Robert Bledsoe
... grew and if war did break out devastation would be great • To increase the size of their armies, almost all western countries established a conscription, or military draft • Military leaders drew up vast and complex plans for quickly mobilizing millions of men and enormous quantities of supplies in ...
... grew and if war did break out devastation would be great • To increase the size of their armies, almost all western countries established a conscription, or military draft • Military leaders drew up vast and complex plans for quickly mobilizing millions of men and enormous quantities of supplies in ...
The Powder Keg of Europe
... • Germany attempted to prevent Britain & France from obtaining supplies from overseas by using submarines to attack shipping • Feb. 1915: Germany announced unrestricted submarine warfare in the waters around Britain – any ships could be attacked without warning ...
... • Germany attempted to prevent Britain & France from obtaining supplies from overseas by using submarines to attack shipping • Feb. 1915: Germany announced unrestricted submarine warfare in the waters around Britain – any ships could be attacked without warning ...
World War I - Reading Community Schools
... produced, how much would be produced, and what the prices were. • Rationing efforts for food, fuel, and other important resources. • Government control and censorship of the media. • Distribution of propaganda. ...
... produced, how much would be produced, and what the prices were. • Rationing efforts for food, fuel, and other important resources. • Government control and censorship of the media. • Distribution of propaganda. ...
World War I and the Russian Revolution: 1914-1920
... • for example: 5.5 million men in the military in Germany during WWI out of a population of 65 million (25 to 30% of the adult male population) ...
... • for example: 5.5 million men in the military in Germany during WWI out of a population of 65 million (25 to 30% of the adult male population) ...
Propoganda Lesson Plan
... American public opinion to the Allied side. Constant British propaganda efforts, culminating in the Zimmermann Telegram of February 1917, coupled with the German resumption of unrestricted submarine warfare and drew America into the war. Wilson quickly developed an ideological goal of freedom and d ...
... American public opinion to the Allied side. Constant British propaganda efforts, culminating in the Zimmermann Telegram of February 1917, coupled with the German resumption of unrestricted submarine warfare and drew America into the war. Wilson quickly developed an ideological goal of freedom and d ...
World War I
... 1. MAIN Causes of World War I Militarism – Countries were building huge armies and weapons. B. Alliances – Agreements among competing nations to help each other if war broke out. C. Imperialism – Race for empires and opening up new markets. D. Nationalism – Intense national loyalty. People wanted i ...
... 1. MAIN Causes of World War I Militarism – Countries were building huge armies and weapons. B. Alliances – Agreements among competing nations to help each other if war broke out. C. Imperialism – Race for empires and opening up new markets. D. Nationalism – Intense national loyalty. People wanted i ...
Causes of WWI Notes 7-4.1 and Vocabulary
... 1. MAIN Causes of World War I Militarism – Countries were building huge armies and weapons. B. Alliances – Agreements among competing nations to help each other if war broke out. C. Imperialism – Race for empires and opening up new markets. D. Nationalism – Intense national loyalty. People wanted i ...
... 1. MAIN Causes of World War I Militarism – Countries were building huge armies and weapons. B. Alliances – Agreements among competing nations to help each other if war broke out. C. Imperialism – Race for empires and opening up new markets. D. Nationalism – Intense national loyalty. People wanted i ...
A Third World War I Quiz - Social Studies With A Smile
... d. President Wilson supported the war aims of Germany and Austria-Hungary. 3. After the sinking of the “Sussex”, Germany a. b. c. d. ...
... d. President Wilson supported the war aims of Germany and Austria-Hungary. 3. After the sinking of the “Sussex”, Germany a. b. c. d. ...
Section II: The War is Fought (Pages 618-623)
... The Central Powers Germany had superior railroads, a large, well trained army, and a good navy. Germany had been planning strategy for 5 years. They knew they’d probably have to fight on two fronts. They were going to use: “the Schlieffen Plan” – Northern France first and then Russia. ...
... The Central Powers Germany had superior railroads, a large, well trained army, and a good navy. Germany had been planning strategy for 5 years. They knew they’d probably have to fight on two fronts. They were going to use: “the Schlieffen Plan” – Northern France first and then Russia. ...
The Great War Notes
... – Building empires by expanding territory to gain colonies – Increased competition between world powers • Early disputes were settled to avoid war ...
... – Building empires by expanding territory to gain colonies – Increased competition between world powers • Early disputes were settled to avoid war ...
Schenk vs. United States, 1919
... • Assassination of Franz Ferdinand of Austria • Hostile alliances take effect---War declared Central Powers vs. Allied Powers • Germany Great Britain • Austria/Hungary France • Ottoman Empire Russia • Trench warfare and the Western Front 3. President Wilson • Calls for neutrality = conflicting sympa ...
... • Assassination of Franz Ferdinand of Austria • Hostile alliances take effect---War declared Central Powers vs. Allied Powers • Germany Great Britain • Austria/Hungary France • Ottoman Empire Russia • Trench warfare and the Western Front 3. President Wilson • Calls for neutrality = conflicting sympa ...
Sarajevo, Bosnia-Herzegovina June 28, 1914
... • The United States became involved when Germany sank four American merchant ships. They joined the side of Russia, France, and Great Britain. ...
... • The United States became involved when Germany sank four American merchant ships. They joined the side of Russia, France, and Great Britain. ...
an economic reason for war?
... soldiers were killed or wounded Another 1 million soldiers were killed or wounded at the Battle of Somme Despite the deaths, neither the Allies nor the Central Powers gained an advantage after these battles ...
... soldiers were killed or wounded Another 1 million soldiers were killed or wounded at the Battle of Somme Despite the deaths, neither the Allies nor the Central Powers gained an advantage after these battles ...
File
... ordered “over the top.” Soldiers would scramble out of their trenches to race across no-man’s land and attack the enemy lines. Most offensives resulted in huge casualties and little gain of territory. During the 11-month battle of Verdun in 1916, the Germans lost 330,000 men trying to overrun the Fr ...
... ordered “over the top.” Soldiers would scramble out of their trenches to race across no-man’s land and attack the enemy lines. Most offensives resulted in huge casualties and little gain of territory. During the 11-month battle of Verdun in 1916, the Germans lost 330,000 men trying to overrun the Fr ...
Goal 8 - Public Schools of Robeson County
... Spread of the theory of Social Darwinism also impacted the rise of nationalism. Multinational empires (Austria-Hungary, Ottoman Empire) were destabilized. This spilled over into economics (industrial output, trade led to the desire for overseas empire). ...
... Spread of the theory of Social Darwinism also impacted the rise of nationalism. Multinational empires (Austria-Hungary, Ottoman Empire) were destabilized. This spilled over into economics (industrial output, trade led to the desire for overseas empire). ...
General John J. Pershing
... They felt that Europe was too far away and that its conflicts were not trustworthy. President Wilson also believed that all Americans needed to "act and speak in a spirit of neutrality." ...
... They felt that Europe was too far away and that its conflicts were not trustworthy. President Wilson also believed that all Americans needed to "act and speak in a spirit of neutrality." ...
Review for WWI Quiz
... Which situation was a major reason for the United States entry into World War I? a) The League of Nations requested help b) The Maine was blown up in Havana Harbor c) Nazi tyranny threatened Western democracy d) Germany’s use of unrestricted submarine ...
... Which situation was a major reason for the United States entry into World War I? a) The League of Nations requested help b) The Maine was blown up in Havana Harbor c) Nazi tyranny threatened Western democracy d) Germany’s use of unrestricted submarine ...
7 - Moved
... rivalries - patriotism, leaders under pressure to take risks and to be aggressive. There were also colonial disputes - such as the Balkan wars, France and Germany nearly fought over Morocco, Germany resented and antagonized Britain and France. 3. Summarize the forces set in motion by the assassinati ...
... rivalries - patriotism, leaders under pressure to take risks and to be aggressive. There were also colonial disputes - such as the Balkan wars, France and Germany nearly fought over Morocco, Germany resented and antagonized Britain and France. 3. Summarize the forces set in motion by the assassinati ...
Review Slides: Lessons 1-10
... inflicting massive casualties * (Attrition Warfare) • Targeted key position French could/would not surrender (Verdun) • French generals had all but abandoned Verdun • Preferred to defend in plains to west • Politicians said “Hold at all cost!” ...
... inflicting massive casualties * (Attrition Warfare) • Targeted key position French could/would not surrender (Verdun) • French generals had all but abandoned Verdun • Preferred to defend in plains to west • Politicians said “Hold at all cost!” ...
PreAP 14 WWI - WordPress.com
... plan was too lenient toward Germany. • The Treaty of Versailles, signed by Germany, weakened Wilson’s proposal. The treaty stripped Germany of its armed forces and made it pay reparations, or war damages to the ...
... plan was too lenient toward Germany. • The Treaty of Versailles, signed by Germany, weakened Wilson’s proposal. The treaty stripped Germany of its armed forces and made it pay reparations, or war damages to the ...
Ch 13 Section 2 War Consumes Europe WWI
... Ottomans still controlled the straits leading from the Mediterranean to the Black Sea. The Russian army had only one asset—its numbers. Throughout the war the Russian army suffered enormous battlefield losses. More than 2 million Russian soldiers were killed, wounded, or captured in 1915 alone. And ...
... Ottomans still controlled the straits leading from the Mediterranean to the Black Sea. The Russian army had only one asset—its numbers. Throughout the war the Russian army suffered enormous battlefield losses. More than 2 million Russian soldiers were killed, wounded, or captured in 1915 alone. And ...
World War I - Fort Bend ISD
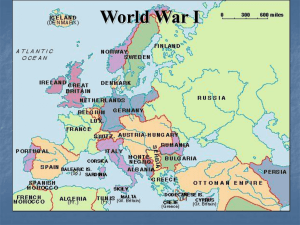
... “powder keg of Europe”. Ethnic rivalries and the interests of the major powers put all of these different groups at odds. Russia wanted access to the Mediterranean Sea. Germany wanted a rail link to the Ottoman Empire. AustriaHungary accused Serbia of undermining their authority in Bosnia. The ‘powd ...
... “powder keg of Europe”. Ethnic rivalries and the interests of the major powers put all of these different groups at odds. Russia wanted access to the Mediterranean Sea. Germany wanted a rail link to the Ottoman Empire. AustriaHungary accused Serbia of undermining their authority in Bosnia. The ‘powd ...
How was America transformed at home during World War I?
... Williamson store, he went in and gathered up everything that was made in Germany, and had a big bonfire out in the middle of the street.” —Lola Gamble Clyde on ...
... Williamson store, he went in and gathered up everything that was made in Germany, and had a big bonfire out in the middle of the street.” —Lola Gamble Clyde on ...
Chapter 19 - MrsBoyer Wikispace
... The Collapse of Germany • November 3, 1918, Austria-Hungary surrenders to Allies • German sailors, soldiers rebel; socialists establish German republic - kaiser gives up throne • Germans exhausted; armistice, or truce, signed November 11, 1918 The Final Toll • World War I bloodiest war in history to ...
... The Collapse of Germany • November 3, 1918, Austria-Hungary surrenders to Allies • German sailors, soldiers rebel; socialists establish German republic - kaiser gives up throne • Germans exhausted; armistice, or truce, signed November 11, 1918 The Final Toll • World War I bloodiest war in history to ...
WWI and The Jazz Age
... World War I World War I began when Austria-Hungary’s soon to be king was assassinated by Serbian Nationalists when he visited Bosnia. Serbia wanted Bosnia to join their “team” or form an alliance them, NOT with Austria-Hungary. So… … Austria-Hungary threatened war on Serbia and new alliances were d ...
... World War I World War I began when Austria-Hungary’s soon to be king was assassinated by Serbian Nationalists when he visited Bosnia. Serbia wanted Bosnia to join their “team” or form an alliance them, NOT with Austria-Hungary. So… … Austria-Hungary threatened war on Serbia and new alliances were d ...