Slide 1
... • AGB stars are left with the stellar core surrounded by a relatively thin sphere of hot gas which looks like planetary disk, and called Planetary Nebulae (PNe) (nothing to do with planets per se) • PNe cores continue to cool and become White Dwarfs (94% stars end up as WDs) ...
... • AGB stars are left with the stellar core surrounded by a relatively thin sphere of hot gas which looks like planetary disk, and called Planetary Nebulae (PNe) (nothing to do with planets per se) • PNe cores continue to cool and become White Dwarfs (94% stars end up as WDs) ...
Class 2 Solar System Characteristics Formation Exosolar Planets
... studying orbital phases scientists can calculate particle sizes in the atmospheres of planets. * Polarimetry: Stellar light becomes polarized when it interacts with atmospheric molecules, which could be detected with a polarimeter. So far, ...
... studying orbital phases scientists can calculate particle sizes in the atmospheres of planets. * Polarimetry: Stellar light becomes polarized when it interacts with atmospheric molecules, which could be detected with a polarimeter. So far, ...
18-3 constellations RG
... 13. When a star or galaxy moves quickly away from an observer, the light it emits appears redder than it usually would, this effect is called _____________________________________________. 14. When a star or galaxy moves quickly toward an observer, the light it emits appears bluer than it usually w ...
... 13. When a star or galaxy moves quickly away from an observer, the light it emits appears redder than it usually would, this effect is called _____________________________________________. 14. When a star or galaxy moves quickly toward an observer, the light it emits appears bluer than it usually w ...
Slide 1
... 1. The womb: Stars are born in dense molecular clouds. --The interstellar medium must be dense enough so H atoms can collide and form H2 molecules. This also is facilitated on dust--for other molecules as well. It increases gravitation enough for stars to form in reasonable time. --Different sized c ...
... 1. The womb: Stars are born in dense molecular clouds. --The interstellar medium must be dense enough so H atoms can collide and form H2 molecules. This also is facilitated on dust--for other molecules as well. It increases gravitation enough for stars to form in reasonable time. --Different sized c ...
Document
... 20. Which of the following nuclear fuels does a one solar mass star use over the course of its entire evolution? a. hydrogen, b. hydrogen and helium, c. hydrogen, helium and carbon d. hydrogen, helium, carbon, and neon, e. hydrogen, helium, carbon, neon, and oxygen. 21. A planetary nebula is a. the ...
... 20. Which of the following nuclear fuels does a one solar mass star use over the course of its entire evolution? a. hydrogen, b. hydrogen and helium, c. hydrogen, helium and carbon d. hydrogen, helium, carbon, and neon, e. hydrogen, helium, carbon, neon, and oxygen. 21. A planetary nebula is a. the ...
Sample Exam 3
... B) stars existed out to such large distances that the Universe must be infinite. C) the Sun was on the outer edge of a giant spiral nebula. D) other stars orbit the Sun but look faint because they are in the outer part of the Solar System. 6) Recent observations indicate that the Milky Way is orbite ...
... B) stars existed out to such large distances that the Universe must be infinite. C) the Sun was on the outer edge of a giant spiral nebula. D) other stars orbit the Sun but look faint because they are in the outer part of the Solar System. 6) Recent observations indicate that the Milky Way is orbite ...
A star is a - Trimble County Schools
... • _____________________________________________________________________ __________________ cannot distinguish the distance a star is from earth • Clusters are stars close to each other due to gravitational attraction Binary Stars • _____________________________ – Pairs of stars that revolve around o ...
... • _____________________________________________________________________ __________________ cannot distinguish the distance a star is from earth • Clusters are stars close to each other due to gravitational attraction Binary Stars • _____________________________ – Pairs of stars that revolve around o ...
Roy - WordPress.com
... objects—in particular, a lot of open star clusters. Cassiopeia is named for the queen form Greek mythology who angered the sea god Poseidon when she boasted that her daughter Andromeda was more beautiful than ...
... objects—in particular, a lot of open star clusters. Cassiopeia is named for the queen form Greek mythology who angered the sea god Poseidon when she boasted that her daughter Andromeda was more beautiful than ...
The Earth
... big it is. I mean, you may think it’s a long way down the road to the chemist’s, but that's just peanuts to space. Douglas ...
... big it is. I mean, you may think it’s a long way down the road to the chemist’s, but that's just peanuts to space. Douglas ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... brilliant objects in their home galaxies, visible from millions or even billions of light-years away. Supernovae are of several distinct types, as is evident from their spectra—the graphs astronomers plot showing the distribution of colors of the supernova light. One major category is core-collapse ...
... brilliant objects in their home galaxies, visible from millions or even billions of light-years away. Supernovae are of several distinct types, as is evident from their spectra—the graphs astronomers plot showing the distribution of colors of the supernova light. One major category is core-collapse ...
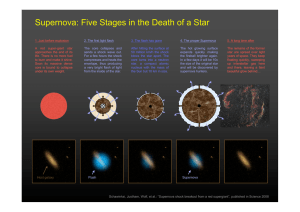
Supernova: Five Stages in the Death of a Star
... to burn and make it shine. Soon its massive dense core is bound to collapse under its own weight. ...
... to burn and make it shine. Soon its massive dense core is bound to collapse under its own weight. ...
Chapter 30 Section 2 Handout
... What does increased temperature from contraction in the core cause the helium core to do? ...
... What does increased temperature from contraction in the core cause the helium core to do? ...
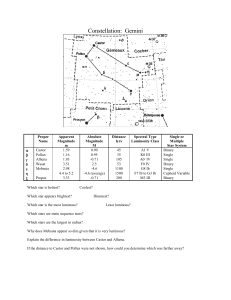
Gemini
... Discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux 1745-46. Independently discovered by John Bevis before 1750. Open star cluster M35 is consisted of several hundred stars (of which Wallenquist has counted 120 brighter than mag 13) scattered over the area covered by the full Moon (30'); the Sky Catalogue 2000. ...
... Discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux 1745-46. Independently discovered by John Bevis before 1750. Open star cluster M35 is consisted of several hundred stars (of which Wallenquist has counted 120 brighter than mag 13) scattered over the area covered by the full Moon (30'); the Sky Catalogue 2000. ...
Chapter 1 Starts and Galaxies
... Nova- star that suddenly increases in brightness in just a few hours or days Nebula- massive cloud of dust and gas between the stars Galaxy- huge collection of stars Spiral Galaxy- galaxy that is shaped like a pin wheel; one of the three types of galaxies Elliptical galaxy- galaxy that may vary in s ...
... Nova- star that suddenly increases in brightness in just a few hours or days Nebula- massive cloud of dust and gas between the stars Galaxy- huge collection of stars Spiral Galaxy- galaxy that is shaped like a pin wheel; one of the three types of galaxies Elliptical galaxy- galaxy that may vary in s ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... 1. In this webquest, you will learn how to identify stars by their magnitude, color, temperature, and spectral class. 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and caus ...
... 1. In this webquest, you will learn how to identify stars by their magnitude, color, temperature, and spectral class. 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and caus ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... 1. In this webquest, you will learn how to identify stars by their magnitude, color, temperature, and spectral class. 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and caus ...
... 1. In this webquest, you will learn how to identify stars by their magnitude, color, temperature, and spectral class. 2. You will investigate the process of nuclear fusion explained by Einstein's famous equation E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and caus ...
Size and Scale
... • An asteroid is a relatively small and rocky object that orbits a star • A comet is a relatively small and icy object that orbits a star ...
... • An asteroid is a relatively small and rocky object that orbits a star • A comet is a relatively small and icy object that orbits a star ...
Stars and Universe Test Review - Garnet Valley School District
... 21. _________________________ uses a curved surface to reflect radio waves from space 22. _________________________ a graph that plots a star’s temperature (x axis) verses its brightness (y-axis) 23. _________________________ irregular shaped galaxies 24. _________________________ the distance from ...
... 21. _________________________ uses a curved surface to reflect radio waves from space 22. _________________________ a graph that plots a star’s temperature (x axis) verses its brightness (y-axis) 23. _________________________ irregular shaped galaxies 24. _________________________ the distance from ...
Round 1
... This is the event that killed the remaining dinosaurs and 2/3 of all life. (K-T extinction) A nova can result when you have these two objects near each other. (White dwarf and other star like red giant) $1000 Variable stars are useful to astronomers because they allow you to tell this. (the distance ...
... This is the event that killed the remaining dinosaurs and 2/3 of all life. (K-T extinction) A nova can result when you have these two objects near each other. (White dwarf and other star like red giant) $1000 Variable stars are useful to astronomers because they allow you to tell this. (the distance ...
Introduction to the Earth
... emissions from a distant supernova and then hoped to make a map of radio emissions from the Milky Way. They adapted a radio dish previously used for communication satellites. They were startled to find that no matter where they pointed the antenna, they measured the same low-level radio signal. Afte ...
... emissions from a distant supernova and then hoped to make a map of radio emissions from the Milky Way. They adapted a radio dish previously used for communication satellites. They were startled to find that no matter where they pointed the antenna, they measured the same low-level radio signal. Afte ...
Stars
... If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hole ...
... If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black hole ...
the life cycle of stars
... become giants or supergiants (Right) and then down to the left to become white dwarfs. ...
... become giants or supergiants (Right) and then down to the left to become white dwarfs. ...
Homework 4
... 4. In figures 3.5 and 3.6 (pp. 74 and 75 in the text), the text shows what is called the “main sequence turnoff” for various open clusters (the text does not call it that, but astronomers use the term). How is the “main sequence turnoff” used to determine the age of an open cluster? ...
... 4. In figures 3.5 and 3.6 (pp. 74 and 75 in the text), the text shows what is called the “main sequence turnoff” for various open clusters (the text does not call it that, but astronomers use the term). How is the “main sequence turnoff” used to determine the age of an open cluster? ...
The Hidden Lives of Galaxies NSTA 2001
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.