Artificial Photosynthesis - The Mars Homestead Project
... Calcium Magnesium Potassium Sodium Iron Phosphorus ...
... Calcium Magnesium Potassium Sodium Iron Phosphorus ...
UNIT 3 – PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
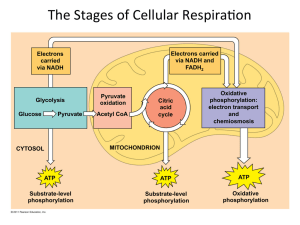
... cycle as acetyl CoA. Fats are excellent fuel. They release twice as many ATP molecules as glucose does per gram. Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle also function as metabolic interchanges that enable our cells to convert some kinds of molecules to others depending on the needs of the cell. Bec ...
... cycle as acetyl CoA. Fats are excellent fuel. They release twice as many ATP molecules as glucose does per gram. Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle also function as metabolic interchanges that enable our cells to convert some kinds of molecules to others depending on the needs of the cell. Bec ...
unit 3 – photosynthesis and cellular respiration
... cycle as acetyl CoA. Fats are excellent fuel. They release twice as many ATP molecules as glucose does per gram. Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle also function as metabolic interchanges that enable our cells to convert some kinds of molecules to others depending on the needs of the cell. Bec ...
... cycle as acetyl CoA. Fats are excellent fuel. They release twice as many ATP molecules as glucose does per gram. Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle also function as metabolic interchanges that enable our cells to convert some kinds of molecules to others depending on the needs of the cell. Bec ...
3.3 Nutrition and Transport
... Nutrition in the Flowering Plant • Plants are autotrophic – they make their own food. • Plants need to be able to transport water, carbon dioxide, oxygen and certain minerals around their body as they need them for metabolism, growth and reproduction ...
... Nutrition in the Flowering Plant • Plants are autotrophic – they make their own food. • Plants need to be able to transport water, carbon dioxide, oxygen and certain minerals around their body as they need them for metabolism, growth and reproduction ...
Name: ______ Date: Period: ATP, Photosynthesis and Cellular
... http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/N100/2k4ch7respirationnotes.html 29. What is the definition of Cellular Respiration?(in purple) 30. What happens during cellular respiration? 31. What’s the equation for Cellular Respiration? Stages of Cellular respiration. http://www.essortment.com/understand ...
... http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/N100/2k4ch7respirationnotes.html 29. What is the definition of Cellular Respiration?(in purple) 30. What happens during cellular respiration? 31. What’s the equation for Cellular Respiration? Stages of Cellular respiration. http://www.essortment.com/understand ...
Cellular Respiration II PPT
... respiration (cellular respiration that occurs in the presence of oxygen). However, organisms can also produce small amounts of ATP through anaerobic respiration as well. • Fermentation is a process that is centered around recycling electron carriers so that at least glycolysis can continue. Glycolys ...
... respiration (cellular respiration that occurs in the presence of oxygen). However, organisms can also produce small amounts of ATP through anaerobic respiration as well. • Fermentation is a process that is centered around recycling electron carriers so that at least glycolysis can continue. Glycolys ...
Root and Leaf Structure
... expenditure of moving ions into and out of the guard cells. Plants actively regulate the movement of these ions and can respond rapidly to changes in the amount of sunlight, relative humidity and carbon dioxide. The epidermis is usually one cell layer thick; however, in plants that grow in very hot ...
... expenditure of moving ions into and out of the guard cells. Plants actively regulate the movement of these ions and can respond rapidly to changes in the amount of sunlight, relative humidity and carbon dioxide. The epidermis is usually one cell layer thick; however, in plants that grow in very hot ...
ION BEAM TECHNIQUES • Ion beam characterization techniques
... • This requires the use of very low ion fluxes (around 1012 cm-2) to ensure that each ion is statistically-likely to impact upon fresh, undamaged surface and that the sputtered secondary ions are representative of the original surface, rather than surface that has already been "damaged" by earlier i ...
... • This requires the use of very low ion fluxes (around 1012 cm-2) to ensure that each ion is statistically-likely to impact upon fresh, undamaged surface and that the sputtered secondary ions are representative of the original surface, rather than surface that has already been "damaged" by earlier i ...
Document
... – considerable evidence indicates that vesicular trafficking through the Golgi complex is not responsible for much cholesterol and phospholipid movement between membranes. Golgi-independent vesicular transport, direct protein-mediated contacts between different membranes, soluble protein carriers, o ...
... – considerable evidence indicates that vesicular trafficking through the Golgi complex is not responsible for much cholesterol and phospholipid movement between membranes. Golgi-independent vesicular transport, direct protein-mediated contacts between different membranes, soluble protein carriers, o ...
Production of the Novel Lipopeptide Antibiotic Trifluorosurfactin via
... by a branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase. 4,4,4-Trifluoro-DL-valine was fed to several different surfactin-producing strains of Bacillus subtilis (NCTC 3610, NCIMB 8872, DSMZ 3256, ATCC 39096), two strains of Staphylococcus aureus and one strain of E. coli, to determine if this biotransformat ...
... by a branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase. 4,4,4-Trifluoro-DL-valine was fed to several different surfactin-producing strains of Bacillus subtilis (NCTC 3610, NCIMB 8872, DSMZ 3256, ATCC 39096), two strains of Staphylococcus aureus and one strain of E. coli, to determine if this biotransformat ...
Presentation @ 1:30 - Bioinformatics at School of Informatics
... Introduction to Proteomics Protein separation Protein digestion by specific enzyme trypsin into peptides Peptides are separated and charged ...
... Introduction to Proteomics Protein separation Protein digestion by specific enzyme trypsin into peptides Peptides are separated and charged ...
Detection of aneuploidy in a single cell using the Ion ReproSeq PGS
... Most normal human somatic cells contain a diploid [2N] set of autosomes (non-sex chromosomes) and a pair of sex chromosomes. Cells that do not contain an exact diploid set are termed aneuploid (Figure 1). Common types of aneuploidy that survive to term are monosomy (the loss of one chromosome) of th ...
... Most normal human somatic cells contain a diploid [2N] set of autosomes (non-sex chromosomes) and a pair of sex chromosomes. Cells that do not contain an exact diploid set are termed aneuploid (Figure 1). Common types of aneuploidy that survive to term are monosomy (the loss of one chromosome) of th ...
File
... 1. Plants carry out cellular respiration. (T or F) 2. Oxidative respiration must follow glycolysis if a cell is to maximize its ATP production. . (T or F) 3. Fermentation and oxidative respiration both take place in the absence of oxygen. . (T or F) 4. Lactic acid fermentation is a type of anaerobic ...
... 1. Plants carry out cellular respiration. (T or F) 2. Oxidative respiration must follow glycolysis if a cell is to maximize its ATP production. . (T or F) 3. Fermentation and oxidative respiration both take place in the absence of oxygen. . (T or F) 4. Lactic acid fermentation is a type of anaerobic ...
Lecture 6
... • CO2 diffuses from the mitochondrial matrix into your blood where it is transported finally to your lungs ...
... • CO2 diffuses from the mitochondrial matrix into your blood where it is transported finally to your lungs ...
Plants
... 4. reaction center donates e- to electron transport chain (ETC) a. ETC is a series of redox rx b. stairs analogy 5. The ETC contains a proton pump a. pumps H+ into the thylakoid … b. [H+] increases and builds up ...
... 4. reaction center donates e- to electron transport chain (ETC) a. ETC is a series of redox rx b. stairs analogy 5. The ETC contains a proton pump a. pumps H+ into the thylakoid … b. [H+] increases and builds up ...
Plants
... 4. reaction center donates e- to electron transport chain (ETC) a. ETC is a series of redox rx b. stairs analogy 5. The ETC contains a proton pump a. pumps H+ into the thylakoid … b. [H+] increases and builds up ...
... 4. reaction center donates e- to electron transport chain (ETC) a. ETC is a series of redox rx b. stairs analogy 5. The ETC contains a proton pump a. pumps H+ into the thylakoid … b. [H+] increases and builds up ...
The Physiological Roles of Enzymes
... b. Each substrate binds at its binding site on the enzyme, which may contain, be near to, or be the same as the active site harboring the amino acid side chains that participate directly in the reaction. c. Enzymes exhibit selectivity or specificity, a preference for catalyzing reactions with substr ...
... b. Each substrate binds at its binding site on the enzyme, which may contain, be near to, or be the same as the active site harboring the amino acid side chains that participate directly in the reaction. c. Enzymes exhibit selectivity or specificity, a preference for catalyzing reactions with substr ...
Acid-Base Balance
... Two mechanisms carried out by type A intercalated cells generate new bicarbonate ions Both involve renal excretion of acid via secretion and excretion of hydrogen ions or ammonium ions (NH4+) ...
... Two mechanisms carried out by type A intercalated cells generate new bicarbonate ions Both involve renal excretion of acid via secretion and excretion of hydrogen ions or ammonium ions (NH4+) ...
RESPIRATION: SYNTHESIS OF ATP
... NADH, FADH2; citric acid cycle stops. ! Without air, some cells regenerate NAD+ (from glycolysis only) by passing e- (+ H+) to pyruvic acid ! Result: continued glycolysis, forming 2 ATP per ...
... NADH, FADH2; citric acid cycle stops. ! Without air, some cells regenerate NAD+ (from glycolysis only) by passing e- (+ H+) to pyruvic acid ! Result: continued glycolysis, forming 2 ATP per ...
Effects of magnesium sulfate on spinal cord tissue lactate and
... Mg2+ plays a pivotal role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins including glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and protein synthesis [19]. Mg 2+ also plays a vital role in regulating ribosomal RNA and DNA structure. From this brief summary, it can be seen that Mg 2+ has actions op ...
... Mg2+ plays a pivotal role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins including glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and protein synthesis [19]. Mg 2+ also plays a vital role in regulating ribosomal RNA and DNA structure. From this brief summary, it can be seen that Mg 2+ has actions op ...
Cellular Respiration CPB
... eukaryotes: series of proteins embedded in the inner membrane of mitochondrion prokaryotes: same chain in cell membrane H-E e- move from 1 carrier protein to the next E is used to move H ions across membrane (ATP synthase) every rotation of ATPase phosphate group is added to A-P-P A-P-P~ ...
... eukaryotes: series of proteins embedded in the inner membrane of mitochondrion prokaryotes: same chain in cell membrane H-E e- move from 1 carrier protein to the next E is used to move H ions across membrane (ATP synthase) every rotation of ATPase phosphate group is added to A-P-P A-P-P~ ...
Cellular Respiration
... • Cellular respiration • Use organic compounds such as glucose and oxygen to make cellular energy (ATP) • Waste: CO2 and H2O ...
... • Cellular respiration • Use organic compounds such as glucose and oxygen to make cellular energy (ATP) • Waste: CO2 and H2O ...
Magnesium in biology

Magnesium is an essential element in biological systems. Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg2+ ion. It is an essential mineral nutrient (i.e., element) for life and is present in every cell type in every organism. For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must be bound to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP. As such, magnesium plays a role in the stability of all polyphosphate compounds in the cells, including those associated with the synthesis of DNA and RNA.Over 300 enzymes require the presence of magnesium ions for their catalytic action, including all enzymes utilizing or synthesizing ATP, or those that use other nucleotides to synthesize DNA and RNA.In plants, magnesium is necessary for synthesis of chlorophyll and photosynthesis.























