BACK AND UPPER LIMB
... Note: A fall on the outstretched forearm with the hand pronated and the wrist extended can result in a fracture of the distal end of the radius or the scaphoid bone. ...
... Note: A fall on the outstretched forearm with the hand pronated and the wrist extended can result in a fracture of the distal end of the radius or the scaphoid bone. ...
25. Motor cranial nerves
... Motor to four eyeball muscles Parasympathetic to ciliary ganglion Injury to nerve causes dilated pupil and ptosis “fixed and dilated” ...
... Motor to four eyeball muscles Parasympathetic to ciliary ganglion Injury to nerve causes dilated pupil and ptosis “fixed and dilated” ...
muscles
... – Describe the ways that muscles work in groups to aid, oppose, or moderate each other’s actions. – Distinguish between intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. – Describe in general terms the nerve supply to the muscles and where these nerves originate. – Explain how the Latin names of muscles can aid in v ...
... – Describe the ways that muscles work in groups to aid, oppose, or moderate each other’s actions. – Distinguish between intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. – Describe in general terms the nerve supply to the muscles and where these nerves originate. – Explain how the Latin names of muscles can aid in v ...
Chapter 10:The Muscular System
... – Describe the ways that muscles work in groups to aid, oppose, or moderate each other’s actions. – Distinguish between intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. – Describe in general terms the nerve supply to the muscles and where these nerves originate. – Explain how the Latin names of muscles can aid in v ...
... – Describe the ways that muscles work in groups to aid, oppose, or moderate each other’s actions. – Distinguish between intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. – Describe in general terms the nerve supply to the muscles and where these nerves originate. – Explain how the Latin names of muscles can aid in v ...
The angiosomes of the body and their supply to perforator flaps
... the body. Br J Plast Surg 1987;40:131; with permission.) (See also Color Plate 3). ...
... the body. Br J Plast Surg 1987;40:131; with permission.) (See also Color Plate 3). ...
Nerves - Drhannah.org
... Posterior hepatic plexus via right cardiac plexus and posterior vagal trunk Celiac plexus (S), vagus nerve (PS), and right phrenic nerve (sensory) Renal plexus (S, PS, visceral afferent) supplied by splanchnic (especially “least”). Suprarenal glands get from celiac plexus and thoracic splanchnic ner ...
... Posterior hepatic plexus via right cardiac plexus and posterior vagal trunk Celiac plexus (S), vagus nerve (PS), and right phrenic nerve (sensory) Renal plexus (S, PS, visceral afferent) supplied by splanchnic (especially “least”). Suprarenal glands get from celiac plexus and thoracic splanchnic ner ...
L16-Anatomy of Shoulder region 2013
... and this is the site of potential weakness of the joint. It is formed of 4 muscles: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor & subscapularis (SITS). The tone of these muscles helps in stabilizing the shoulder joint. ...
... and this is the site of potential weakness of the joint. It is formed of 4 muscles: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor & subscapularis (SITS). The tone of these muscles helps in stabilizing the shoulder joint. ...
FORM A
... d) cranial nerve 9, 10 and 11 exit the skull thru the foramen magnum e) the dural sinus located in the groove for the sigmoid sinus exits the skull through the hypoglossal canal as the jugular vein 3) Choose the INCORRECT statement. a) the musculospiral groove runs superior to the deltoid tuberosity ...
... d) cranial nerve 9, 10 and 11 exit the skull thru the foramen magnum e) the dural sinus located in the groove for the sigmoid sinus exits the skull through the hypoglossal canal as the jugular vein 3) Choose the INCORRECT statement. a) the musculospiral groove runs superior to the deltoid tuberosity ...
021~030.박경식
... brevis tendon, superior peroneal retinacula, calcaneofibular ligament, inferior extensor retinaculum, abductor digiti minimi, sheath of flexor tendon at outer layer, biceps femoris, semimembranosus, plantaris, soleus, posterior tibialis, fibularis brevis, extensor digitorum brevis, flexor digiti min ...
... brevis tendon, superior peroneal retinacula, calcaneofibular ligament, inferior extensor retinaculum, abductor digiti minimi, sheath of flexor tendon at outer layer, biceps femoris, semimembranosus, plantaris, soleus, posterior tibialis, fibularis brevis, extensor digitorum brevis, flexor digiti min ...
Knee
... the tibia and the femur, made of cartilage, which is called the meniscus or meniscal cartilage. • It helps to protect the joint and allows the bones to slide freely on each other. ...
... the tibia and the femur, made of cartilage, which is called the meniscus or meniscal cartilage. • It helps to protect the joint and allows the bones to slide freely on each other. ...
the vertebral column, rib cage, and muscles of the back and abdomen
... Even giraffes have only seven cervical vertebrae. ...
... Even giraffes have only seven cervical vertebrae. ...
Variant heads of biceps brachii muscle with clinical
... Materials and Methods: The 50 specimens of the 25 donated embalmed cadavers were dissected and observed for variations in the origin and insertion of biceps brachii muscle bilaterally in the department of Anatomy at K.J.Somaiya Medical College, Sion, Mumbai, INDIA. The dissection of arm and forearm ...
... Materials and Methods: The 50 specimens of the 25 donated embalmed cadavers were dissected and observed for variations in the origin and insertion of biceps brachii muscle bilaterally in the department of Anatomy at K.J.Somaiya Medical College, Sion, Mumbai, INDIA. The dissection of arm and forearm ...
The Mouth
... skin at the margins of the lips, and here the stratified squamous epithelium changes from a non-keratinizing to a keratinizing type. At its reflection on to the jaws, the mucous membrane forms a median, raised fold, the frenulum of the lip. The chief bulk of the lip is the muscular layer which is fo ...
... skin at the margins of the lips, and here the stratified squamous epithelium changes from a non-keratinizing to a keratinizing type. At its reflection on to the jaws, the mucous membrane forms a median, raised fold, the frenulum of the lip. The chief bulk of the lip is the muscular layer which is fo ...
THE SHOULDER JOINT LEARNING OBJECTIVES
... This ligament is taut during external rotation and plays a small role in the stability of the shoulder. ...
... This ligament is taut during external rotation and plays a small role in the stability of the shoulder. ...
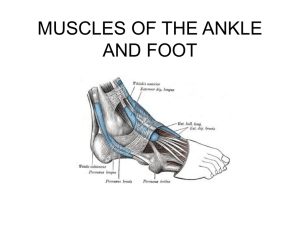
THE ANKLE AND FOOT
... • Origin: upper 2/3 of the posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula • Insertion: posterior surface of the calcaneus via Achilles tendon • Action: – plantar flexion • Superficial posterior compartment ...
... • Origin: upper 2/3 of the posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula • Insertion: posterior surface of the calcaneus via Achilles tendon • Action: – plantar flexion • Superficial posterior compartment ...
Axillary artery
... The examination of the axillary lymph nodes always forms part of the clinical examination of the breast. With the patient standing or sitting, he or she is asked to place the hand of the side to be examined on the hip and push hard medially. This action of adduction of the shoulder joint causes the ...
... The examination of the axillary lymph nodes always forms part of the clinical examination of the breast. With the patient standing or sitting, he or she is asked to place the hand of the side to be examined on the hip and push hard medially. This action of adduction of the shoulder joint causes the ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.