Proposal for a New Osteopathic Treatment Method for
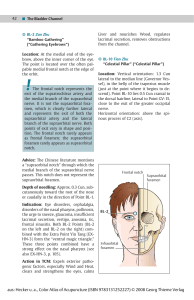
... The elevator of the soft palate (LVPM) has a cylindrical shape and runs below the tube, entering into the cartilaginous portion and forming a sling with fixed inserts between the petrous apex of the temporal bone and the midline of the soft palate; it sits posteriorly and medially to TPV, with anato ...
... The elevator of the soft palate (LVPM) has a cylindrical shape and runs below the tube, entering into the cartilaginous portion and forming a sling with fixed inserts between the petrous apex of the temporal bone and the midline of the soft palate; it sits posteriorly and medially to TPV, with anato ...
TSM31 - Mouth and Tongue
... o Pharyngeal part – both glossopharyngeal (CNIX); gustatory via vallate papillae only (CNIX) Principal blood supply is from the lingual artery (branch of external carotid artery ...
... o Pharyngeal part – both glossopharyngeal (CNIX); gustatory via vallate papillae only (CNIX) Principal blood supply is from the lingual artery (branch of external carotid artery ...
The Upper Extremity - Fisiokinesiterapia
... Latissimus dorsi = Thoracodorsal nerve Subscapularis, Teres Major = Subscapular nerves Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus = Suprascapular nerves Teres Minor = Axillary nerve ...
... Latissimus dorsi = Thoracodorsal nerve Subscapularis, Teres Major = Subscapular nerves Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus = Suprascapular nerves Teres Minor = Axillary nerve ...
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction in Dancers
... alignment, dancers also tend to overuse and over stretch muscles. One of the more prominent muscle groups used by dancers are the deep rotators of the hip, especially during ballet training to susta ...
... alignment, dancers also tend to overuse and over stretch muscles. One of the more prominent muscle groups used by dancers are the deep rotators of the hip, especially during ballet training to susta ...
Principles of Functional Exercise
... Our daily activities can actually cause muscle imbalances. No matter what your line of work, you probably have some type of routine consisting of repetitive activities. This can overwork some muscles and under-work others. This is one reason why many people often say, “I do not know how this happene ...
... Our daily activities can actually cause muscle imbalances. No matter what your line of work, you probably have some type of routine consisting of repetitive activities. This can overwork some muscles and under-work others. This is one reason why many people often say, “I do not know how this happene ...
An accessory digastric abductor pollicis longus muscle
... and thenar muscles are known. A bilateral digastric muscle formed by abductor pollicis logus and abductor brevis was present (Saeed et al., 2002) The tendon of abductor pollicis longus had a thenar insertion, most frequently inserting on either the abductor pollicis brevis or opponens pollicis fasci ...
... and thenar muscles are known. A bilateral digastric muscle formed by abductor pollicis logus and abductor brevis was present (Saeed et al., 2002) The tendon of abductor pollicis longus had a thenar insertion, most frequently inserting on either the abductor pollicis brevis or opponens pollicis fasci ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Pectoral region
... The pectoralis major muscle is the largest and most superficial of the pectoral region muscles It is a large, fan-shaped muscle that covers the superior part of the thorax. It directly underlies the breast. Pectoralis major has clavicular and sternocostal heads. The sternocostal head is much larger, ...
... The pectoralis major muscle is the largest and most superficial of the pectoral region muscles It is a large, fan-shaped muscle that covers the superior part of the thorax. It directly underlies the breast. Pectoralis major has clavicular and sternocostal heads. The sternocostal head is much larger, ...
9/30/09 Abdomen Continued Ureters: They are muscular ducts
... comes off of the diaphragm. The kidneys receive 20-25% of Cardiac Output at rest and thus, the most active tissue in the body. Each of those arteries enters the hilum (a doorway) and divides into 5 segmental arteries. The right renal artery is lower than the left renal artery due to space (this is b ...
... comes off of the diaphragm. The kidneys receive 20-25% of Cardiac Output at rest and thus, the most active tissue in the body. Each of those arteries enters the hilum (a doorway) and divides into 5 segmental arteries. The right renal artery is lower than the left renal artery due to space (this is b ...
Applied anatomy of the hip and buttock
... proximal part of the iliotibial tract – a strong band which thickens the fascia lata at its lateral aspect. Thus the course of the tensor is dorsal and distal. Acting through the iliotibial tract the muscle extends and rotates the knee laterally. It may also assist in flexion, abduction and medial r ...
... proximal part of the iliotibial tract – a strong band which thickens the fascia lata at its lateral aspect. Thus the course of the tensor is dorsal and distal. Acting through the iliotibial tract the muscle extends and rotates the knee laterally. It may also assist in flexion, abduction and medial r ...
Sample Page
... gō-mat′i-kŭs mı̄′nŏr mŭs′ĕl) Facial muscle of anterior cheek extending to upper lip; origin, zygomatic bone posterior to zygomaticomaxillary suture; insertion, orbicularis oris of upper lip; action, draws upper lip upward and outward; nerve supply, facial. SYN caput zygomaticum quadrati labii s ...
... gō-mat′i-kŭs mı̄′nŏr mŭs′ĕl) Facial muscle of anterior cheek extending to upper lip; origin, zygomatic bone posterior to zygomaticomaxillary suture; insertion, orbicularis oris of upper lip; action, draws upper lip upward and outward; nerve supply, facial. SYN caput zygomaticum quadrati labii s ...
Anatomy Description Posterior Leg Anatomy
... ii. Arises from the pelvic surfaces of the second, third and fourth sacral vertebrae between and lateral to the pelvic sacral foramina iii. The muscle is directed toward the greater Sciatic Foramen iv. Its rounded tendon inserts into the upper border and medial side of the greater trochanter of the ...
... ii. Arises from the pelvic surfaces of the second, third and fourth sacral vertebrae between and lateral to the pelvic sacral foramina iii. The muscle is directed toward the greater Sciatic Foramen iv. Its rounded tendon inserts into the upper border and medial side of the greater trochanter of the ...
THE BACK
... part of the appendicular skeleton, they are someFmes referred to as the appendicular group. Muscles in the superficial group include the: ...
... part of the appendicular skeleton, they are someFmes referred to as the appendicular group. Muscles in the superficial group include the: ...
Thieme: Color Atlas of Acupuncture
... lateral bony ridges of the middle phalanges of fingers II to V. Innervation: Median nerve (C7 to T1). Action: Flexes the metacarpophalangeal joints II to V and the proximal interphalangeal joints II to V. Miscellaneous: The tendons of the deep flexor muscle of the fingers pass between the parts of t ...
... lateral bony ridges of the middle phalanges of fingers II to V. Innervation: Median nerve (C7 to T1). Action: Flexes the metacarpophalangeal joints II to V and the proximal interphalangeal joints II to V. Miscellaneous: The tendons of the deep flexor muscle of the fingers pass between the parts of t ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.