Network interface cards (NIC)
... • A type of communications where a channel or circuit is established for the duration of the call. • That circuit is dedicated to the two end nodes using it. • 1950’s/60’s the networks were analog, circuit switched networks. • Telephony companies invested millions/billions of dollars in equipment ov ...
... • A type of communications where a channel or circuit is established for the duration of the call. • That circuit is dedicated to the two end nodes using it. • 1950’s/60’s the networks were analog, circuit switched networks. • Telephony companies invested millions/billions of dollars in equipment ov ...
Networking Equipment
... given its final destination (IP address). Usually, routers forward packets to other routers, but sometimes routers also forward to other pieces of network equipment. A router is usually used to connect a home computer to an “always-on” Internet connection through the home network. To appreciate wha ...
... given its final destination (IP address). Usually, routers forward packets to other routers, but sometimes routers also forward to other pieces of network equipment. A router is usually used to connect a home computer to an “always-on” Internet connection through the home network. To appreciate wha ...
Subnet and Packet Tracer Task
... administrator. Your first assignment is to setup the local network and make everything function correctly. You have decided to first build your simulated network using packet tracer and test the setup before modifying the live network. ...
... administrator. Your first assignment is to setup the local network and make everything function correctly. You have decided to first build your simulated network using packet tracer and test the setup before modifying the live network. ...
Common Computer Terminology - Mr-Johnsons
... Provides an interface that helps you interact with the computer. Most operating systems use a GUI. Graphical User Interface (GUI):displays images and pictures that allow the user to interact with a computer easily. Example of an Operating System (Windows XP) ...
... Provides an interface that helps you interact with the computer. Most operating systems use a GUI. Graphical User Interface (GUI):displays images and pictures that allow the user to interact with a computer easily. Example of an Operating System (Windows XP) ...
lecture02
... • Header checksum (error check on header) • Source and destination IP addresses • Upper-level protocol (e.g., TCP, UDP) • Length in bytes (up to 65,535 bytes) • IP options (security, routing, timestamping, etc.) ...
... • Header checksum (error check on header) • Source and destination IP addresses • Upper-level protocol (e.g., TCP, UDP) • Length in bytes (up to 65,535 bytes) • IP options (security, routing, timestamping, etc.) ...
Computer Network
... Part 3: Interntworking (Cont’d) IP Datagrams and Datagram Forwarding IP Encapsulation, Fragmentation and Reassembly TCP/IP ...
... Part 3: Interntworking (Cont’d) IP Datagrams and Datagram Forwarding IP Encapsulation, Fragmentation and Reassembly TCP/IP ...
44_ExploringNetworkProperties
... Define client and protocol and explain the purpose of each. Explain the purpose of the NetBEUI, IPX/SPX, and TCP/IP protocols. Change the client, services, and protocol of a local area network connection in a Windows XP Pro computer. ...
... Define client and protocol and explain the purpose of each. Explain the purpose of the NetBEUI, IPX/SPX, and TCP/IP protocols. Change the client, services, and protocol of a local area network connection in a Windows XP Pro computer. ...
Networking
... The Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) standard transmits data in little chunks called packets Break long messages into short “packets” Keeps one user from hogging a line Each packet is tagged with where it’s going ...
... The Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) standard transmits data in little chunks called packets Break long messages into short “packets” Keeps one user from hogging a line Each packet is tagged with where it’s going ...
The Internet and the World Wide Web
... human brains and computing machines will be coupled together very tightly, and that the resulting partnership will think as no human brain has ever thought and process data in a way not approached by the information-handling machines we know today. ...
... human brains and computing machines will be coupled together very tightly, and that the resulting partnership will think as no human brain has ever thought and process data in a way not approached by the information-handling machines we know today. ...
The Next Generation of IP
... T. Bonald, S. O. Boulahia and J.W. Roberts, “IP traffic and QoS control: the need for a flow-aware architecture”, World Telecommunications Congress, September 2002 T. Bonald, S. Oueslati and J. W. Robert, “Flow-aware admission control for a ...
... T. Bonald, S. O. Boulahia and J.W. Roberts, “IP traffic and QoS control: the need for a flow-aware architecture”, World Telecommunications Congress, September 2002 T. Bonald, S. Oueslati and J. W. Robert, “Flow-aware admission control for a ...
CSCI 3421 Data communications and Networking
... Propagation Delay: Time to get to the destination End-to-End Delay: (Latency, Ping Time), sum of all delays from source to destination Run traceroute and ping to explore delay Other delay can occur (e.g., SMTP congestion control) ...
... Propagation Delay: Time to get to the destination End-to-End Delay: (Latency, Ping Time), sum of all delays from source to destination Run traceroute and ping to explore delay Other delay can occur (e.g., SMTP congestion control) ...
CSCI6268L10 - Computer Science
... gateway on our local Ethernet? – ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) • Translates IP addresses into MAC addresses • Caches old lookups, so we probably already have the MAC address of the gateway • If not, we send an ARP Request to the LAN, including the IP address whose MAC we seek • Owner (ie, the ga ...
... gateway on our local Ethernet? – ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) • Translates IP addresses into MAC addresses • Caches old lookups, so we probably already have the MAC address of the gateway • If not, we send an ARP Request to the LAN, including the IP address whose MAC we seek • Owner (ie, the ga ...
CSCI6268L10 - Computer Science
... gateway on our local Ethernet? – ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) • Translates IP addresses into MAC addresses • Caches old lookups, so we probably already have the MAC address of the gateway • If not, we send an ARP Request to the LAN, including the IP address whose MAC we seek • Owner (ie, the ga ...
... gateway on our local Ethernet? – ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) • Translates IP addresses into MAC addresses • Caches old lookups, so we probably already have the MAC address of the gateway • If not, we send an ARP Request to the LAN, including the IP address whose MAC we seek • Owner (ie, the ga ...
Networking
... together to form a new network • Operates by forwarding data to specific systems on the network • May be able to be piggy-backed, but may also require crossover cables • Have unmanaged and managed modes where unmanaged refers to plug-and-play ...
... together to form a new network • Operates by forwarding data to specific systems on the network • May be able to be piggy-backed, but may also require crossover cables • Have unmanaged and managed modes where unmanaged refers to plug-and-play ...
Chpt 10 - 07 test.doc
... A network that covers a large geographical area and is made up of many smaller networks A measure of how much data can travel over a given communication system in a given amount of time A pass-through and distribution point for every device connected to it, without regard for what kind of data is pa ...
... A network that covers a large geographical area and is made up of many smaller networks A measure of how much data can travel over a given communication system in a given amount of time A pass-through and distribution point for every device connected to it, without regard for what kind of data is pa ...
Word 2000 - UCLA.edu
... The idea of distributed systems is appealing because it is cheaper and easier to massproduce simple computers. Also, a company can incrementally increase the computing power using off-the-shelf components. The advent of distributed systems promises the following properties. ...
... The idea of distributed systems is appealing because it is cheaper and easier to massproduce simple computers. Also, a company can incrementally increase the computing power using off-the-shelf components. The advent of distributed systems promises the following properties. ...
ppt3
... The networks can run different protocols at the network interface and physical layers Internally they can be structured ...
... The networks can run different protocols at the network interface and physical layers Internally they can be structured ...
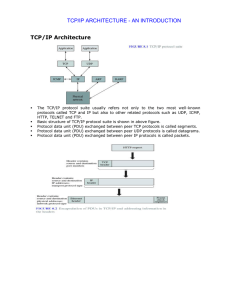
TCP/IP Architecture TCP/IP ARCHITECTURE
... Example: Ethernet uses 48-bit addresses o Each Ethernet network interface card (NIC) has globally unique Medium Access Control (MAC) or physical address o First 24 bits identify NIC manufacturer; second 24 bits are serial number o 00:90:27:96:68:07 12 hex numbers ...
... Example: Ethernet uses 48-bit addresses o Each Ethernet network interface card (NIC) has globally unique Medium Access Control (MAC) or physical address o First 24 bits identify NIC manufacturer; second 24 bits are serial number o 00:90:27:96:68:07 12 hex numbers ...
SMC1255TX / SMC1255TX/LP www.smc.com
... firewall that can filter traffic based on website name, IP address, and TCP/UDP protocol, while the WinEtool application monitors your network traffic with a built-in Wake-on-LAN packet generator and packet analysis tool. These tools monitor each packet of data as it is sent through your network. To ...
... firewall that can filter traffic based on website name, IP address, and TCP/UDP protocol, while the WinEtool application monitors your network traffic with a built-in Wake-on-LAN packet generator and packet analysis tool. These tools monitor each packet of data as it is sent through your network. To ...
Only $7000 USD - Network Forensics | Lawful Interception
... infrastructure in enterprises, ISP, IDC and LTE/WiMAX operators ...
... infrastructure in enterprises, ISP, IDC and LTE/WiMAX operators ...
Networks
... CAT 6 (standardized cable for Gigabit Ethernet) G3 (wireless connection used for PANs) Bluetooth (wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances) Fiber optic (a glass fiber that uses pulses of light to transmit data) ...
... CAT 6 (standardized cable for Gigabit Ethernet) G3 (wireless connection used for PANs) Bluetooth (wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances) Fiber optic (a glass fiber that uses pulses of light to transmit data) ...
Network_Layer
... The main design goals for Network Layer services: (see the book “Computer Networks by Tanenbaum” P345). ...
... The main design goals for Network Layer services: (see the book “Computer Networks by Tanenbaum” P345). ...
Course: CEG3185 Professor: Jiying Zhao Semester: Winter 2015
... N = number of hops between two given end systems L = message length in bits B = data rate, in bits per second (bps), on all links P = fixed packet size, in bits H = overhead (header), bits per packet S = call setup time (circuits switching or virtual circuit) in seconds R = call release time (circui ...
... N = number of hops between two given end systems L = message length in bits B = data rate, in bits per second (bps), on all links P = fixed packet size, in bits H = overhead (header), bits per packet S = call setup time (circuits switching or virtual circuit) in seconds R = call release time (circui ...
Basic Networking Terminology
... It defines the way different nodes are placed and interconnected with each other 12. an Ethernet cabling standard that supports high-speed networking 13. router that uses the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands 14. a physical location that offers Internet access over a wireless local area network 16. ...
... It defines the way different nodes are placed and interconnected with each other 12. an Ethernet cabling standard that supports high-speed networking 13. router that uses the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands 14. a physical location that offers Internet access over a wireless local area network 16. ...
Wake-on-LAN
Wake-on-LAN (WoL) is an Ethernet or Token ring computer networking standard that allows a computer to be turned on or awakened by a network message.The message is usually sent by a program executed on another computer on the same local area network. It is also possible to initiate the message from another network by using subnet directed broadcasts or a WOL gateway service. Equivalent terms include wake on WAN, remote wake-up, power on by LAN, power up by LAN, resume by LAN, resume on LAN and wake up on LAN. In case the computer being awakened is communicating via Wi-Fi, a supplementary standard called Wake on Wireless LAN (WoWLAN) must be employed.The WOL and WoWLAN standards are often supplemented by vendors to provide protocol-transparent on-demand services, for example in the Apple Bonjour wake-on-demand (Sleep Proxy) feature.