
practice exam #1
... a. The low-density planets all have weaker gravity, so they have moved further away b. The high-density planets have very strong magnetic fields that pull them closer c. During solar system formation, the inner solar system was too hot to retain most ice and gases d. Astronomers don’t know why 12. W ...
... a. The low-density planets all have weaker gravity, so they have moved further away b. The high-density planets have very strong magnetic fields that pull them closer c. During solar system formation, the inner solar system was too hot to retain most ice and gases d. Astronomers don’t know why 12. W ...
And let there be light!
... The Universe – Everything there is; all energy, space, and matter Astronomy – The study of the universe beyond the earth’s atmosphere. Solar System – the Sun and all the objects that travel around it due to gravitational force. Objects = planets, over 60 satellites (moons) orbiting the planets, thou ...
... The Universe – Everything there is; all energy, space, and matter Astronomy – The study of the universe beyond the earth’s atmosphere. Solar System – the Sun and all the objects that travel around it due to gravitational force. Objects = planets, over 60 satellites (moons) orbiting the planets, thou ...
Physical Attributes of Stars
... c. Explain why the pattern of stars in a constellation stays the same, but a planet can be seen in different locations at different times. d. Identify how technology is used to observe distant objects in the sky. S4E2. Students will model the position and motion of the earth in the solar system and ...
... c. Explain why the pattern of stars in a constellation stays the same, but a planet can be seen in different locations at different times. d. Identify how technology is used to observe distant objects in the sky. S4E2. Students will model the position and motion of the earth in the solar system and ...
File - Prairie Science
... leading to the release of new elements into the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, ...
... leading to the release of new elements into the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, ...
Space Unit Exam /31
... e. ____ In the early days of our solar system, all planets were made of the same solids, liquids and gases. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ...
... e. ____ In the early days of our solar system, all planets were made of the same solids, liquids and gases. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ...
Planets and Stars Study Guide Test Date: ______ Vocabulary to
... different place each night for a week, what is the object? Why does this happen? ...
... different place each night for a week, what is the object? Why does this happen? ...
The Planets in the Solar System There are an uncountable number
... formed during the collapse of a nebula into a thin disk of gas and dust. A proto-star (proto = early) forms at the core, surrounded by a rotating proto-planetary disk. Through a process called accretion (i.e., sticky collision) dust particles in the disk steadily accumulate mass to form ever-larger ...
... formed during the collapse of a nebula into a thin disk of gas and dust. A proto-star (proto = early) forms at the core, surrounded by a rotating proto-planetary disk. Through a process called accretion (i.e., sticky collision) dust particles in the disk steadily accumulate mass to form ever-larger ...
Solar System Notes
... Solar System Notes Solar System- A group of planets, moons and other satellites that orbit around a star. The Sun-the most important object in our solar system. Our sun provides light and heat for earth Our sun is a star When the sun rises and sets it looks like it is moving but it is not actually m ...
... Solar System Notes Solar System- A group of planets, moons and other satellites that orbit around a star. The Sun-the most important object in our solar system. Our sun provides light and heat for earth Our sun is a star When the sun rises and sets it looks like it is moving but it is not actually m ...
Homework #5 Chapter 3: Solar System Due
... highly elliptical orbits. Many of these worlds are very close to their stars, some within 0.1 AU, even planets massive enough to be "gas giants." It is possible, however, that planetary systems such as our own would not produce enough motion in their stars to detect from Earth. The effects of such s ...
... highly elliptical orbits. Many of these worlds are very close to their stars, some within 0.1 AU, even planets massive enough to be "gas giants." It is possible, however, that planetary systems such as our own would not produce enough motion in their stars to detect from Earth. The effects of such s ...
Gravity - Pulling it all Together
... the Sun. a. Find the net force on the Moon due to the gravitational attraction of both the Earth and the Sun when they are aligned Earth, Moon, Sun. (2.4x1020 N towards Sun) ...
... the Sun. a. Find the net force on the Moon due to the gravitational attraction of both the Earth and the Sun when they are aligned Earth, Moon, Sun. (2.4x1020 N towards Sun) ...
Extra-Solar Planets continued
... star called Gliese 436, that lies about 33 light-years from Earth in the direction of the constellation of Leo. This Neptune-sized planet also sits 3 million miles from its star and whips around in a tight circular orbit once every 2.64 days. Besides the exoplanet's size, what makes the discovery re ...
... star called Gliese 436, that lies about 33 light-years from Earth in the direction of the constellation of Leo. This Neptune-sized planet also sits 3 million miles from its star and whips around in a tight circular orbit once every 2.64 days. Besides the exoplanet's size, what makes the discovery re ...
Space - mrhandley.co.uk
... sun. In ancient Greece, the sun was called Helios. Every planet in the solar system and Pluto rotate around the sun. The sun is not a planet and is actually a big star. The solar system is named after the scientific name for the sun, sol. The sun is definitely the largest thing in the solar system. ...
... sun. In ancient Greece, the sun was called Helios. Every planet in the solar system and Pluto rotate around the sun. The sun is not a planet and is actually a big star. The solar system is named after the scientific name for the sun, sol. The sun is definitely the largest thing in the solar system. ...
File
... solid, but a sphere of plasma held together by its own gravity. We can see stars at night due to a process called thermonuclear fusion. This process changes hydrogen into helium at the core of a star, releasing energy that radiates out into outer space. That is why we can see stars so brightly in th ...
... solid, but a sphere of plasma held together by its own gravity. We can see stars at night due to a process called thermonuclear fusion. This process changes hydrogen into helium at the core of a star, releasing energy that radiates out into outer space. That is why we can see stars so brightly in th ...
Centre of Mass
... • For life to exist on a palnet, it must also be in the habitable zone. This is the region in the solar system which is neither too hot nor too cold, but just right. Astronomers believe that in other solar systems, too, such habitable zones exist and life is more probable in those planets which fall ...
... • For life to exist on a palnet, it must also be in the habitable zone. This is the region in the solar system which is neither too hot nor too cold, but just right. Astronomers believe that in other solar systems, too, such habitable zones exist and life is more probable in those planets which fall ...
SEM 1.4_Astronomy
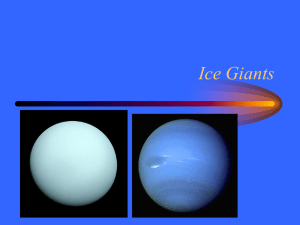
... Of the terrestrial planets, Earth is the most dense. Four of the five outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) are gas giants consisting of thick, outer layers of gaseous materials (perhaps with small rocky cores). The fifth outer planet (Pluto) has an unknown composition, but it app ...
... Of the terrestrial planets, Earth is the most dense. Four of the five outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) are gas giants consisting of thick, outer layers of gaseous materials (perhaps with small rocky cores). The fifth outer planet (Pluto) has an unknown composition, but it app ...
121mtr09
... Answered pretty well but some left out the actual density of the moon which is an important part of the overall answer If the moon formed by accretion then its density should be identical to the Earth’s ...
... Answered pretty well but some left out the actual density of the moon which is an important part of the overall answer If the moon formed by accretion then its density should be identical to the Earth’s ...
ASTRONOMY 101 SAMPLE FIRST EXAM [1] Kepler`s Law relating
... Kepler’s third law states that a planet in an elliptical orbit moves with a velocity such that (a) the planet moves slower as it approaches nearer the sun. (b) the line between the Sun and the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times. (c) it won’t need to stop for the comets going by. __________ ...
... Kepler’s third law states that a planet in an elliptical orbit moves with a velocity such that (a) the planet moves slower as it approaches nearer the sun. (b) the line between the Sun and the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times. (c) it won’t need to stop for the comets going by. __________ ...
Name____________________________________________________________________ Astronomy Packet 3
... what Italian astronomer to reexamine the heavens? ______________________.Using this tool Galileo was able to see that the moon was not_______________ but was able to see______________ and ____________________ as well what he thought were _____________________but was actually ________________________ ...
... what Italian astronomer to reexamine the heavens? ______________________.Using this tool Galileo was able to see that the moon was not_______________ but was able to see______________ and ____________________ as well what he thought were _____________________but was actually ________________________ ...
planets
... barest perceptible trace of charged particles from the Sun. Shrouded in the cloak of mystery, Venus, our nearest planetary neighbor, takes the name of the Roman goddess of love. For some unknown reason, Venus rotates on its axis in retrograde—that is, in the reverse direction of its revolution aroun ...
... barest perceptible trace of charged particles from the Sun. Shrouded in the cloak of mystery, Venus, our nearest planetary neighbor, takes the name of the Roman goddess of love. For some unknown reason, Venus rotates on its axis in retrograde—that is, in the reverse direction of its revolution aroun ...
lung volumes and capacities
... Rocks that orbit mostly between Mars and Jupiter. Objects in space made of frozen gases, rock pieces, and dust. They orbit the Sun in long, narrow orbits CONSTELLATION A group of stars that forms a pattern Large system of gases, dust, and many stars GALAXY The mutual force of attractions that exists ...
... Rocks that orbit mostly between Mars and Jupiter. Objects in space made of frozen gases, rock pieces, and dust. They orbit the Sun in long, narrow orbits CONSTELLATION A group of stars that forms a pattern Large system of gases, dust, and many stars GALAXY The mutual force of attractions that exists ...
ppt
... Gas cloud starts to collapse in on itself due to its own gravitational pull. As it collapses, it rotates faster and flattens. The central part of the gas cloud forms the Sun – nuclear reactions start in its core. ...
... Gas cloud starts to collapse in on itself due to its own gravitational pull. As it collapses, it rotates faster and flattens. The central part of the gas cloud forms the Sun – nuclear reactions start in its core. ...
Summing up the solar system
... Jupiter, which was also thought to be a storm Uranus & Neptune are about the same size Jupiter is the largest planet ...
... Jupiter, which was also thought to be a storm Uranus & Neptune are about the same size Jupiter is the largest planet ...
Our Solar System Formation
... planets. Where gas giants are formed there is rocky solid material and much more gas. The rocky material first accretes solid material to become planetesimals and then with its gravity it will collect the gasses around making them a giant like Jupiter. At the beginning of our solar system there wher ...
... planets. Where gas giants are formed there is rocky solid material and much more gas. The rocky material first accretes solid material to become planetesimals and then with its gravity it will collect the gasses around making them a giant like Jupiter. At the beginning of our solar system there wher ...
Satellite system (astronomy)

A satellite system is a set of gravitationally bound objects in orbit around a planetary mass object or minor planet. Generally speaking, it is a set of natural satellites (moons), although such systems may also consist of bodies such as circumplanetary disks, ring systems, moonlets, minor-planet moons and artificial satellites any of which may themselves have satellite systems of their own. Some satellite systems have complex interactions with both their parent and other moons, including magnetic, tidal, atmospheric and orbital interactions such as orbital resonances and libration. Individually major satellite objects are designated in Roman numerals. Satellite systems are referred to either by the possessive adjectives of their primary (e.g. ""Jovian system""), or less commonly by the name of their primary (e.g. ""Jupiter system""). Where only one satellite is known, or it is a binary orbiting a common centre of gravity, it may be referred to using the hyphenated names of the primary and major satellite (e.g. the ""Earth-Moon system"").Many Solar System objects are known to possess satellite systems, though their origin is still unclear. Notable examples include the largest satellite system, the Jovian system, with 67 known moons (including the large Galilean moons) and the Saturnian System with 62 known moons (and the most visible ring system in the Solar System). Both satellite systems are large and diverse. In fact all of the giant planets of the Solar System possess large satellite systems as well as planetary rings, and it is inferred that this is a general pattern. Several objects farther from the Sun also have satellite systems consisting of multiple moons, including the complex Plutonian system where multiple objects orbit a common center of mass, as well as many asteroids and plutinos. Apart from the Earth-Moon system and Mars' system of two tiny natural satellites, the other terrestrial planets are generally not considered satellite systems, although some have been orbited by artificial satellites originating from Earth.Little is known of satellite systems beyond the Solar System, although it is inferred that natural satellites are common. J1407b is an example of an extrasolar satellite system. It is also theorised that Rogue planets ejected from their planetary system could retain a system of satellites.
















![ASTRONOMY 101 SAMPLE FIRST EXAM [1] Kepler`s Law relating](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017742958_1-c5c5f19bce1080c6ad7c1fc92906a06f-300x300.png)





