Adverbs and Prepositions
... because, since, after, although, or when or a relative pronoun such as that, who, or which. Ex: When he handed in his homework, he forgot to give the teacher the last ...
... because, since, after, although, or when or a relative pronoun such as that, who, or which. Ex: When he handed in his homework, he forgot to give the teacher the last ...
Sentence Diagramming glencoe
... an action verb. Almost always, a sentence has an indirect object only if it has a direct object as well. In the sentence, the indirect object appears between the verb and the direct object. To diagram the sentence, draw a line that slants down from the verb, bends, and extends horizontally to the ri ...
... an action verb. Almost always, a sentence has an indirect object only if it has a direct object as well. In the sentence, the indirect object appears between the verb and the direct object. To diagram the sentence, draw a line that slants down from the verb, bends, and extends horizontally to the ri ...
Regular Present Tense –er and –ir Verbs
... an unconjugated verb. In English it usually includes the word “to” – to be, to swim, to eat, to live, etc. It has no tense (present, past, future) or form (alignment with a subject). In Spanish all infinitives end in either -ar, -er-, ir. ...
... an unconjugated verb. In English it usually includes the word “to” – to be, to swim, to eat, to live, etc. It has no tense (present, past, future) or form (alignment with a subject). In Spanish all infinitives end in either -ar, -er-, ir. ...
7 The Minor Parts of Speech
... function words; they account for about 60% of words used in speech and 45% of those used in writing. (You can check this for yourself by counting the words in this paragraph, then counting the words belonging to the major parts of speech, and subtracting that number from the whole. The remainder is ...
... function words; they account for about 60% of words used in speech and 45% of those used in writing. (You can check this for yourself by counting the words in this paragraph, then counting the words belonging to the major parts of speech, and subtracting that number from the whole. The remainder is ...
Direct and indirect objects
... We showed the photos to David. OR We showed David the photos. We can use for with these verbs: book, bring, build, buy, choose, cook, fetch, find, get, leave, make, order, pick, reserve, save They found a spare ticket for me. OR They found me a spare ticket. I’ve saved a seat for you. OR I’ve saved y ...
... We showed the photos to David. OR We showed David the photos. We can use for with these verbs: book, bring, build, buy, choose, cook, fetch, find, get, leave, make, order, pick, reserve, save They found a spare ticket for me. OR They found me a spare ticket. I’ve saved a seat for you. OR I’ve saved y ...
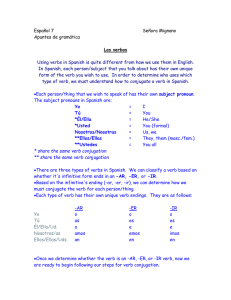
Español 7
... form of the verb you wish to use. In order to determine who uses which type of verb, we must understand how to conjugate a verb in Spanish. Each person/thing that we wish to speak of has their own subject pronoun. The subject pronouns in Spanish are: Yo ...
... form of the verb you wish to use. In order to determine who uses which type of verb, we must understand how to conjugate a verb in Spanish. Each person/thing that we wish to speak of has their own subject pronoun. The subject pronouns in Spanish are: Yo ...
2. Word OrderW2
... • The indirect object answers the question "To whom?" or "For whom?". • The indirect object is the recipient of the direct object. • The indirect object is an object that often comes after a preposition. • The indirect object should always stay with the verb or direct object. Example: Carol gave the ...
... • The indirect object answers the question "To whom?" or "For whom?". • The indirect object is the recipient of the direct object. • The indirect object is an object that often comes after a preposition. • The indirect object should always stay with the verb or direct object. Example: Carol gave the ...
Gramática - Beechen Cliff
... indicate that the action is done by the subject to itself. For example, levantar is to lift, but adding the reflexive pronoun makes levantarse, to get (oneself) up. The ‘reflexive’ meaning of some verbs is obvious, e.g. lavarse, to wash (oneself). Others are less obvious and have to be learnt, e.g. ...
... indicate that the action is done by the subject to itself. For example, levantar is to lift, but adding the reflexive pronoun makes levantarse, to get (oneself) up. The ‘reflexive’ meaning of some verbs is obvious, e.g. lavarse, to wash (oneself). Others are less obvious and have to be learnt, e.g. ...
The Grammar Rules for Basic Clause Structure in English
... [the verb give can also be used without to before indirect object] 13. A typical word order for an English one-clause-sentence would therefore be: Subject-Verb-Direct Object-Indirect Object The teacher gave an assignment to the students. 14. To expand the basic one-clause-sentence, you can add manne ...
... [the verb give can also be used without to before indirect object] 13. A typical word order for an English one-clause-sentence would therefore be: Subject-Verb-Direct Object-Indirect Object The teacher gave an assignment to the students. 14. To expand the basic one-clause-sentence, you can add manne ...
Parts of a Sentence
... Consider, make, and any verbs that can be replaced by consider or make such as call, keep, name, find, choose, elect, appoint, paint, color, and render. My grandpa considers the Steelers to be exquisite. He called them the best team in the league. (or considered them to be the best team) The Sup ...
... Consider, make, and any verbs that can be replaced by consider or make such as call, keep, name, find, choose, elect, appoint, paint, color, and render. My grandpa considers the Steelers to be exquisite. He called them the best team in the league. (or considered them to be the best team) The Sup ...
10 Complements
... equals the subject. You are the captain of your own fate. Captain of your own fate (well, actually, just the word captain) is the predicate nominative. It follows the linking verb are and equals the subject. As a matter of fact, you should be able to switch the subject and predicate nominative aroun ...
... equals the subject. You are the captain of your own fate. Captain of your own fate (well, actually, just the word captain) is the predicate nominative. It follows the linking verb are and equals the subject. As a matter of fact, you should be able to switch the subject and predicate nominative aroun ...
Prepositions - BasicComposition.Com
... Grammar Prepositions Prepositions begin phrases that m odify other w ord s in the sentence. Often, they d escribe tim e or space relationships, show ing how a noun or pronoun relates to another w ord w ithin a sentence. ...
... Grammar Prepositions Prepositions begin phrases that m odify other w ord s in the sentence. Often, they d escribe tim e or space relationships, show ing how a noun or pronoun relates to another w ord w ithin a sentence. ...
How to Teach Sentence Diagramming
... Expanding the Baseline Compound subjects (Tom and Sue) and compound predicates (talked and shopped) are drawn as multiple horizontal lines stacked vertically and are joined at each end by a fan of diagonal lines. The coordinating conjunction (and) is placed next to a dotted vertical line that connec ...
... Expanding the Baseline Compound subjects (Tom and Sue) and compound predicates (talked and shopped) are drawn as multiple horizontal lines stacked vertically and are joined at each end by a fan of diagonal lines. The coordinating conjunction (and) is placed next to a dotted vertical line that connec ...
Quick Reference: Parts of Speech
... Personal pronouns change form to show how they function in sentences. Different functions are shown by different cases: nominative, objective, and possessive. For examples, see Section 2.1. A nominative pronoun is used as a subject or a predicate nominative in a sentence. An objective pronoun is use ...
... Personal pronouns change form to show how they function in sentences. Different functions are shown by different cases: nominative, objective, and possessive. For examples, see Section 2.1. A nominative pronoun is used as a subject or a predicate nominative in a sentence. An objective pronoun is use ...
Repaso rápido: informal and formal subject pronouns
... Remember the following expressions to ask for and to say what time it is: What time is it? It is (number) o’clock. ¿Qué hora es? Es la (+ number)./Son las (+ number). Use y (+ number of minutes through veintinueve) to add minutes after the hour or menos (+ number of minutes through veintinueve) to i ...
... Remember the following expressions to ask for and to say what time it is: What time is it? It is (number) o’clock. ¿Qué hora es? Es la (+ number)./Son las (+ number). Use y (+ number of minutes through veintinueve) to add minutes after the hour or menos (+ number of minutes through veintinueve) to i ...
The Gerund
... the noun in the predicate phrase that tells who or what receives the action of the verb. • The result of the action (verb) performed by the subject (noun) is the direct object (noun) • Ramen NoOdLes loves jumping. • “jumping” is the direct object, and it is also a gerund. Why? Because it is an activ ...
... the noun in the predicate phrase that tells who or what receives the action of the verb. • The result of the action (verb) performed by the subject (noun) is the direct object (noun) • Ramen NoOdLes loves jumping. • “jumping” is the direct object, and it is also a gerund. Why? Because it is an activ ...
Definition: All German nouns belong to one of three grammatical
... the action of the verb occurs. In English usually it is preceded by a preposition, “I give the book to Katja”, the name “Katja” is an indirect object noun, to replace it with a pronoun we would say in English “her”, in German we would say “ihr”, note that since the IOP is associated with the dative, ...
... the action of the verb occurs. In English usually it is preceded by a preposition, “I give the book to Katja”, the name “Katja” is an indirect object noun, to replace it with a pronoun we would say in English “her”, in German we would say “ihr”, note that since the IOP is associated with the dative, ...
Appositive Phrase?
... Each year, thousands of Americans travel (1) to hundreds of vacation spots in the United States and other countries. (2) Anticipating all kinds of weather and activities, many eager travelers pack far too much clothing and equipment. The most effective way to pack is (3) to set out clothes for the t ...
... Each year, thousands of Americans travel (1) to hundreds of vacation spots in the United States and other countries. (2) Anticipating all kinds of weather and activities, many eager travelers pack far too much clothing and equipment. The most effective way to pack is (3) to set out clothes for the t ...
Prepositional phrases
... • A phrase is not a sentence; it does not contain a subject and verb. in the café • A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition and its object (a noun or pronoun) to her • The subject of a sentence can NEVER be found in a prepositional phrase. ...
... • A phrase is not a sentence; it does not contain a subject and verb. in the café • A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition and its object (a noun or pronoun) to her • The subject of a sentence can NEVER be found in a prepositional phrase. ...
Presentation Exercise: Chapter 38
... True or False. A relative clause will take the subjunctive mood in Latin, if it’s attached to an antecedent which is part of indirect discourse. Fill in the Blank. __________________________ is the term used for the phenomenon in which a speaker produces faulty grammar by importing a linguistic rule ...
... True or False. A relative clause will take the subjunctive mood in Latin, if it’s attached to an antecedent which is part of indirect discourse. Fill in the Blank. __________________________ is the term used for the phenomenon in which a speaker produces faulty grammar by importing a linguistic rule ...
Conjugating –AR Verbs in the Preterite Tense
... ie…Hay - There is (are) Hay que- One must Debe - should Debe de - must ...
... ie…Hay - There is (are) Hay que- One must Debe - should Debe de - must ...
Sentences: Kinds and Parts
... Every sentence or independent clause can be divided into two parts: subject and predicate. The subject half contains the subject (simple or compound), together with its modifiers. The predicate half contains the verb (simple or compound), with its modifiers and any other words or phrases that comple ...
... Every sentence or independent clause can be divided into two parts: subject and predicate. The subject half contains the subject (simple or compound), together with its modifiers. The predicate half contains the verb (simple or compound), with its modifiers and any other words or phrases that comple ...
DEFINITE REFERENTIAL NULL OBJECTS IN ANCIENT GREEK
... can see from the English translation, no pronominal objects need to be supplied. In fact, there is a semantic difference between the two couples of verbs, both in Greek and in English: these are verbs that have two different predicate frames, a bivalent (transitive) and a monovalent (intransitive) o ...
... can see from the English translation, no pronominal objects need to be supplied. In fact, there is a semantic difference between the two couples of verbs, both in Greek and in English: these are verbs that have two different predicate frames, a bivalent (transitive) and a monovalent (intransitive) o ...