Viral mechanisms of immune evasion
... size of RNA viruses is limited. Although this confers the advantage Antigenic variability was one of the first viral immune-evasion of being able to use mutation to escape immune control, there is strategies to be identified. Because of the low fidelity of RNA polylittle room in the genome to allow ...
... size of RNA viruses is limited. Although this confers the advantage Antigenic variability was one of the first viral immune-evasion of being able to use mutation to escape immune control, there is strategies to be identified. Because of the low fidelity of RNA polylittle room in the genome to allow ...
A Piscine Birnavirus Induces Inhibition of Protein Synthesis in CHSE
... Cells employ inhibition of protein synthesis as a defensive mechanism in response to virus invasion, the aim being to limit the production of virus progeny and consequently arrest the spread within the organism. In higher vertebrates, there are mainly three well-known mechanisms by which inhibition ...
... Cells employ inhibition of protein synthesis as a defensive mechanism in response to virus invasion, the aim being to limit the production of virus progeny and consequently arrest the spread within the organism. In higher vertebrates, there are mainly three well-known mechanisms by which inhibition ...
03-Necrosis and apoptosis 2008
... The fragments remain membrane-bound and contain cell organelles with or without nuclear fragments. ...
... The fragments remain membrane-bound and contain cell organelles with or without nuclear fragments. ...
Section 7.2 Cell Structure
... endoplasmic reticulum, or ER. The portion of the ER involved in making proteins is called rough ER. It is given this name because of the ribosomes found on its surface. Newly made proteins leave the ribosomes and move into the rough ER, where they may be chemically modified. ...
... endoplasmic reticulum, or ER. The portion of the ER involved in making proteins is called rough ER. It is given this name because of the ribosomes found on its surface. Newly made proteins leave the ribosomes and move into the rough ER, where they may be chemically modified. ...
Non-neoplastic globe pathology non-neoplastic globe
... apoptosis has been linked to hyperglycemia and retinal pericyte death hyperglycemic states deplete intracellular glutathione (defense against peroxidation) hyperglycemic environments trigger upregulation of bax (apoptosis activator) and downregulation of bcl-2 (apoptosis inhibitor) eventually causin ...
... apoptosis has been linked to hyperglycemia and retinal pericyte death hyperglycemic states deplete intracellular glutathione (defense against peroxidation) hyperglycemic environments trigger upregulation of bax (apoptosis activator) and downregulation of bcl-2 (apoptosis inhibitor) eventually causin ...
cells
... describe and give examples of chemical reactions required to sustain life (…role of enzymes) describe the relationship between structure and function ...
... describe and give examples of chemical reactions required to sustain life (…role of enzymes) describe the relationship between structure and function ...
Signaling
... 3. Signaling between adjacent cells via Notch & Delta (or other related ligands). 4. Notch is a single-pass transmembrane protein undergoing proteolytic process to function. 5. Deregulated Notch signaling is often found in cancer development. ...
... 3. Signaling between adjacent cells via Notch & Delta (or other related ligands). 4. Notch is a single-pass transmembrane protein undergoing proteolytic process to function. 5. Deregulated Notch signaling is often found in cancer development. ...
ABSTRACT Title of Document:
... conserved among the animals and plant kingdoms (Abramovitch 2004, Iriti 2007). Since apoptosis plays an important role in the innate immune response against pathogens, it is essential for a pathogen to combat apoptosis in order to persist. One study showed that apoptotic cell death reduced the viabi ...
... conserved among the animals and plant kingdoms (Abramovitch 2004, Iriti 2007). Since apoptosis plays an important role in the innate immune response against pathogens, it is essential for a pathogen to combat apoptosis in order to persist. One study showed that apoptotic cell death reduced the viabi ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 2 Review
... The function of the organelle that the arrow is pointing to is 1. Control center of the cell. 2. Powerhouse of the cell. 3. Synthesizes proteins. 4. Contains enzymes that digest substances. ...
... The function of the organelle that the arrow is pointing to is 1. Control center of the cell. 2. Powerhouse of the cell. 3. Synthesizes proteins. 4. Contains enzymes that digest substances. ...
Cell-A-Bration
... – Receptor proteins: bind specific substances outside the cell; act like antennae for the cell, collecting info about extracellular conditions – Enzymes: proteins that assist in reactions inside the cell – Transport proteins: move substances in & out of cell – See page 177 ...
... – Receptor proteins: bind specific substances outside the cell; act like antennae for the cell, collecting info about extracellular conditions – Enzymes: proteins that assist in reactions inside the cell – Transport proteins: move substances in & out of cell – See page 177 ...
Cell is the universal functional unit of all forms of life. On the basis of
... 6. Some reactions of gluconeogenesis and urea cycle also occurs in mitochondria. Mitochondria is capable of synthesizing some of its proteins. 7. Mitochondria contains some DNA known as mitochondrial DNA and ribosomes. 8. Mitochondria which are essential for life because of their involvement in ATP ...
... 6. Some reactions of gluconeogenesis and urea cycle also occurs in mitochondria. Mitochondria is capable of synthesizing some of its proteins. 7. Mitochondria contains some DNA known as mitochondrial DNA and ribosomes. 8. Mitochondria which are essential for life because of their involvement in ATP ...
Syllabus for Medical Cell Biology
... principles, focusing on cells, but also applying modern physics, chemistry and test biology the experimental method. It deals with the structure and functions or the interaction of cell components by using different approaches, namely at the whole cell, subcellular and molecular levels, it is concer ...
... principles, focusing on cells, but also applying modern physics, chemistry and test biology the experimental method. It deals with the structure and functions or the interaction of cell components by using different approaches, namely at the whole cell, subcellular and molecular levels, it is concer ...
Review of the Cell and its Organelles
... Attached to the nucleus are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER) releases lipids, such as hormones, that are used both in the cell and in neighbouring tissues. The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) looks rough because it is studded with ribosomes. ...
... Attached to the nucleus are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER) releases lipids, such as hormones, that are used both in the cell and in neighbouring tissues. The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) looks rough because it is studded with ribosomes. ...
Therapeutic opportunities for cell cycle re-entry
... complete before mitosis can occur and is the period during which the chromosomes start to condense. Cell cycle progression is controlled by a complex system of proteins that coordinate the biochemical events within the cell necessary for cell division. These proteins include cyclins, cyclin-dependen ...
... complete before mitosis can occur and is the period during which the chromosomes start to condense. Cell cycle progression is controlled by a complex system of proteins that coordinate the biochemical events within the cell necessary for cell division. These proteins include cyclins, cyclin-dependen ...
cell communication powerpoint
... • G protein-linked receptors (GPLRs) are the largest family of cell-surface receptors • A GPLR is a plasma membrane receptor that works with the help of a G protein • The G protein acts as an on/off switch: If GDP is bound to the G protein, the G protein is inactive. If GTP is attached = active. ...
... • G protein-linked receptors (GPLRs) are the largest family of cell-surface receptors • A GPLR is a plasma membrane receptor that works with the help of a G protein • The G protein acts as an on/off switch: If GDP is bound to the G protein, the G protein is inactive. If GTP is attached = active. ...
10ProjectINBPages
... 3. Does my model show the detailed exterior AND interior structure of my assigned organelle? 4. Do I know how many of my organelles would be present and where they’d be found in the cell? 5. Have I researched important facts for my presentation by looking at several different websites/sources? 6. Do ...
... 3. Does my model show the detailed exterior AND interior structure of my assigned organelle? 4. Do I know how many of my organelles would be present and where they’d be found in the cell? 5. Have I researched important facts for my presentation by looking at several different websites/sources? 6. Do ...
Email: , Ph. +1-305-348-0674
... Dr. Chand received his PhD from the University of Delhi, India and got his postdoctoral training in Department of Pathology at UNM Health Science Center, Albuquerque, NM. As an Assistant Professor (Research) at Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology (CIDI), UNM School of Medicine Dr. Chand wo ...
... Dr. Chand received his PhD from the University of Delhi, India and got his postdoctoral training in Department of Pathology at UNM Health Science Center, Albuquerque, NM. As an Assistant Professor (Research) at Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology (CIDI), UNM School of Medicine Dr. Chand wo ...
BCL-2 Expression and Mitochondrial Activity in
... complexes with death-accelerating homologs7 and functions in antioxidant pathways in preventing apoptosis.8The precise biochemical activities of bcl-2 protein and its homologs are not known, however. Because of its localization to mitochondrial membranes,' protection by BCL-2 has been previously ass ...
... complexes with death-accelerating homologs7 and functions in antioxidant pathways in preventing apoptosis.8The precise biochemical activities of bcl-2 protein and its homologs are not known, however. Because of its localization to mitochondrial membranes,' protection by BCL-2 has been previously ass ...
The Miracle of How We See
... infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm. The space within the ER is called the ER lumen. Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newl ...
... infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm. The space within the ER is called the ER lumen. Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newl ...
The Cell Project
... infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm. The space within the ER is called the ER lumen. Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newl ...
... infolded and convoluted tubes that are located in the cell's cytoplasm. The space within the ER is called the ER lumen. Smooth ER transports materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newl ...
Constitutive caspase-like machinery executes programmed cell
... are conserved from the nematode to humans. Most animal ...
... are conserved from the nematode to humans. Most animal ...
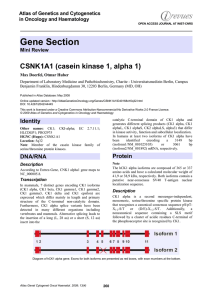
Gene Section CSNK1A1 (casein kinase 1, alpha 1) in Oncology and Haematology
... Recently is has been shown, that CK1 is involved in negatively regulating apoptosis through phosphorylation of diverse cellular proteins including the p75 tumor necrosis factor, proteins of the deathinducing signaling complex (TRAIL induced apoptosis) or Bid (FAS-mediated apoptosis). It is thought, ...
... Recently is has been shown, that CK1 is involved in negatively regulating apoptosis through phosphorylation of diverse cellular proteins including the p75 tumor necrosis factor, proteins of the deathinducing signaling complex (TRAIL induced apoptosis) or Bid (FAS-mediated apoptosis). It is thought, ...
Apoptosis

Apoptosis (/ˌæpəˈtoʊsɪs/; from Ancient Greek ἀπό apo, ""by, from, of, since, than"" and πτῶσις ptōsis, ""fall"") is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, chromosomal DNA fragmentation, and global mRNA decay.In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's lifecycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic bodies that phagocytic cells are able to engulf and quickly remove before the contents of the cell can spill out onto surrounding cells and cause damage.Between 50 and 70 billion cells die each day due to apoptosis in the average human adult. For an average child between the ages of 8 and 14, approximately 20 billion to 30 billion cells die a day.Research in and around apoptosis has increased substantially since the early 1990s. In addition to its importance as a biological phenomenon, defective apoptotic processes have been implicated in a wide variety of diseases. Excessive apoptosis causes atrophy, whereas an insufficient amount results in uncontrolled cell proliferation, such as cancer.Some factors like Fas receptor, caspases (C-cysteine rich, asp- aspartic acid moiety containing, ase – proteases) etc. promote apoptosis, while members of Bcl-2 inhibit apoptosis.