* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TSM31 - Mouth and Tongue
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
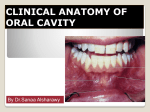
TSM31: MOUTH AND TONGUE 14/10/08 LEARNING OUTCOMES Describe the anatomy of the oral cavity The oral cavity is bounded: o Inferiorly by the tongue and floor of mouth muscles (see below) o Superiorly by the hard palate o Laterally by the cheeks o Posteriorly by the soft palate The uvula hangs down from the roof of mouth as an extension of the soft palate o The palatoglossal arch is a soft arch immediately posterior to the uvula o The palatopharyngeal arch is another soft arch and the anterior border of the oropharynx The palatine tonsils are situated between the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches FLOOR OF MOUTH The floor of mouth itself is made up of two main muscles apart from the (superior-most) tongue itself: o The mylohyoid muscles are the sheet-like inferior-most muscles of the floor of mouth Run from the sides of the mandible to the hyoid bone Innervated by nerve to mylohyoid (inferior alveolar branch of trigeminal V3) o The geniohyoid muscles are cords that lie superior to mylohyoid along the midline Arise from the superior mental tubercles and insert onto the medial hyoid bone Innervated by C1 o Both of the above depress the mandible when the hyoid is fixed and elevate the vice-versa Describe the functional anatomy of the tongue OVERVIEW OF THE TONGUE The tongue (or glossa) is a muscular mass attached at its root to the floor of mouth o The frenulum linguae is a central mucous membrane fold linking it to the floor of mouth o It is divided into oral (ant. 2/3) and pharyngeal (post. 1/3) ‘parts’ by the terminal sulcus Its surface is rough and appears furred due to the presence of minute surface projections – papillae o Vallate papillae are found anterior and parallel to the terminal sulcus o Foliate papillae are found on the lateral edges of the tongue o Fungiform papillae are found medial to the foliate papillae o Filiform papillae are found most medially and are the thinnest projections Gustatory and sensory innervation to the tongue is divided according to the parts: o Oral part – sensory lingual nerve (of V3); gustatory chorda timpani (of facial nerve) o Pharyngeal part – both glossopharyngeal (CNIX); gustatory via vallate papillae only (CNIX) Principal blood supply is from the lingual artery (branch of external carotid artery MUSCLES OF THE TONGUE The tongue is divided in the midline by a connective tissue septum; as such all its muscles are paired There are both intrinsic and extrinsic muscle groups: o The intrinsic muscles arise from the substance of the tongue itself Superior and inferior longitudinal, vertical and transverse muscles These alter the shape rather than the position of the tongue o The extrinsic muscles arise from structures external to the tongue and insert onto it Palatoglossus arises from the soft palate and elevates the dorsum Styloglossus arises from the styloid process and elevates / retracts the tongue Hyoglossus arises from the hyoid bone and depresses the tongue Genioglossus arises from the superior mental tubercles and protrudes the tongue o All of the above except palatoglossus are innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CNXII) The hypoglossal nerve provides the sole motor supply to the tongue Palatoglossus is supplied by the vagus nerve (CNX) Describe the course and distribution of the hypoglossal nerve and chorda tympani CHORDA TYMPANI The chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve (CNVII) o Arises at the posterior part of the tympanic cavity o Passes beneath the inner surface of the tympanic membrane o Passes through the temporal bone to the infratemporal fossa At the infratemporal fossa it joins the lingual nerve (branch of trigeminal V3) o Travels inferiorly along the oral cavity o Passes beneath the submandibular duct o Parasympathetic supply to all glands below the oral fissure including all salivary glands o Conveys gustatory sensory information from oral part of tongue HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE Arises from the hypoglossal nucleus near the midline in the dorsal caudal medulla o Fibres travel along the medial lemniscus and emerge between the pyramid and olive o Descends through the hypoglossal canal below the angle of the mandible o Moves anteriorly crossing over the external carotid artery o Follows the hyoglossus muscle to the tongue Damage to the hypoglossal nerve can be tested through asking the patient to protrude their tongue o Nerve supply to the two halves of the tongue is ipsilateral o Deviation to one side indicates hypoglossal nerve damage on the ipsilateral side Describe the anatomy of the palate The palate is divided into hard (anterior) and soft (posterior) regions The hard palate has a bony roof formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and palatine bones o Anteriorly there are numerous longitudinal ridges – palatine rugae The soft palate is continuous with the hard palate and extends posteriorly into the oropharynx o It acts as a valve between the naso- and oropharynx Several muscles are involved in the movement of the soft palate: o Tensor veli palatini – tenses the soft palate; facilitates tympanic-oral pressure equalisation Arises as bilateral muscular projections from the base of skull Projections descend between the medial and lateral pterygoid plates Hook around hamulus to form palatine aponeurosis (essentially the soft palate) o Levator veli palatini – elevates the soft palate (only muscle to do so) Inserts from base of skull directly onto palatine aponeurosis o Palatopharyngeus – depresses the soft palate; elevates the pharynx Arises from superior surface of the palatine aponeurosis Descends bilaterally along the pharyngeal walls Forms palatopharyngeal arches o Palatoglossus – depresses the soft palate; elevates the dorsum of the tongue Arises from inferior surface of the palatine aponeurosis Inserts bilaterally onto the lateral margins of the tongue o All of the above muscles are innervated by branches of the vagus nerve (CNX) except: Tensor veli palatini which is innervated by trigeminal V3