Prediction practice - unlinked
... • Used to separate fragments of DNA or proteins according to size (uses an electric field to separate charge molecules) DNA is all negatively charged so everything moves in the same ...
... • Used to separate fragments of DNA or proteins according to size (uses an electric field to separate charge molecules) DNA is all negatively charged so everything moves in the same ...
Large Scale Gene Expression Analysis
... variety of genes that are involved in nitrogen utilization by contacting simultaneously a binding site on the DNA and RNA polymerase complexed with the 54 sigma factor at the promoter. ...
... variety of genes that are involved in nitrogen utilization by contacting simultaneously a binding site on the DNA and RNA polymerase complexed with the 54 sigma factor at the promoter. ...
5echap12guidedreading
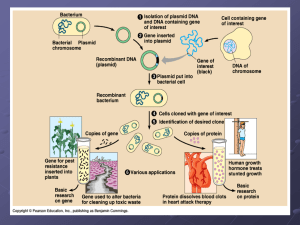
... 12. Human growth hormone and insulin produced by DNA technology are used in the treatment of which diseases? ...
... 12. Human growth hormone and insulin produced by DNA technology are used in the treatment of which diseases? ...
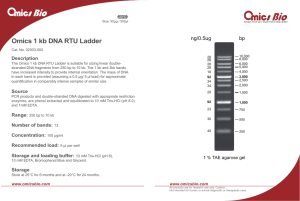
Omics 1 kb DNA RTU Ladder
... in each band is provided (assuming a 0.5 μg/ 5 μl load) for approximate quantification in comparably intense samples of similar size. ...
... in each band is provided (assuming a 0.5 μg/ 5 μl load) for approximate quantification in comparably intense samples of similar size. ...
ANNEX B: Selected Biotechnology Terms
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) – a method for the selective amplification of a DNA bas sequence using heatstable polymerase and two 20-base primers. Because the newly synthesized DNA strands can serve as templates for the same primer sequences successive rounds of primer annealing, strand elongatio ...
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) – a method for the selective amplification of a DNA bas sequence using heatstable polymerase and two 20-base primers. Because the newly synthesized DNA strands can serve as templates for the same primer sequences successive rounds of primer annealing, strand elongatio ...
Real-time polymerase chain reaction

A real-time polymerase chain reaction is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR, i.e. in real-time, and not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively (Quantitative real-time PCR), semi-quantitatively, i.e. above/below a certain amount of DNA molecules (Semi quantitative real-time PCR) or qualitatively (Qualitative real-time PCR).Two common methods for the detection of PCR products in real-time PCR are: (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA, and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence.The Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments (MIQE) guidelines propose that the abbreviation qPCR be used for quantitative real-time PCR and that RT-qPCR be used for reverse transcription–qPCR [1]. The acronym ""RT-PCR"" commonly denotes reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and not real-time PCR, but not all authors adhere to this convention.