycle of the Stars - Christos N. Hadjichristidis
... The Beginning of the End: Red Giants After Hydrogen is exhausted in core ... Energy released from nuclear fusion counter-acts inward force of gravity. ...
... The Beginning of the End: Red Giants After Hydrogen is exhausted in core ... Energy released from nuclear fusion counter-acts inward force of gravity. ...
Arcturus and Pollux
... • The sun of Neptune with an amazon huntress as a mother. He became the world’s greatest hunter, became overly confident, and came to a tragic end when an itty-bitty scorpion stung him. • Another version, he got a little too close with Diana, and Apollo in anger bet his sister that she couldn’t hit ...
... • The sun of Neptune with an amazon huntress as a mother. He became the world’s greatest hunter, became overly confident, and came to a tragic end when an itty-bitty scorpion stung him. • Another version, he got a little too close with Diana, and Apollo in anger bet his sister that she couldn’t hit ...
Astr40 HWIII(new) - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... 35. The spiral arm disk of the Milky Way is roughly how many light years across? A. 10,000 B. 100,000 C. a million 36. Stars in the disk of the Milky Way orbit in circles. (T or F) 37. There is a mass of about a hundred billion solar masses inside of the Sun's orbit about galactic center. The sun' o ...
... 35. The spiral arm disk of the Milky Way is roughly how many light years across? A. 10,000 B. 100,000 C. a million 36. Stars in the disk of the Milky Way orbit in circles. (T or F) 37. There is a mass of about a hundred billion solar masses inside of the Sun's orbit about galactic center. The sun' o ...
Star project
... • They are extremely burning hot. • The nearest star to us is the sun. • They are made up of mainly hydrogen and helium, but have a little bit of other elements like oxygen and carbon as well. ...
... • They are extremely burning hot. • The nearest star to us is the sun. • They are made up of mainly hydrogen and helium, but have a little bit of other elements like oxygen and carbon as well. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... – Example: Star with 4L and 3M uses 4 times more mass for energy production, but has 3 times more mass, so its life time is a factor ¾=0.75 compared to the sun: 7.5 billion years ([0.75] goes in the box) ...
... – Example: Star with 4L and 3M uses 4 times more mass for energy production, but has 3 times more mass, so its life time is a factor ¾=0.75 compared to the sun: 7.5 billion years ([0.75] goes in the box) ...
Stages 12 to 14
... If a 200 lb (as measured on the earth) person could stand on the surface of a while dwarf, they would ...
... If a 200 lb (as measured on the earth) person could stand on the surface of a while dwarf, they would ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
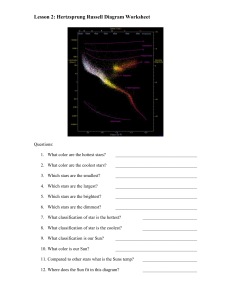
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
here - Boise State University
... 14. What is the cycle or phase a star will spend most of its life in? 15. If our sun is currently 5 billion years old, how much longer will the sun shine brightly for before it runs out of fuel to burn? 16. After our Sun runs our of Hydrogen fuel, what kind of star will it become? 17. What is the na ...
... 14. What is the cycle or phase a star will spend most of its life in? 15. If our sun is currently 5 billion years old, how much longer will the sun shine brightly for before it runs out of fuel to burn? 16. After our Sun runs our of Hydrogen fuel, what kind of star will it become? 17. What is the na ...
Cosmic Collisions
... scattered in random directions, but gravity acts so gradually that planetary orbits are not disturbed. A collision takes about a billion years; during the last billion years, life on Earth evolved from single-celled organisms to amazingly primative apes who still think digital watches are pretty nea ...
... scattered in random directions, but gravity acts so gradually that planetary orbits are not disturbed. A collision takes about a billion years; during the last billion years, life on Earth evolved from single-celled organisms to amazingly primative apes who still think digital watches are pretty nea ...
TU Muscae and the Early-type Overcontact Binaries
... Provide accurate data that are very difficult to determine for single stars such as masses and radii. ...
... Provide accurate data that are very difficult to determine for single stars such as masses and radii. ...
presentation source
... Temperature (or colour or spectral type). – Main Sequence – Red Giants – White Dwarfs ...
... Temperature (or colour or spectral type). – Main Sequence – Red Giants – White Dwarfs ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • Collapsing due to gravity • The collapse is stopped by electron degeneracy pressure ...
... • Collapsing due to gravity • The collapse is stopped by electron degeneracy pressure ...
Scale of the Cosmos ppt.
... Convenient way to write extremely large or extremely small numbers Has 2 parts: base and exponent Base exponent Examples: 103 = 10x10x10 = 1000 10-2 = 1/10x1/10 = 0.01 ...
... Convenient way to write extremely large or extremely small numbers Has 2 parts: base and exponent Base exponent Examples: 103 = 10x10x10 = 1000 10-2 = 1/10x1/10 = 0.01 ...
Stars_Galaxies_Introduction - Etiwanda E
... question to each group Project may still include typical science assignments/routines Incorporates technology at many different levels Students are able to differentiate within the project by choice of assignment ...
... question to each group Project may still include typical science assignments/routines Incorporates technology at many different levels Students are able to differentiate within the project by choice of assignment ...
Star Formation Regions and Planetary Nebulae
... has been thought that the interaction of the fast wind with AGB ejecta leads to the shaping of the resulting PN. In particular, the presence of a (small) initial asphericity will become amplified, and the variety of PN shapes (spherical, elliptical, butterfly, bipolar, etc.) and structural features ...
... has been thought that the interaction of the fast wind with AGB ejecta leads to the shaping of the resulting PN. In particular, the presence of a (small) initial asphericity will become amplified, and the variety of PN shapes (spherical, elliptical, butterfly, bipolar, etc.) and structural features ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... pressure due to heat generated (outward) • Stars neither shrink nor expand, they are in hydrostatic equilibrium, i.e. the forces are equally strong ...
... pressure due to heat generated (outward) • Stars neither shrink nor expand, they are in hydrostatic equilibrium, i.e. the forces are equally strong ...
hw4
... radial motion, magnetic properties, rotation, and color to be determined. An indication (but not direct measurement) of stellar radius, mass, and absolute magnitude can also be obtained from spectral information. The temperature can be determined by scanning the spectrum for the peak (most intense) ...
... radial motion, magnetic properties, rotation, and color to be determined. An indication (but not direct measurement) of stellar radius, mass, and absolute magnitude can also be obtained from spectral information. The temperature can be determined by scanning the spectrum for the peak (most intense) ...
Slide 1 - Fort Bend ISD
... Absolute Magnitude • Brightness a star would have if it were at a standard distance from the Earth • Scientists study globular clusters to compare brightness of stars • All about same distance from Earth ...
... Absolute Magnitude • Brightness a star would have if it were at a standard distance from the Earth • Scientists study globular clusters to compare brightness of stars • All about same distance from Earth ...
Measuring Distances Beyond the Solar System The Characteristics
... The Sun is approximately 150 million (1.5 X 108) km away from Earth. Proxima Centauri is approximately 40 trillion (4.01 X 1013) km away from Earth. Most stars are more than 100 trillion (1.0 X 1014) km from Earth. Astronomers use light years to measure distance to stars or other celestial objects o ...
... The Sun is approximately 150 million (1.5 X 108) km away from Earth. Proxima Centauri is approximately 40 trillion (4.01 X 1013) km away from Earth. Most stars are more than 100 trillion (1.0 X 1014) km from Earth. Astronomers use light years to measure distance to stars or other celestial objects o ...
I : Internal structure of main sequence stars
... The luminosity L The efficiency of the fusion η The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
... The luminosity L The efficiency of the fusion η The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.