reviewTWO
... REVIEW TIME DEFINE THE FOLLOWING: Atom, element, compound, mixture, proton, neutron, electron, atomic number, Mass number, atomic mass, isotope, ion, ionic charge, cation, anion, polyatomic ions, diatomic ions. Write the Chemical Formula (1) sodium nitrite (2) copper (II)oxide (3) sodium iodide (4) ...
... REVIEW TIME DEFINE THE FOLLOWING: Atom, element, compound, mixture, proton, neutron, electron, atomic number, Mass number, atomic mass, isotope, ion, ionic charge, cation, anion, polyatomic ions, diatomic ions. Write the Chemical Formula (1) sodium nitrite (2) copper (II)oxide (3) sodium iodide (4) ...
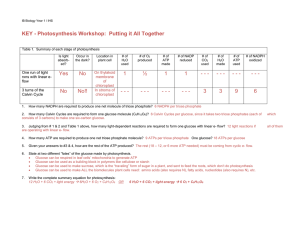
KEY - Photosynthesis Workshop: Putting it All Together
... consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
... consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
abstracts_e
... Presently, a trapping system for cooling highly-charged ions that were extracted from the new Stockholm electron-beam ion trap (S-EBIT) is being set up at AlbaNova (Fig.1). The experiment aims at production of low temperature (emittance) highly-charged ions at very low energy for injection into the ...
... Presently, a trapping system for cooling highly-charged ions that were extracted from the new Stockholm electron-beam ion trap (S-EBIT) is being set up at AlbaNova (Fig.1). The experiment aims at production of low temperature (emittance) highly-charged ions at very low energy for injection into the ...
On the Generation and Injection of Heavy
... accelerated to an energy of 100 MeV. Some sets of random numbers gave results which seemed too optimistic; others gave believable results, while others gave no results. The problem is that random numbers generated by a computer are not truly random. The numbers in Table 2 are representative of the o ...
... accelerated to an energy of 100 MeV. Some sets of random numbers gave results which seemed too optimistic; others gave believable results, while others gave no results. The problem is that random numbers generated by a computer are not truly random. The numbers in Table 2 are representative of the o ...
Lifeline Week 6 Follow-Along Sheet Cellular Respiration
... Within the ETC, electrons are passed along the _________ membrane of the mitochondria by transport proteins. H+ ions move across the membrane, creating a __________________________. This proton gradient creates a __________________________________ across the membrane. This separation of charge is ha ...
... Within the ETC, electrons are passed along the _________ membrane of the mitochondria by transport proteins. H+ ions move across the membrane, creating a __________________________. This proton gradient creates a __________________________________ across the membrane. This separation of charge is ha ...
Module 1 (Review)
... form from monomers. ● Compare the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids in organisms. ...
... form from monomers. ● Compare the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids in organisms. ...
Ion Mobility Spectrometry Study of Negative Corona Discharge in N
... experiment the pure N2 contains approximately 7 ppm H2O and this H2O density is sufficient to form water clusters at the negative ions. Therefore we have assigned the peaks observed to the ions NO3.(H2O), CO4.(H2O) and CO3.(H2O), according to Eisele et al. [10]. Similar assignment was possible al ...
... experiment the pure N2 contains approximately 7 ppm H2O and this H2O density is sufficient to form water clusters at the negative ions. Therefore we have assigned the peaks observed to the ions NO3.(H2O), CO4.(H2O) and CO3.(H2O), according to Eisele et al. [10]. Similar assignment was possible al ...
1 NORMAL and ABNORMAL CELLULAR FUNCTION Lois E
... and into interstitial spaces. Capillary filtration is a function of the arterial pressure, venous pressure and also the effects of gravity. Edema (swelling) which occurs when inflammation results histamine release which, in turn, causes dilation of precapillary sphincters and arterioles in the affec ...
... and into interstitial spaces. Capillary filtration is a function of the arterial pressure, venous pressure and also the effects of gravity. Edema (swelling) which occurs when inflammation results histamine release which, in turn, causes dilation of precapillary sphincters and arterioles in the affec ...
Enzymes
... • Cooperativity is a form of allosteric regulation that can amplify enzyme activity • In cooperativity, binding by a substrate to one active site stabilizes favorable conformational changes at all ...
... • Cooperativity is a form of allosteric regulation that can amplify enzyme activity • In cooperativity, binding by a substrate to one active site stabilizes favorable conformational changes at all ...
The surface charge of a cell lipid membrane
... The surface charge of the cell membrane has been studied in many experimental works. We will not consider all works and may refer only to [9,10], where the experimental data of the surface charge of cell membranes obtained by different methods are given. A range of results is broad enough: σ m = 0.3 ...
... The surface charge of the cell membrane has been studied in many experimental works. We will not consider all works and may refer only to [9,10], where the experimental data of the surface charge of cell membranes obtained by different methods are given. A range of results is broad enough: σ m = 0.3 ...
Harvesting Energy: Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration
... Under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted into lactate or ethanol, a process called fermentation Fermentation does not produce more ATP, but is necessary to regenerate the high-energy electron carrier molecule NAD+, which must be available for glycolysis to continue ...
... Under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted into lactate or ethanol, a process called fermentation Fermentation does not produce more ATP, but is necessary to regenerate the high-energy electron carrier molecule NAD+, which must be available for glycolysis to continue ...
Plant Notes
... The air spaces in the spongy mesophyll connect with the exterior through stomata, small openings in the epidermis that allow carbon dioxide, water, and oxygen to diffuse into and out of the leaf. ...
... The air spaces in the spongy mesophyll connect with the exterior through stomata, small openings in the epidermis that allow carbon dioxide, water, and oxygen to diffuse into and out of the leaf. ...
Mitochondria
... called them "bioblasts". • The term "mitochondria" was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. • Leonor Michaelis discovered Janus green can be used as a supravital stain for mitochondria in 1900. • In 1913 particles from extracts of guinea-pig liver were linked to respiration by Otto Heinrich Warburg, which ...
... called them "bioblasts". • The term "mitochondria" was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. • Leonor Michaelis discovered Janus green can be used as a supravital stain for mitochondria in 1900. • In 1913 particles from extracts of guinea-pig liver were linked to respiration by Otto Heinrich Warburg, which ...
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... • Also produces 2 NADH and 4 ATP • Pyruvate is oxidized to Acetyl CoA and CO2 is removed ...
... • Also produces 2 NADH and 4 ATP • Pyruvate is oxidized to Acetyl CoA and CO2 is removed ...
Enzymes lecture 2
... The region that contains the catalytic residues, binds the substrate, and then carries out the reaction is known as the active site. Enzymes can also contain sites that bind cofactors, which are needed for catalysis. Some enzymes also have binding sites for small molecules, which are often direct or ...
... The region that contains the catalytic residues, binds the substrate, and then carries out the reaction is known as the active site. Enzymes can also contain sites that bind cofactors, which are needed for catalysis. Some enzymes also have binding sites for small molecules, which are often direct or ...
England - Food Standards Agency
... will make amendments to the Food Supplements (England) Regulations 2003 which: Remove Schedules 1 and 2 which list the vitamins, minerals and their sources permitted for use in food supplements. Replace the references to the Schedules in Regulation 5 with direct, ‘ambulatory’, references to the Anne ...
... will make amendments to the Food Supplements (England) Regulations 2003 which: Remove Schedules 1 and 2 which list the vitamins, minerals and their sources permitted for use in food supplements. Replace the references to the Schedules in Regulation 5 with direct, ‘ambulatory’, references to the Anne ...
File - Pomp
... • H+ potential E is stockpiled inside the inner membrane of mitochondria via redox reactions • E-'s from H atoms are passed to ETS and uses the energy to pump H+ through ...
... • H+ potential E is stockpiled inside the inner membrane of mitochondria via redox reactions • E-'s from H atoms are passed to ETS and uses the energy to pump H+ through ...
Enzymes
... and control the rates of chemical reactions. • In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates, and the enzyme converts them into different molecules, the products. • Almost all processes in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at significant r ...
... and control the rates of chemical reactions. • In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates, and the enzyme converts them into different molecules, the products. • Almost all processes in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at significant r ...
Chapter 7
... • One glucose (6C) is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid (3C) • If oxygen is available, the pyruvic acid will move into the mitochondria and aerobic respiration will begin. • 4 ATP molecules are produced. Two are used to break apart the next glucose molecule and keep glycolysis going. • This ...
... • One glucose (6C) is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid (3C) • If oxygen is available, the pyruvic acid will move into the mitochondria and aerobic respiration will begin. • 4 ATP molecules are produced. Two are used to break apart the next glucose molecule and keep glycolysis going. • This ...
Check Your Knowledge QuestionSet 2(Download)
... Q.7-A 42-year-old obese female presented to theemergency center with complaints of worsening nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.Her pain was located in the midepigastric area and right upper quadrant. Blood biochemistry revealed high serum amylase level.What is the probable diagnosis for this pati ...
... Q.7-A 42-year-old obese female presented to theemergency center with complaints of worsening nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.Her pain was located in the midepigastric area and right upper quadrant. Blood biochemistry revealed high serum amylase level.What is the probable diagnosis for this pati ...
AQA Biology: Energy transfers and changes in
... 7 Ribulose bisphosphate/RuBP combines with CO2; forms two molecules of GP; GP is reduced to TP by reduced NADP; ATP provides energy. ...
... 7 Ribulose bisphosphate/RuBP combines with CO2; forms two molecules of GP; GP is reduced to TP by reduced NADP; ATP provides energy. ...
Cellular Respiration
... membrane, enough energy is created to cause ADP to combine with P to form ATP This step produces 32 ATP for a net yield of 36 Water is also produced as a product ...
... membrane, enough energy is created to cause ADP to combine with P to form ATP This step produces 32 ATP for a net yield of 36 Water is also produced as a product ...
Magnesium in biology

Magnesium is an essential element in biological systems. Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg2+ ion. It is an essential mineral nutrient (i.e., element) for life and is present in every cell type in every organism. For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must be bound to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP. As such, magnesium plays a role in the stability of all polyphosphate compounds in the cells, including those associated with the synthesis of DNA and RNA.Over 300 enzymes require the presence of magnesium ions for their catalytic action, including all enzymes utilizing or synthesizing ATP, or those that use other nucleotides to synthesize DNA and RNA.In plants, magnesium is necessary for synthesis of chlorophyll and photosynthesis.