Canada and Latin America in WWI
... ultimatum to Germany to withdraw its army from Belgium expired on 4 August 1914. Aug. 5th, 1914: Britain declares then war. Canada is automatically at war with them. Canada is allied with Serbia, Russia, Britain and France against the German and Austro-Hungarian empires. ...
... ultimatum to Germany to withdraw its army from Belgium expired on 4 August 1914. Aug. 5th, 1914: Britain declares then war. Canada is automatically at war with them. Canada is allied with Serbia, Russia, Britain and France against the German and Austro-Hungarian empires. ...
world war i
... would be set up with the Australian and British flags side by side as a back drop to the speeches. Among those who were offered to enlist were Aboriginal Australians. Only 400 Aboriginal people were accepted for service, and they were all deemed to be ‘of substantial European origin or descent’. Whe ...
... would be set up with the Australian and British flags side by side as a back drop to the speeches. Among those who were offered to enlist were Aboriginal Australians. Only 400 Aboriginal people were accepted for service, and they were all deemed to be ‘of substantial European origin or descent’. Whe ...
ICT2
... • Historians have traditionally cited four longterm causes of the First World War – NATIONALISM – a devotion to the interests and culture of one’s nation – IMPERIALISM – Economic and political control over ...
... • Historians have traditionally cited four longterm causes of the First World War – NATIONALISM – a devotion to the interests and culture of one’s nation – IMPERIALISM – Economic and political control over ...
The Great War - cloudfront.net
... In less than a week, Central Powers of Germany and Austria-Hungary (later joined by the Ottoman Empire) were at war against the Allied Powers of Britain, France, Russia, and Serbia. ...
... In less than a week, Central Powers of Germany and Austria-Hungary (later joined by the Ottoman Empire) were at war against the Allied Powers of Britain, France, Russia, and Serbia. ...
World History Text: Patterns of Interaction Cha
... A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield. In World War I, the region along the German-Russian border where Russians and Serbs battled Germans, Austrians, and Turks. The use of submarines to sink without warning any ship (including neutral ships ...
... A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield. In World War I, the region along the German-Russian border where Russians and Serbs battled Germans, Austrians, and Turks. The use of submarines to sink without warning any ship (including neutral ships ...
World War I - Denton ISD
... • Today in History: 10/31/1941, the U.S. Navy destroyer Reuben James was torpedoed by a German U-boat off Iceland with the loss of 115 lives, even though the United States had not yet entered World War II. ...
... • Today in History: 10/31/1941, the U.S. Navy destroyer Reuben James was torpedoed by a German U-boat off Iceland with the loss of 115 lives, even though the United States had not yet entered World War II. ...
World War I or The Great War
... within the Ottoman Empire. With British military & economic support and promises of independence for the different Arab nationalities, Lawrence waged a successful guerilla war against the Ottoman Turks causing them to waste valuable resources, keeping troops off the front lines, and leading to their ...
... within the Ottoman Empire. With British military & economic support and promises of independence for the different Arab nationalities, Lawrence waged a successful guerilla war against the Ottoman Turks causing them to waste valuable resources, keeping troops off the front lines, and leading to their ...
World War I and The 1920s" PowerPoint
... • Imperialism- European nations searched for colonies during the 19th century because they produced more goods than they needed. • Military Expansion-Europeans maintained large standing armies in peace time in case of war. • Alliances- Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy formed the Triple Alliance. ...
... • Imperialism- European nations searched for colonies during the 19th century because they produced more goods than they needed. • Military Expansion-Europeans maintained large standing armies in peace time in case of war. • Alliances- Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy formed the Triple Alliance. ...
WWI_and_Russian_Revolution
... Militarism: aggressive preparation for war Germany had set up an army reserve system by 1890. Britain had always depended on its navy so they were not alarmed by ground troops. In 1897 Germany began building a sea power which alarmed Britain. Italy, Japan, and the US quickly joined the naval a ...
... Militarism: aggressive preparation for war Germany had set up an army reserve system by 1890. Britain had always depended on its navy so they were not alarmed by ground troops. In 1897 Germany began building a sea power which alarmed Britain. Italy, Japan, and the US quickly joined the naval a ...
Unit 5: 20th Century Crises
... Militarism: aggressive preparation for war Germany had set up an army reserve system by 1890. Britain had always depended on its navy so they were not alarmed by ground troops. In 1897 Germany began building a sea power which alarmed Britain. Italy, Japan, and the US quickly joined the naval a ...
... Militarism: aggressive preparation for war Germany had set up an army reserve system by 1890. Britain had always depended on its navy so they were not alarmed by ground troops. In 1897 Germany began building a sea power which alarmed Britain. Italy, Japan, and the US quickly joined the naval a ...
World War I and Aftermath
... too lenient toward Germany. • The Treaty of Versailles, signed by Germany, weakened Wilson’s proposal. The treaty stripped Germany of its armed forces and made it pay reparations, or war damages to the Allies. • The Treaty of Versailles and the League of Nations were opposed by many United States la ...
... too lenient toward Germany. • The Treaty of Versailles, signed by Germany, weakened Wilson’s proposal. The treaty stripped Germany of its armed forces and made it pay reparations, or war damages to the Allies. • The Treaty of Versailles and the League of Nations were opposed by many United States la ...
What caused World War I, and why did the United States enter the war
... • The assassination triggered a chain of events that drew two sets of allies into a bloody conflict. Europe’s alliance system caused the conflict to spread quickly, creating two main combatants. • Allied Powers included Britain, France, Russia, and Serbia. • Central Powers included Germany and Austr ...
... • The assassination triggered a chain of events that drew two sets of allies into a bloody conflict. Europe’s alliance system caused the conflict to spread quickly, creating two main combatants. • Allied Powers included Britain, France, Russia, and Serbia. • Central Powers included Germany and Austr ...
World War I-Causes (1914
... In 1914, many European countries were preparing for war. The conflict they would engage in is called World War I. You can remember the causes of the war by thinking of the word MAIN. Each letter stands for one of the major causes – militarism, alliances, imperialism, nationalism. Many European count ...
... In 1914, many European countries were preparing for war. The conflict they would engage in is called World War I. You can remember the causes of the war by thinking of the word MAIN. Each letter stands for one of the major causes – militarism, alliances, imperialism, nationalism. Many European count ...
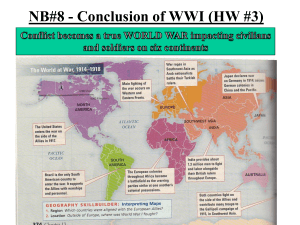
Conclusion of War Slideshow
... political life. Covenants [Agreements] must now be entered into which will render such things impossible for the future; and those covenants must be backed by the united force of all nations that love justice and are willing to maintain it at any cost... Woodrow Wilson ...
... political life. Covenants [Agreements] must now be entered into which will render such things impossible for the future; and those covenants must be backed by the united force of all nations that love justice and are willing to maintain it at any cost... Woodrow Wilson ...
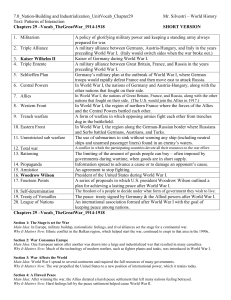
CHAPTER 24 THE NATION AT WAR
... & war of attrition comparison to other Allied forces: Powers had 57% ...
... & war of attrition comparison to other Allied forces: Powers had 57% ...
File
... taken quickly & Russia got ready too fast, Germany had to abandon the Schlieffen Plan & fight a 2-front war ...
... taken quickly & Russia got ready too fast, Germany had to abandon the Schlieffen Plan & fight a 2-front war ...
WWI test hon - A More Perfect Union
... 10. _____ A vital straight connecting the Black Sea and the Mediterranean. 11. _____ Horrible acts committed against innocent people. 12. _____ Term that means when a country prepares its military forces for war. 13. _____ This was the first revolution that pushed the Czar out of power and saw women ...
... 10. _____ A vital straight connecting the Black Sea and the Mediterranean. 11. _____ Horrible acts committed against innocent people. 12. _____ Term that means when a country prepares its military forces for war. 13. _____ This was the first revolution that pushed the Czar out of power and saw women ...
Presentation 3
... But Britain remains more aloof Alliance system rigidifies: –antagonistic blocs confront each other ...
... But Britain remains more aloof Alliance system rigidifies: –antagonistic blocs confront each other ...
No Slide Title
... w Neither soldiers nor officers were prepared for the new, highly efficient killing machines used in WW I. w Machine guns, hand grenades, artillery shells, and poison gas killed thousands of soldiers who left their trenches to attack the enemy. w As morale fell, the lines between soldiers and civili ...
... w Neither soldiers nor officers were prepared for the new, highly efficient killing machines used in WW I. w Machine guns, hand grenades, artillery shells, and poison gas killed thousands of soldiers who left their trenches to attack the enemy. w As morale fell, the lines between soldiers and civili ...
TheCourse_2 - Loudon High School
... The Central Powers: Germany, Austria-Hungry, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria. ...
... The Central Powers: Germany, Austria-Hungry, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria. ...
World War I SOL10
... (Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy) and the Triple Entente (Great Britain, France and Russia) Formed. Nationalist feelings in Serbia provided the “Spark” that started the war. Archduke Ferdinand was assassinated by a Serbian Nationalist named Gavrilo Princip who hoped the assassination would help ...
... (Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy) and the Triple Entente (Great Britain, France and Russia) Formed. Nationalist feelings in Serbia provided the “Spark” that started the war. Archduke Ferdinand was assassinated by a Serbian Nationalist named Gavrilo Princip who hoped the assassination would help ...