Unit 1: The Big Picture
... – Thought Milky Way made up entire universe until 1920s – Small fuzzy patches in telescopes appeared as nebulae, Latin for clouds – Edwin Hubble measured approximate distance to nearby Andromeda…no way Milky Way was that large – 3 Types: spiral, elliptical, irregular ...
... – Thought Milky Way made up entire universe until 1920s – Small fuzzy patches in telescopes appeared as nebulae, Latin for clouds – Edwin Hubble measured approximate distance to nearby Andromeda…no way Milky Way was that large – 3 Types: spiral, elliptical, irregular ...
Star Powerpoint notes
... miles) away. It takes light about 4 years to reach the Earth from there. How luminous is the Sun compared with other stars? The most luminous stars are about a million times brighter and the least luminous stars are about a hundred thousand times dimmer than the Sun. ...
... miles) away. It takes light about 4 years to reach the Earth from there. How luminous is the Sun compared with other stars? The most luminous stars are about a million times brighter and the least luminous stars are about a hundred thousand times dimmer than the Sun. ...
to view SGN5-3-13 - Block Island School
... In math this week, we continued to use measurements. The focus was on estimating the lengths of objects in yards, feet, inches, meters, and centimeters. The main objective was for the children to increase their mathematical proficiency by making use of the structure of objects and measuring tools. F ...
... In math this week, we continued to use measurements. The focus was on estimating the lengths of objects in yards, feet, inches, meters, and centimeters. The main objective was for the children to increase their mathematical proficiency by making use of the structure of objects and measuring tools. F ...
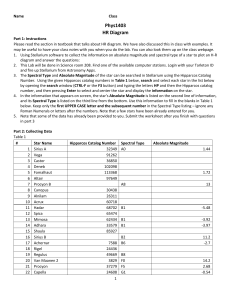
H-R Diagram - Faculty Website Listing
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics
... Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and brightness. ...
... Classifying Stars (pages 753–754) Key Concept: Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and brightness. ...
Slide 1
... Therefore, two stars that appear equally bright might be a closer, dimmer star and a farther, brighter one: ...
... Therefore, two stars that appear equally bright might be a closer, dimmer star and a farther, brighter one: ...
Stellar Physics - University of Reading
... Classical Mechanics and Optics Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics Atomic and Molecular Physics Ideas from Observational Astronomy ...
... Classical Mechanics and Optics Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics Atomic and Molecular Physics Ideas from Observational Astronomy ...
3-Stars AM Adapted - vhs-ees-am
... type of death for Massive and Giant Blue Stars. They are a ...
... type of death for Massive and Giant Blue Stars. They are a ...
Hubble`s Law is the relation between the recession velocity of a
... Hubble's Law is the relation between the recession velocity of a galaxy and its distance: Vr = H d, that is, the velocity of recession Vr equals the distance d times the Hubble constant H. Assuming the galaxies have receded at a constant velocity since the big bang and all galaxies expanded from the ...
... Hubble's Law is the relation between the recession velocity of a galaxy and its distance: Vr = H d, that is, the velocity of recession Vr equals the distance d times the Hubble constant H. Assuming the galaxies have receded at a constant velocity since the big bang and all galaxies expanded from the ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... together by gravity and is composed of gas and emits light. • A star is born when the gases inside a nebula contract together. Inside the nebula you will find new starts. ...
... together by gravity and is composed of gas and emits light. • A star is born when the gases inside a nebula contract together. Inside the nebula you will find new starts. ...
elementary measuring stars
... If brightness (in magnitudes) and distance are known, it is straightforward to establish the intrinsic brightness of a star. Astronomers use another magnitude scale for that, called absolute magnitude. Apparent magnitude is designated as m, absolute magnitude as M. Absolute magnitude is defined as ...
... If brightness (in magnitudes) and distance are known, it is straightforward to establish the intrinsic brightness of a star. Astronomers use another magnitude scale for that, called absolute magnitude. Apparent magnitude is designated as m, absolute magnitude as M. Absolute magnitude is defined as ...
Opakování z minulého cvičení
... (because 2,5125 = 100). A star that is 2 magnitude brighter than another is 2.5122 times brighter, and so on. This is the scale used by astronomers today, with the actual brightness measured by lightdetecting machines, no longer estimated by eye. Because of the way Hipparchus defined the original ma ...
... (because 2,5125 = 100). A star that is 2 magnitude brighter than another is 2.5122 times brighter, and so on. This is the scale used by astronomers today, with the actual brightness measured by lightdetecting machines, no longer estimated by eye. Because of the way Hipparchus defined the original ma ...
HighRedshiftGalaxies
... decrements), somebody suggests that some fraction of their UV-selected population must be suffering star formation which is erratic in its time history. In such a situation, different diagnostics will be sensitive to bursts of activity for different periods, corresponding to the time over which the ...
... decrements), somebody suggests that some fraction of their UV-selected population must be suffering star formation which is erratic in its time history. In such a situation, different diagnostics will be sensitive to bursts of activity for different periods, corresponding to the time over which the ...
Bellringer - Madison County Schools
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its SIZE and TEMPERATURE. ...
... • The brightness of a star depends on both its SIZE and TEMPERATURE. ...
answers
... 1) Measure and calculate the speed of a student walking around the classroom without leaving your seat. Describe how you did this. v = d/t = 2r/T. They need to estimate the distance and use phones to measure the time. 2) This same technique can be used to measure the speed of the Earth as it orbits ...
... 1) Measure and calculate the speed of a student walking around the classroom without leaving your seat. Describe how you did this. v = d/t = 2r/T. They need to estimate the distance and use phones to measure the time. 2) This same technique can be used to measure the speed of the Earth as it orbits ...
6. 1 Star Distances 6. 2 Apparent Brightness, Intrinsic Brightness
... star system in which the stars are too close together to be visible separately. We see a single point of light, and only by taking a spectrum can we determine that there are two stars. ...
... star system in which the stars are too close together to be visible separately. We see a single point of light, and only by taking a spectrum can we determine that there are two stars. ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... 4. Summary of Stellar Properties * Range of temperature, luminosity, mass & radius 5. Stars in the Night Sky * Nearest stars dim & cool * Brightest-appearing stars distant & luminous ...
... 4. Summary of Stellar Properties * Range of temperature, luminosity, mass & radius 5. Stars in the Night Sky * Nearest stars dim & cool * Brightest-appearing stars distant & luminous ...
Oct 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... and hugs close to the Sun, so you see it for a short time in the longer in its group. west after sunset or in the east before sunrise. Jupiter can be out Globular Clusters look like fuzzy balls because they contain all night and always outshines any star. Everyone enjoys its 4 tens of thousands star ...
... and hugs close to the Sun, so you see it for a short time in the longer in its group. west after sunset or in the east before sunrise. Jupiter can be out Globular Clusters look like fuzzy balls because they contain all night and always outshines any star. Everyone enjoys its 4 tens of thousands star ...
2 Measurements in Astronomy
... distances? For stars that are further away, astronomers use the inverse square law. Inverse square law states that apparent brightness is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. If you know how bright the star should be, and you know how bright it appears to be, you can calculate ...
... distances? For stars that are further away, astronomers use the inverse square law. Inverse square law states that apparent brightness is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. If you know how bright the star should be, and you know how bright it appears to be, you can calculate ...
Lecture 12
... The relationship between redshift and distance is linear for low values of z, but becomes rather complex when we look at very distant objects (very far back in time). As the Universe expands the value of H0 changes as the geometry of the Universe changes. Partly this is a ‘standard’ result from appl ...
... The relationship between redshift and distance is linear for low values of z, but becomes rather complex when we look at very distant objects (very far back in time). As the Universe expands the value of H0 changes as the geometry of the Universe changes. Partly this is a ‘standard’ result from appl ...
ppt
... “star” in the galaxy and assume that it is the same as the brightest star in nearby galaxies. BUT, brightest object may not be a star at all! Overall galactic apparent brightness method – for distant galaxies, simply use overall brightness of galaxy to gauge distance. Very error prone! ...
... “star” in the galaxy and assume that it is the same as the brightest star in nearby galaxies. BUT, brightest object may not be a star at all! Overall galactic apparent brightness method – for distant galaxies, simply use overall brightness of galaxy to gauge distance. Very error prone! ...
Watching Galaxies Form Near the Beginning of Time
... at z=2.4, from NASA Infrared Telescope Facility, April 2003) ...
... at z=2.4, from NASA Infrared Telescope Facility, April 2003) ...
Malmquist bias
The Malmquist bias is an effect in observational astronomy which leads to the preferential detection of intrinsically bright objects. It was first described in 1922 by Swedish astronomer Gunnar Malmquist (1893–1982), who then greatly elaborated upon this work in 1925. In statistics, this bias is referred to as a selection bias and affects the survey results in a brightness limited survey, where stars below a certain apparent brightness are not included. Since observed stars and galaxies appear dimmer when farther away, the brightness that is measured will fall off with distance until their brightness falls below the observational threshold. Objects which are more luminous, or intrinsically brighter, can be observed at a greater distance, creating a false trend of increasing intrinsic brightness, and other related quantities, with distance. This effect has led to many spurious claims in the field of astronomy. Properly correcting for these effects has become an area of great focus.