Topologies
... hosts • Hosts are not part of any layer • Operate at all layers • Symbols not standardized – Bear a resemblance to device ...
... hosts • Hosts are not part of any layer • Operate at all layers • Symbols not standardized – Bear a resemblance to device ...
05. Example Networks..
... Wireless LANs: 802.11 • IEEE committee that standardized the wired LANs was given the task of drawing up a wireless LAN standard – result 802.11 • Common known as WiFi • The proposed standard had to work in two modes: – In the presence of a base station – In the absence of a base station ...
... Wireless LANs: 802.11 • IEEE committee that standardized the wired LANs was given the task of drawing up a wireless LAN standard – result 802.11 • Common known as WiFi • The proposed standard had to work in two modes: – In the presence of a base station – In the absence of a base station ...
Networks_10
... Used to divide data that needs to be transmitted into a number of packets, each with a sequence number The TCP at the destination address assembles the data and notifies the sender if any packets are not received within a certain time (‘timeout’) ...
... Used to divide data that needs to be transmitted into a number of packets, each with a sequence number The TCP at the destination address assembles the data and notifies the sender if any packets are not received within a certain time (‘timeout’) ...
Cisco certified network associate
... • Session – Build and tear down of session (Layer 5) • Transport – TCP/UDP (Layer 4) – a.ka. segment • Network – IP Address (Layer 3) – a.k.a. packet • Data Link – MAC (Layer 2) – a.k.a. frame ...
... • Session – Build and tear down of session (Layer 5) • Transport – TCP/UDP (Layer 4) – a.ka. segment • Network – IP Address (Layer 3) – a.k.a. packet • Data Link – MAC (Layer 2) – a.k.a. frame ...
Networks Adrian Janson
... Used to divide data that needs to be transmitted into a number of packets, each with a sequence number The TCP at the destination address assembles the data and notifies the sender if any packets are not received within a certain time (‘timeout’) ...
... Used to divide data that needs to be transmitted into a number of packets, each with a sequence number The TCP at the destination address assembles the data and notifies the sender if any packets are not received within a certain time (‘timeout’) ...
Covert channel
... is a type of computer security attack that creates a capability to transfer information objects between processes that are not supposed to be allowed to communicate by the computer security policy. ...
... is a type of computer security attack that creates a capability to transfer information objects between processes that are not supposed to be allowed to communicate by the computer security policy. ...
NETWORK DEVICES.doc
... Many of these NIC have more than one type of port, which enables different types of cable to attach to the card. For example, some cable modems and DSL modems require that one end of a cable plug in the modem and the other end in a network card. Wireless transmission of data is available through wir ...
... Many of these NIC have more than one type of port, which enables different types of cable to attach to the card. For example, some cable modems and DSL modems require that one end of a cable plug in the modem and the other end in a network card. Wireless transmission of data is available through wir ...
Chapter 10 Exercises
... to send data at the same time, a collision occurs and the computers must attempt to send their messages again. The variations of Ethernet primarily are distinguished from one another by speed: 10-Mbps Ethernet, 100-Mbps or Fast Ethernet, and Gigabit and 10-Gigabit Ethernet. Ethernet uses UTP, STP, ...
... to send data at the same time, a collision occurs and the computers must attempt to send their messages again. The variations of Ethernet primarily are distinguished from one another by speed: 10-Mbps Ethernet, 100-Mbps or Fast Ethernet, and Gigabit and 10-Gigabit Ethernet. Ethernet uses UTP, STP, ...
Packet switching
... – A header with information, such as destination address, source address, time to live (TTL), protocol. – A payload: The data to be sent. This may be a packet of an upper layer. ...
... – A header with information, such as destination address, source address, time to live (TTL), protocol. – A payload: The data to be sent. This may be a packet of an upper layer. ...
- Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... • Each computer and router interface maintains an ARP table for Layer 2 communication. The ARP table is only effective for the broadcast domain (or LAN) that it is connected to. • The router also maintains a routing table that allows it to route data outside of the broadcast domain • Each ARP table ...
... • Each computer and router interface maintains an ARP table for Layer 2 communication. The ARP table is only effective for the broadcast domain (or LAN) that it is connected to. • The router also maintains a routing table that allows it to route data outside of the broadcast domain • Each ARP table ...
Configuring a Network Adapter
... – Non-Plug and Play adapters must be installed with the Add Hardware Wizard in Control Panel ...
... – Non-Plug and Play adapters must be installed with the Add Hardware Wizard in Control Panel ...
The Internet is a global communication network which acts as a
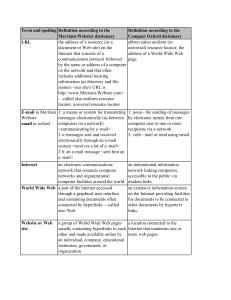
... Draw a diagram including the devices below and record a brief description of how the following Network Hardware devices are used to connect in a network. a. NIC, Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Gateway, Wireless Access Point, ADSL and Cable Modems ...
... Draw a diagram including the devices below and record a brief description of how the following Network Hardware devices are used to connect in a network. a. NIC, Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Gateway, Wireless Access Point, ADSL and Cable Modems ...
Dark Matter and Dark Energy - Hitoshi Murayama Home Page
... Request L&S to continue supporting the admin Give the admin an office in Physics User Group reviews the cost model every year ...
... Request L&S to continue supporting the admin Give the admin an office in Physics User Group reviews the cost model every year ...
Communications and networking history and background Internet
... – each host has a unique 48-bit identification number – data sent from one host to another in "packets" of 100-1500 bytes including source and destination address and error checking bits typical data rate 10-1000 Mbits/sec; limits on cable length ...
... – each host has a unique 48-bit identification number – data sent from one host to another in "packets" of 100-1500 bytes including source and destination address and error checking bits typical data rate 10-1000 Mbits/sec; limits on cable length ...
Table 9.1 Spelling and definitions.pdf
... 1: noun - the sending of messages by electronic means from one computer user to one or more recipients via a network. 2: verb - mail or send using email. ...
... 1: noun - the sending of messages by electronic means from one computer user to one or more recipients via a network. 2: verb - mail or send using email. ...
Data Link Layer
... Link Control Protocol – brings lines up, tears down, etc Network Control Protocol – negotiating network protocol ...
... Link Control Protocol – brings lines up, tears down, etc Network Control Protocol – negotiating network protocol ...
投影片 1
... Object Invocation, .Net Remoting and Java RMI. The switching mechanism is implemented on IXP1200. Porting the switching mechanism to IXP2400. Future work: Parsing header, transcoding ...
... Object Invocation, .Net Remoting and Java RMI. The switching mechanism is implemented on IXP1200. Porting the switching mechanism to IXP2400. Future work: Parsing header, transcoding ...
Network Environments
... sharing of data, software and printers are provided. Generally easier to set up and maintain than servers. OK for small ...
... sharing of data, software and printers are provided. Generally easier to set up and maintain than servers. OK for small ...
Vulnerability analysis consists of several steps: Defining and
... NMAP - Nmap (“Network Mapper”) is an open source tool for network exploration and security auditing. It was designed to rapidly scan large networks, although it works fine against single hosts. Nmap uses raw IP packets in novel ways to determine what hosts are available on the network, what services ...
... NMAP - Nmap (“Network Mapper”) is an open source tool for network exploration and security auditing. It was designed to rapidly scan large networks, although it works fine against single hosts. Nmap uses raw IP packets in novel ways to determine what hosts are available on the network, what services ...
Chapter 4 PowerPoint
... offices for a large company may set up an VPN over the Internet to communicate to the parent office. This is cheaper than purchasing expensive private data lines. Security and encryption is essential since the Internet is a public network. ...
... offices for a large company may set up an VPN over the Internet to communicate to the parent office. This is cheaper than purchasing expensive private data lines. Security and encryption is essential since the Internet is a public network. ...
Wake-on-LAN
Wake-on-LAN (WoL) is an Ethernet or Token ring computer networking standard that allows a computer to be turned on or awakened by a network message.The message is usually sent by a program executed on another computer on the same local area network. It is also possible to initiate the message from another network by using subnet directed broadcasts or a WOL gateway service. Equivalent terms include wake on WAN, remote wake-up, power on by LAN, power up by LAN, resume by LAN, resume on LAN and wake up on LAN. In case the computer being awakened is communicating via Wi-Fi, a supplementary standard called Wake on Wireless LAN (WoWLAN) must be employed.The WOL and WoWLAN standards are often supplemented by vendors to provide protocol-transparent on-demand services, for example in the Apple Bonjour wake-on-demand (Sleep Proxy) feature.