* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Common Computer Terminology - Mr-Johnsons
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
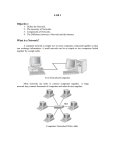
Digital Literacy Lesson 2 Hardware Hardware: the physical components of a computer. Includes input devices, processing devices, storage devices, and output devices. Examples Keyboard Mouse Hard disk Cables Printer Operating System Operating System: controls and manages the hardware connected to the computer. Provides an interface that helps you interact with the computer. Most operating systems use a GUI. Graphical User Interface (GUI):displays images and pictures that allow the user to interact with a computer easily. Example of an Operating System (Windows XP) Programs Platform: the hardware and operating system working together Program: Instructions that allow the user to complete a task. Examples of programs: Microsoft Word, Calculator Data: information input into the computer by the user. Can be text, graphics, audio or video. Networks Network: A group of computers and devices linked together that are able to share information , data, and devices and communicate with other users. Networks Three Components Server: the main computer on the network that provides services to other computers on the network. Workstation: a computer connected to a network. Communication channel: the path/link that connects the computers and devices. May use cables or be wireless. Types of Networks Local Area Network (LAN): connects computers and devices within a limited area such as a house or office. Usually share printers or scanners. Wide Area Network (WAN): connects computers that are in different areas (different buildings or cities). Example: the Internet