Anatomy Lab Practical #2 Helpful Hints Sheet Tara Fay In no
... Anatomy Lab Practical #2 Helpful Hints Sheet ...
... Anatomy Lab Practical #2 Helpful Hints Sheet ...
Anatomical Directions
... Directions: Fill in the blank with the correct word from the list below. Some words from the list will be used more than once. Most of the answers will come from the list below, but some answers are not in the list of words. superior inferior ...
... Directions: Fill in the blank with the correct word from the list below. Some words from the list will be used more than once. Most of the answers will come from the list below, but some answers are not in the list of words. superior inferior ...
The “Micro” and “Macro” of Tissues
... have a chicken thigh, you may be able to differentiate the hamstring muscles from the anterior thigh muscles. If you have a chicken leg, the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles are clearly evident as they connect to the Achilles’ tendon. Recall that cartilage is a subcategory of connective tissue; more ...
... have a chicken thigh, you may be able to differentiate the hamstring muscles from the anterior thigh muscles. If you have a chicken leg, the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles are clearly evident as they connect to the Achilles’ tendon. Recall that cartilage is a subcategory of connective tissue; more ...
Strabismus Terminology
... The EOM are innervated at a ratio of nerve fiber to muscle fiber up to 10 times that of skeletal muscle. This difference may allow for more accurate eye movements controlled by an array of systems ranging from the primitive vestibulo ocular reflex to highly evolved vergence movements. The EOM exhibi ...
... The EOM are innervated at a ratio of nerve fiber to muscle fiber up to 10 times that of skeletal muscle. This difference may allow for more accurate eye movements controlled by an array of systems ranging from the primitive vestibulo ocular reflex to highly evolved vergence movements. The EOM exhibi ...
Left Subclavian Vein Anatomy
... SP Notes - in an adult: 3-4cm in length an 1-2cm in diameter - formed from the axillary veins at the lateral border of the first rib - joins the brachiocephalic vein to become the superior vena cava ANATOMICAL RELATIONSHIPS - superior: clavicle - inferior: pleura - posterior: anterior scalene muscle ...
... SP Notes - in an adult: 3-4cm in length an 1-2cm in diameter - formed from the axillary veins at the lateral border of the first rib - joins the brachiocephalic vein to become the superior vena cava ANATOMICAL RELATIONSHIPS - superior: clavicle - inferior: pleura - posterior: anterior scalene muscle ...
midterm review packet _2 skeletal and muscular systems student
... -What happens to the sarcomere during muscle contraction? ______________________________________________________ - What makes up a motor unit? ______________________________________________________________ -Why are you out of breath after a hard workout? Why do your muscles burn? How does this help ...
... -What happens to the sarcomere during muscle contraction? ______________________________________________________ - What makes up a motor unit? ______________________________________________________________ -Why are you out of breath after a hard workout? Why do your muscles burn? How does this help ...
Quadriceps Muscle Strain. - Roland Jeffery Physiotherapy
... muscles. The quadriceps muscle is actually made up of four main muscles – the rectus femoris, vastis lateralis, vastis medialis and vastis intermedius. These muscles are located at the front of the thigh (See Figure 1). The rectus femoris, one of the quadriceps muscles, passes over 2 joints, the hip ...
... muscles. The quadriceps muscle is actually made up of four main muscles – the rectus femoris, vastis lateralis, vastis medialis and vastis intermedius. These muscles are located at the front of the thigh (See Figure 1). The rectus femoris, one of the quadriceps muscles, passes over 2 joints, the hip ...
One stage correction of hypoplastic–tuberous breast with the hockey
... Background: A lot of different techniques have been described for the correction of tuberous breast. We believe that two abnormalities are presented in tuberous breast: 1. Herniation of breast tissue through the nipple – areola complex. 2. Skin shortening at the level of Inframammary Fold (IMF) only ...
... Background: A lot of different techniques have been described for the correction of tuberous breast. We believe that two abnormalities are presented in tuberous breast: 1. Herniation of breast tissue through the nipple – areola complex. 2. Skin shortening at the level of Inframammary Fold (IMF) only ...
Document
... • Effort: force (supplied by muscle contraction) applied to a lever to move a resistance (load) • Load: resistance (bone + tissues + any added weight) moved by the effort ...
... • Effort: force (supplied by muscle contraction) applied to a lever to move a resistance (load) • Load: resistance (bone + tissues + any added weight) moved by the effort ...
Chapters 12-13 Practice Quiz/Questions
... MATCHING. Choose the item in column 2 that best matches each item in column 1. Match the following: 1) Formed by the union of a cranial and a spinal root. ...
... MATCHING. Choose the item in column 2 that best matches each item in column 1. Match the following: 1) Formed by the union of a cranial and a spinal root. ...
Chapter 2
... articulate- To fit into each other fracture- A break in the bone skeletal (voluntary) muscle- Muscle that is under direct voluntary control of the brain smooth muscle- The muscles found in the walls of the internal organs and blood vessels, generally not under voluntary control involuntary muscle- S ...
... articulate- To fit into each other fracture- A break in the bone skeletal (voluntary) muscle- Muscle that is under direct voluntary control of the brain smooth muscle- The muscles found in the walls of the internal organs and blood vessels, generally not under voluntary control involuntary muscle- S ...
L - BEHS Science
... The origin of the obturator internus (F) on the right cannot be seen, but the origin of the muscle on the contralateral side can be colored. See plate 44 for additional views of these muscles. ...
... The origin of the obturator internus (F) on the right cannot be seen, but the origin of the muscle on the contralateral side can be colored. See plate 44 for additional views of these muscles. ...
Circle the term that does not belong
... ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
Pilates to correct overactive upper trapezius muscles
... looking to completely change themselves and lose weight while improving their cardiorespiratory strength. These programs definitely helped me in all of these areas of health and fitness, but as I’ve relied on them as my primary source of exercise for several months, I’ve suffered from joint injuries ...
... looking to completely change themselves and lose weight while improving their cardiorespiratory strength. These programs definitely helped me in all of these areas of health and fitness, but as I’ve relied on them as my primary source of exercise for several months, I’ve suffered from joint injuries ...
Chapter 11: The Muscular System
... Circular muscles, also known as sphincters, surround internal and external openings and regulate flow through these openings. Examples include the orbicularis oculi around the eye, the orbicularis oris around the mouth, and the esophageal and anal sphincters at the beginning and end of the digestive ...
... Circular muscles, also known as sphincters, surround internal and external openings and regulate flow through these openings. Examples include the orbicularis oculi around the eye, the orbicularis oris around the mouth, and the esophageal and anal sphincters at the beginning and end of the digestive ...
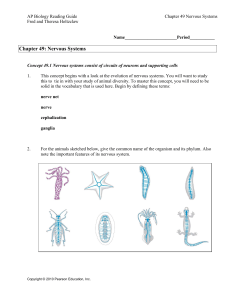
AP Bio Ch 49 Reading Guide
... A reflex arc is illustrated and explained in Figure 49.3. It is important for you to understand this pathway, so take some time with the figure below. Label the following: stimulus, receptors (sensors), sensory neuron, interneuron, spinal cord, gray matter, white matter, motor neuron, effector (musc ...
... A reflex arc is illustrated and explained in Figure 49.3. It is important for you to understand this pathway, so take some time with the figure below. Label the following: stimulus, receptors (sensors), sensory neuron, interneuron, spinal cord, gray matter, white matter, motor neuron, effector (musc ...
Untitled - Deragopyan
... Axial fat-suppressed fast spin-echo T2weighted image and correlate illustration show diffuse edema and increased signal intensity within the quadratus femoris muscle on the right hip (arrow). There is a bilateral narrowing space between the ischial tuberosity and the lesser ...
... Axial fat-suppressed fast spin-echo T2weighted image and correlate illustration show diffuse edema and increased signal intensity within the quadratus femoris muscle on the right hip (arrow). There is a bilateral narrowing space between the ischial tuberosity and the lesser ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.