Center for Origins Studies: CalSpace
... Roots of Science in Mysticism Mystical concepts of elements & reasons for change Babylonian argument that water = “theory of everything” Source of all life between Tigris & Euphrates Capable of change from solid to liquid to gas Water, Fire, Earth, Air, and Aether/Quintessence (Greece) Water, Fire, ...
... Roots of Science in Mysticism Mystical concepts of elements & reasons for change Babylonian argument that water = “theory of everything” Source of all life between Tigris & Euphrates Capable of change from solid to liquid to gas Water, Fire, Earth, Air, and Aether/Quintessence (Greece) Water, Fire, ...
astronomy review sheet2
... 19. How many degrees in its orbit does the Earth move each day? (think about what the shape of our orbit is close to and how many days are in a year) 20. Calculate the eccentricity of the ellipse below: ...
... 19. How many degrees in its orbit does the Earth move each day? (think about what the shape of our orbit is close to and how many days are in a year) 20. Calculate the eccentricity of the ellipse below: ...
AST 1002 Fall 2014 Midterm Exam Version 1
... it is during this slower period that they appear to move backwards. B) Apparent retrograde motion is an illusion created by turbulence in Earth's atmosphere. C) As Earth passes another planet, the other planet appears to move backward with respect to the background stars, but the planet's motion doe ...
... it is during this slower period that they appear to move backwards. B) Apparent retrograde motion is an illusion created by turbulence in Earth's atmosphere. C) As Earth passes another planet, the other planet appears to move backward with respect to the background stars, but the planet's motion doe ...
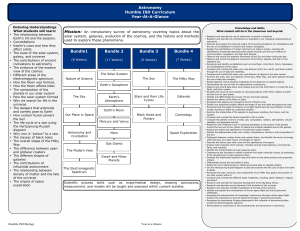
Astronomy Humble ISD Curriculum Year-At-A
... Mission: An introductory survey of astronomy covering topics about the solar system, galaxies, evolution of the cosmos, and the history and methods used to explore these phenomena. ...
... Mission: An introductory survey of astronomy covering topics about the solar system, galaxies, evolution of the cosmos, and the history and methods used to explore these phenomena. ...
Document
... Plato (c. 350 B.C.) suggested the need for a framework (e.g. stars revolve around the Earth which is fixed) “Geocentric Universe”: fixed relationship between stars Ptolemy (c. 100 A.D.) refined the system introduced (most notably) by Hipparchus to explain the observed motions of the stars and planet ...
... Plato (c. 350 B.C.) suggested the need for a framework (e.g. stars revolve around the Earth which is fixed) “Geocentric Universe”: fixed relationship between stars Ptolemy (c. 100 A.D.) refined the system introduced (most notably) by Hipparchus to explain the observed motions of the stars and planet ...
The Solar System - Teachers TryScience
... objects that revolve around it. • Our Solar System consists of the Sun and nine known planets and the moons that orbit those planets. • The force of gravity keeps planets in orbit around the sun. ...
... objects that revolve around it. • Our Solar System consists of the Sun and nine known planets and the moons that orbit those planets. • The force of gravity keeps planets in orbit around the sun. ...
Astronomy
... Astronomy differs from Astrology in that one is based on observable and quantifiable data. The body of knowledge in this field has grown through the centuries due to measurable and reproducible investigations. The other is more subjective. ...
... Astronomy differs from Astrology in that one is based on observable and quantifiable data. The body of knowledge in this field has grown through the centuries due to measurable and reproducible investigations. The other is more subjective. ...
File
... Changes in the length and direction of an object’s shadow show the changing position of the Sun during the day although the patterns of the stars in the sky, to include the Sun, stay the same. Orbit- The path an object takes as it moves around another object in space Planet- A large body of rock or ...
... Changes in the length and direction of an object’s shadow show the changing position of the Sun during the day although the patterns of the stars in the sky, to include the Sun, stay the same. Orbit- The path an object takes as it moves around another object in space Planet- A large body of rock or ...
lecture9 Solar System1
... Protoplanets / planet core grew larger gravity captured hydrogen & helium composition similar to Sun gaseous accretion disk forms around planet Moons form in disk around planet ...
... Protoplanets / planet core grew larger gravity captured hydrogen & helium composition similar to Sun gaseous accretion disk forms around planet Moons form in disk around planet ...
Earth, Moon, Sun Study Guide
... The earth is spinning (rotating) on its axis. This makes it look like the moon and sun move across the sky. 5) How long does it take the earth to make one rotation? 24 hours (one day) 6) What is an earth revolution and how long is it? It is when the earth orbits, or goes around, the sun. It takes 36 ...
... The earth is spinning (rotating) on its axis. This makes it look like the moon and sun move across the sky. 5) How long does it take the earth to make one rotation? 24 hours (one day) 6) What is an earth revolution and how long is it? It is when the earth orbits, or goes around, the sun. It takes 36 ...
some interesting facts about planets
... All the planets in the solar system have been explored with telescopes .So far,nothing living has been found.The other planets in our system all seem to be too hot, too cold, or made entirely of gases. ...
... All the planets in the solar system have been explored with telescopes .So far,nothing living has been found.The other planets in our system all seem to be too hot, too cold, or made entirely of gases. ...
The Planets in our Solar System Solar System Basics
... More on planet formation . . . • Temperature and distance from the Sun influenced the condensation of various substances within the evolving solar system. • Eventually, the condensing material merged to form large bodies hundreds of kilometers in diameter. ...
... More on planet formation . . . • Temperature and distance from the Sun influenced the condensation of various substances within the evolving solar system. • Eventually, the condensing material merged to form large bodies hundreds of kilometers in diameter. ...
exercise 3
... Nine major planets are currently known. They are commonly divided into two groups: the inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) and the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune). The inner planets are small and are composed primarily of rock and iron. The outer planets are much lar ...
... Nine major planets are currently known. They are commonly divided into two groups: the inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) and the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune). The inner planets are small and are composed primarily of rock and iron. The outer planets are much lar ...
The Solar System
... objects that revolve around it. • Our Solar System consists of the Sun and nine known planets and the moons that orbit those planets. • The force of gravity keeps planets in orbit around the sun. ...
... objects that revolve around it. • Our Solar System consists of the Sun and nine known planets and the moons that orbit those planets. • The force of gravity keeps planets in orbit around the sun. ...
Coursework 2 File
... (iii). By assuming that the planets in the Solar System are on circular orbits, Copernicus devised a method for calculating the sidereal period for either an inferior or superior planet based on knowledge of the Earth’s sidereal period and observations of the synodic period. In lectures we derived t ...
... (iii). By assuming that the planets in the Solar System are on circular orbits, Copernicus devised a method for calculating the sidereal period for either an inferior or superior planet based on knowledge of the Earth’s sidereal period and observations of the synodic period. In lectures we derived t ...
Universal Gravitation
... The gravitational influence of every object is exerted through all space. ...
... The gravitational influence of every object is exerted through all space. ...
Telephone Quizzes for ASTR 200 1999 Revision
... the easy fragmentation of comets when in the strong gravitational fields of other bodies. spacecraft experiments which have sampled comets directly. the orbital characteristics of comets. the presence of the Oort cloud . the fact that comet tails point away from the Sun. ...
... the easy fragmentation of comets when in the strong gravitational fields of other bodies. spacecraft experiments which have sampled comets directly. the orbital characteristics of comets. the presence of the Oort cloud . the fact that comet tails point away from the Sun. ...
Sample Chapter
... The sun isn’t a planet. It is a star at the centre of the solar system. It formed 5 billion years ago from a cloud of gas and dust. The sun’s diameter is 1,392,000 kilometres. It is much bigger than the Earth. ...
... The sun isn’t a planet. It is a star at the centre of the solar system. It formed 5 billion years ago from a cloud of gas and dust. The sun’s diameter is 1,392,000 kilometres. It is much bigger than the Earth. ...
star chart - Ontario Science Centre
... During this full Moon, the Moon will be at its closest point in its orbit around Earth JULY 28 Southern Delta Aquariid meteor shower peaks; Not always the best to see from Canada but at least the Moon will set early this night AUG 10 * Second Supermoon of the year; This will be the largest full Moon ...
... During this full Moon, the Moon will be at its closest point in its orbit around Earth JULY 28 Southern Delta Aquariid meteor shower peaks; Not always the best to see from Canada but at least the Moon will set early this night AUG 10 * Second Supermoon of the year; This will be the largest full Moon ...
Task 1: The Solar System Task 2: Orbits of the
... The Earth spins on an axis that is tilted. The North Pole has summer when it is tilted towards the Sun. The North Pole has winter when it is tilted towards the Sun. The South Pole and North Pole have summer at the same time. It is warmer in summer because the earth is closer to the Sun. It is warmer ...
... The Earth spins on an axis that is tilted. The North Pole has summer when it is tilted towards the Sun. The North Pole has winter when it is tilted towards the Sun. The South Pole and North Pole have summer at the same time. It is warmer in summer because the earth is closer to the Sun. It is warmer ...
Aims You are going to create a poster about space. First work
... The Earth spins on an axis that is tilted. The North Pole has summer when it is tilted towards the Sun. The North Pole has winter when it is tilted towards the Sun. The South Pole and North Pole have summer at the same time. It is warmer in summer because the earth is closer to the Sun. It is warmer ...
... The Earth spins on an axis that is tilted. The North Pole has summer when it is tilted towards the Sun. The North Pole has winter when it is tilted towards the Sun. The South Pole and North Pole have summer at the same time. It is warmer in summer because the earth is closer to the Sun. It is warmer ...
History of Astronomy Notes
... Bright surface of the Sun had dark spots (imperfections) that changed and moved across its surface. Observed solar rotation. Conclusions: The sun is huge, imperfect and rotating. If the sun rotates, why not the Earth? ...
... Bright surface of the Sun had dark spots (imperfections) that changed and moved across its surface. Observed solar rotation. Conclusions: The sun is huge, imperfect and rotating. If the sun rotates, why not the Earth? ...
SCI 103
... 18) Kepler’s first two Laws of Planetary Motion contradicted the Aristotelian/Ptolemaic Model of the Universe in two fundamental ways. What are Kepler’s first two Laws of Planetary Motion and how were they anti-Aristotelian? Kepler’s 1ST law states that planets orbit, not on circles, but on ellipse ...
... 18) Kepler’s first two Laws of Planetary Motion contradicted the Aristotelian/Ptolemaic Model of the Universe in two fundamental ways. What are Kepler’s first two Laws of Planetary Motion and how were they anti-Aristotelian? Kepler’s 1ST law states that planets orbit, not on circles, but on ellipse ...
GLY 1001 Answers to Chapter 21 Review Questions
... amount of retrograde motion observed for each planet. 3. Copernicus placed the Sun at the center of the solar system. Next to the theory of organic evolution, this proposal perhaps most disrupted the human concept of our role in the universe. 4. Tycho Brahe's greatest contribution to science was his ...
... amount of retrograde motion observed for each planet. 3. Copernicus placed the Sun at the center of the solar system. Next to the theory of organic evolution, this proposal perhaps most disrupted the human concept of our role in the universe. 4. Tycho Brahe's greatest contribution to science was his ...
Satellite system (astronomy)

A satellite system is a set of gravitationally bound objects in orbit around a planetary mass object or minor planet. Generally speaking, it is a set of natural satellites (moons), although such systems may also consist of bodies such as circumplanetary disks, ring systems, moonlets, minor-planet moons and artificial satellites any of which may themselves have satellite systems of their own. Some satellite systems have complex interactions with both their parent and other moons, including magnetic, tidal, atmospheric and orbital interactions such as orbital resonances and libration. Individually major satellite objects are designated in Roman numerals. Satellite systems are referred to either by the possessive adjectives of their primary (e.g. ""Jovian system""), or less commonly by the name of their primary (e.g. ""Jupiter system""). Where only one satellite is known, or it is a binary orbiting a common centre of gravity, it may be referred to using the hyphenated names of the primary and major satellite (e.g. the ""Earth-Moon system"").Many Solar System objects are known to possess satellite systems, though their origin is still unclear. Notable examples include the largest satellite system, the Jovian system, with 67 known moons (including the large Galilean moons) and the Saturnian System with 62 known moons (and the most visible ring system in the Solar System). Both satellite systems are large and diverse. In fact all of the giant planets of the Solar System possess large satellite systems as well as planetary rings, and it is inferred that this is a general pattern. Several objects farther from the Sun also have satellite systems consisting of multiple moons, including the complex Plutonian system where multiple objects orbit a common center of mass, as well as many asteroids and plutinos. Apart from the Earth-Moon system and Mars' system of two tiny natural satellites, the other terrestrial planets are generally not considered satellite systems, although some have been orbited by artificial satellites originating from Earth.Little is known of satellite systems beyond the Solar System, although it is inferred that natural satellites are common. J1407b is an example of an extrasolar satellite system. It is also theorised that Rogue planets ejected from their planetary system could retain a system of satellites.