Anatomy – Whole Block 4 Review
... o Tendon of the Quadriceps Femoris Where does the IT Band insert? o Gerdy’s Tubercle of the Tibia (lateral) What are the three compartments of the Leg? o Anterior, Posterior, and Lateral What are the muscles of the Anterior Compartment of the leg? o Tibialis Anterior M o Extensor Digitorium Longus M ...
... o Tendon of the Quadriceps Femoris Where does the IT Band insert? o Gerdy’s Tubercle of the Tibia (lateral) What are the three compartments of the Leg? o Anterior, Posterior, and Lateral What are the muscles of the Anterior Compartment of the leg? o Tibialis Anterior M o Extensor Digitorium Longus M ...
Effects of Lumbar Stabilization Using a Pressure Biofeedback Unit
... to prevent musculoskeletal injuries, to rehabilitate, and to improve performance. Lumbar stabilization refers to internal stabilization achieved by the isometric contraction of abdominal and lumbar muscles to maintain stability.1 It has also been referred to in the literature as core strengthening, ...
... to prevent musculoskeletal injuries, to rehabilitate, and to improve performance. Lumbar stabilization refers to internal stabilization achieved by the isometric contraction of abdominal and lumbar muscles to maintain stability.1 It has also been referred to in the literature as core strengthening, ...
Medical Science Variant attachment of bicipital aponeurosis and
... IJSR - INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH ...
... IJSR - INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH ...
Skeletal Muscular system
... voluntary movements of body through space includes skeletal striated muscle every cell innervated (neuropathy or denervation atrophy) (levels of severity: neuropraxia, axonotmesis, neurotmesis) Origin – stationary point of muscle attachment Slip – segmented origin Insertion – affected point of mus ...
... voluntary movements of body through space includes skeletal striated muscle every cell innervated (neuropathy or denervation atrophy) (levels of severity: neuropraxia, axonotmesis, neurotmesis) Origin – stationary point of muscle attachment Slip – segmented origin Insertion – affected point of mus ...
Vagina - yeditepetip4
... Obstetrics and Gynecology Anatomy and Physiology Assoc. Prof. Gazi YILDIRIM, M.D. ...
... Obstetrics and Gynecology Anatomy and Physiology Assoc. Prof. Gazi YILDIRIM, M.D. ...
Scapula
... middle-aged and elderly people. In younger people, results from a fall on the hand when the arm is abducted. ...
... middle-aged and elderly people. In younger people, results from a fall on the hand when the arm is abducted. ...
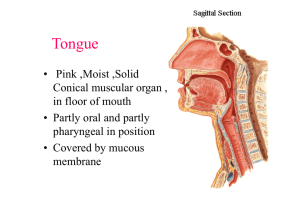
Tongue
... Root • Attached to hyoid and mandible and is in contact inferiorly with geniohyoid and mylohyoid muscles ...
... Root • Attached to hyoid and mandible and is in contact inferiorly with geniohyoid and mylohyoid muscles ...
Perenium - Dr. Krieg
... The pelvic diaphragm is made up of two muscles: the levator ani and the coccygeus. 1. The levator ani arises in part from the pubis as the puboccygeus muscle. The puborectalis muscle is a bundle that passes around the rectum to form the puborectalis sling. This sling is important to the suppo ...
... The pelvic diaphragm is made up of two muscles: the levator ani and the coccygeus. 1. The levator ani arises in part from the pubis as the puboccygeus muscle. The puborectalis muscle is a bundle that passes around the rectum to form the puborectalis sling. This sling is important to the suppo ...
Sciatic Nerve
... Nerve supply: Long head: tibial portion of sciatic nerve Short head: common peroneal portion of sciatic nerve Actions: Flexes and laterally rotates leg at knee joint; long head also extends thigh at hip joint ...
... Nerve supply: Long head: tibial portion of sciatic nerve Short head: common peroneal portion of sciatic nerve Actions: Flexes and laterally rotates leg at knee joint; long head also extends thigh at hip joint ...
Cranial nerves of face, tongue, jaw, palate, larynx, shoulders
... Tongue has sensation of two types (touch and taste) and is also able to move. Each of these functions is filled by different ...
... Tongue has sensation of two types (touch and taste) and is also able to move. Each of these functions is filled by different ...
MORPHOLOGY OF KNEE JOINT-CLASS-AVES-GENUS
... the patella while in man it is inserted on the tibia. This suggests that the sartorius muscle in chicken is acting just like a part of quadriceps femoris so as to extend the knee and flex the hip. The popliteus muscle is absent in chicken while in man it is the single most important stabilizer of th ...
... the patella while in man it is inserted on the tibia. This suggests that the sartorius muscle in chicken is acting just like a part of quadriceps femoris so as to extend the knee and flex the hip. The popliteus muscle is absent in chicken while in man it is the single most important stabilizer of th ...
CATEDRA Anatomia omului
... Historical evolution of the Human Anatomy. Anatomy in ancient period and in the Middle Ages. The role of Renaissance in anatomy development. Leonardo da Vinci and bases of modern anatomy. Development of anatomy in the XVIII-XX centuries. History of Human Anatomy as a science in Moldova. The main sta ...
... Historical evolution of the Human Anatomy. Anatomy in ancient period and in the Middle Ages. The role of Renaissance in anatomy development. Leonardo da Vinci and bases of modern anatomy. Development of anatomy in the XVIII-XX centuries. History of Human Anatomy as a science in Moldova. The main sta ...
review
... and a sportsman’s hernia coexisting. This makes the clinical diagnosis even more problematic. Conservative treatment is not always ideal for these people, particularly in the elite sports person who wants to get back to the playing field as soon as possible [5]. Ultrasound is an excellent tool for d ...
... and a sportsman’s hernia coexisting. This makes the clinical diagnosis even more problematic. Conservative treatment is not always ideal for these people, particularly in the elite sports person who wants to get back to the playing field as soon as possible [5]. Ultrasound is an excellent tool for d ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.