Hormones and Signal Transduction III
... RAS RAS is a Family of Related Proteins Each is Monomeric and like the α-subunit of G-Proteins RAS Proteins Bind Guanine Nucleotides RAS Swaps GDP for GTP on Activation RAS Slowly Cleaves GTP to GDP ...
... RAS RAS is a Family of Related Proteins Each is Monomeric and like the α-subunit of G-Proteins RAS Proteins Bind Guanine Nucleotides RAS Swaps GDP for GTP on Activation RAS Slowly Cleaves GTP to GDP ...
Chapter 25
... phosphorylated form, NRI-P • NRI is phosphorylated by NRII, a protein kinase • If NRII is complexed with PIIA it acts as a phosphatase, not a kinase ...
... phosphorylated form, NRI-P • NRI is phosphorylated by NRII, a protein kinase • If NRII is complexed with PIIA it acts as a phosphatase, not a kinase ...
Enzymes - CEA Workshop Teacher Notes.pptx
... • When a molecule cannot be superimposed on its mirror image the molecule is described as chiral. • This situaJon occurs when a carbon atom is aUached to four different groups: ...
... • When a molecule cannot be superimposed on its mirror image the molecule is described as chiral. • This situaJon occurs when a carbon atom is aUached to four different groups: ...
Enzymes of the mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid
... These enzymes had been isolated and classical enzymological and biochemical characterization had been performed prior to the evolution of experimental tools that have expedited the understanding the molecular basis of enzyme function. These enzymes are significant in animals since several have been ...
... These enzymes had been isolated and classical enzymological and biochemical characterization had been performed prior to the evolution of experimental tools that have expedited the understanding the molecular basis of enzyme function. These enzymes are significant in animals since several have been ...
5-Aminoimidazole-4-Carboxamide Riboside Mimics the
... gene expression. The Saccharomyces cerivisiae homolog of AMPK is the SNF1 complex, which regulates gene expression in response to the availability of glucose (26). AMPK is activated by treatments that deplete ATP, such as heat shock or arsenite in hepatocytes (29), exercise in skeletal muscle (30), ...
... gene expression. The Saccharomyces cerivisiae homolog of AMPK is the SNF1 complex, which regulates gene expression in response to the availability of glucose (26). AMPK is activated by treatments that deplete ATP, such as heat shock or arsenite in hepatocytes (29), exercise in skeletal muscle (30), ...
Severe Phenotype of Phosphorylase Kinase-Deficient Liver
... severe symptoms, and emerging data suggest a genotypephenotype correlation. The functional impact of PHKB mutations, both on residual enzyme activity and clinical condition, appears to be the mildest (7–9). PHKA2 mutations, which are most common, are usually associated with a benign disease although ...
... severe symptoms, and emerging data suggest a genotypephenotype correlation. The functional impact of PHKB mutations, both on residual enzyme activity and clinical condition, appears to be the mildest (7–9). PHKA2 mutations, which are most common, are usually associated with a benign disease although ...
Glycolysis - Rose
... cells using anaerobic glycolysis grow faster than cells using the more energy efficient, but much slower, oxidation of pyruvate. The fact that some microorganisms perform primarily anaerobic glycolysis under some conditions is also of benefit to humans: the production of ethanol and carbon dioxide f ...
... cells using anaerobic glycolysis grow faster than cells using the more energy efficient, but much slower, oxidation of pyruvate. The fact that some microorganisms perform primarily anaerobic glycolysis under some conditions is also of benefit to humans: the production of ethanol and carbon dioxide f ...
Document
... protein or other organic molecule. • kinases (phosphorylation) and phosphatases (dephosphorylation) are involved in this process. Many enzymes and receptors are switched "on" or "off" by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. • Reversible phosphorylation results in a conformational change in the str ...
... protein or other organic molecule. • kinases (phosphorylation) and phosphatases (dephosphorylation) are involved in this process. Many enzymes and receptors are switched "on" or "off" by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. • Reversible phosphorylation results in a conformational change in the str ...
Bioenergetics and Metabolism
... 1. Two substrate level phosphorylation reactions catalyzed by the enzymes phosphoglycerate kinase and pyruvate kinase generate a total of 4 ATP/glucose (net yield of 2ATP) in stage 2 of glycolysis. 2. An oxidation reaction catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-P dehydrogenase generates 2 NADH molecules that ...
... 1. Two substrate level phosphorylation reactions catalyzed by the enzymes phosphoglycerate kinase and pyruvate kinase generate a total of 4 ATP/glucose (net yield of 2ATP) in stage 2 of glycolysis. 2. An oxidation reaction catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-P dehydrogenase generates 2 NADH molecules that ...
Note Set 11 1 GLYCOLYSIS (also known as: EMBDEN
... *contraction in muscle stimulated by Ca release which also stimulates glycogenolysis D. non hormonal control 1. phosphorylase b also can be activated by AMP (not cyclic AMP) •usually doesn't occur in cell because ATP competes for binding with AMP -ATP usually much more abundant than AMP •under energ ...
... *contraction in muscle stimulated by Ca release which also stimulates glycogenolysis D. non hormonal control 1. phosphorylase b also can be activated by AMP (not cyclic AMP) •usually doesn't occur in cell because ATP competes for binding with AMP -ATP usually much more abundant than AMP •under energ ...
Enhancing the Six Phase II Detoxification
... The detoxification system of the body consists of three phases that process toxins for excretion from the body. The Phase I detoxification pathway is responsible for breaking fat-soluble toxins down and then sending the metabolites to the Phase II detoxification pathways, which builds new substances fr ...
... The detoxification system of the body consists of three phases that process toxins for excretion from the body. The Phase I detoxification pathway is responsible for breaking fat-soluble toxins down and then sending the metabolites to the Phase II detoxification pathways, which builds new substances fr ...
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA FOR DUPLICATED SACCHAROMYCES
... than additive, and the role of MCK1 is the most prominent among all four paralogs in yeast [12]. Sequence comparison indicates that all residues important for kinase activity are conserved in MCK1, RIM11 and MRK1, but not in YGK3 [12]. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is a ubiquitous serine/threonine/tyro ...
... than additive, and the role of MCK1 is the most prominent among all four paralogs in yeast [12]. Sequence comparison indicates that all residues important for kinase activity are conserved in MCK1, RIM11 and MRK1, but not in YGK3 [12]. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is a ubiquitous serine/threonine/tyro ...
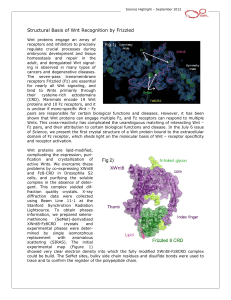
Structural Basis of Wnt Recognition by Frizzled
... XWnt8 has an unusual two-domain structure (Figure 2), and each domain extends a betastrand or ‘finger’, which ‘grasps’ the Fz8-CRD on opposite faces. Site 1 interaction is primarily mediated by a palmitoleic acid covalently attached to a conserved Serine at the tip of ‘thumb’, which binds within a ...
... XWnt8 has an unusual two-domain structure (Figure 2), and each domain extends a betastrand or ‘finger’, which ‘grasps’ the Fz8-CRD on opposite faces. Site 1 interaction is primarily mediated by a palmitoleic acid covalently attached to a conserved Serine at the tip of ‘thumb’, which binds within a ...
9 The AMP-activated protein kinase: more than an energy sensor
... At any time, intracellular ATP concentrations reflect the balance between energy supply-and-demand. In most cells, ATP supply relies on mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, whereas ATP demand depends on the energy required to perform various cell functions. Any decrease in supply (e.g. hypoxia) ...
... At any time, intracellular ATP concentrations reflect the balance between energy supply-and-demand. In most cells, ATP supply relies on mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, whereas ATP demand depends on the energy required to perform various cell functions. Any decrease in supply (e.g. hypoxia) ...
Autophagy regulation by nutrient signaling
... mTOR is a highly conserved serine/threonine kinase that is capable of integrating signals from many stimuli including amino acids, energy levels, oxygen, growth factors, and stress to coordinate cell growth and maintain metabolic homeostasis [59]. mTOR forms two functionally distinct complexes in ma ...
... mTOR is a highly conserved serine/threonine kinase that is capable of integrating signals from many stimuli including amino acids, energy levels, oxygen, growth factors, and stress to coordinate cell growth and maintain metabolic homeostasis [59]. mTOR forms two functionally distinct complexes in ma ...
Enzymes
... catalytic reaction, the product is then passed on to another enzyme. Sometimes more than one enzyme can catalyze the same reaction in parallel; this can allow more complex regulation: with, for example, a low constant activity provided by one enzyme but an inducible high activity from a second enzym ...
... catalytic reaction, the product is then passed on to another enzyme. Sometimes more than one enzyme can catalyze the same reaction in parallel; this can allow more complex regulation: with, for example, a low constant activity provided by one enzyme but an inducible high activity from a second enzym ...
Lecture 3 - Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... molecules to two molecules of pyruvic acid (C3H4O3). Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or ...
... molecules to two molecules of pyruvic acid (C3H4O3). Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or ...
Lecture 3 - Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis 1 2 3 4
... molecules to two molecules of pyruvic acid (C3H4O3). Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or ...
... molecules to two molecules of pyruvic acid (C3H4O3). Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or ...
Effects of signaling on subcellular localization of MITF
... Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) is the master regulator of melanocytes and plays a crucial role in melanoma. MITF is known from the literature to be regulated by signaling, for example through the MAPK pathway which mediates signals with protein phosphorylations. The MAPK pathw ...
... Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) is the master regulator of melanocytes and plays a crucial role in melanoma. MITF is known from the literature to be regulated by signaling, for example through the MAPK pathway which mediates signals with protein phosphorylations. The MAPK pathw ...
"Central Pathways of Carbohydrate Metabolism". In: Microbial
... High basal levels of KDPG aldolase activity are present regardless of the carbon source. This enzyme plays a major role in the metabolism of pectin and aldohexuronate by Erwinia and other related organisms, as discussed in Chapter 10. In E. coli the edd and eda genes are closely linked to zwf, which ...
... High basal levels of KDPG aldolase activity are present regardless of the carbon source. This enzyme plays a major role in the metabolism of pectin and aldohexuronate by Erwinia and other related organisms, as discussed in Chapter 10. In E. coli the edd and eda genes are closely linked to zwf, which ...
A Patch of Surface-Exposed Residues Mediates
... which encodes another protein kinase, and Pti 4/5/6, a family of transcription factor–like genes (Zhou et al., 1995, 1997). Both PtiI and Pti4 are substrates of Pto in vitro (Gu et al., 2000), although it is unknown whether these proteins interact with Pto in vivo. Protein kinases are frequent point ...
... which encodes another protein kinase, and Pti 4/5/6, a family of transcription factor–like genes (Zhou et al., 1995, 1997). Both PtiI and Pti4 are substrates of Pto in vitro (Gu et al., 2000), although it is unknown whether these proteins interact with Pto in vivo. Protein kinases are frequent point ...
Protein Kinase A Regulatory Subunit Interacts with P
... interact in this system (data not shown). This indicates that interactions of TcPKAr and these P-type ATPases are specific. One of the candidates turned out to be a Na+-ATPase mediating adaptation for high Na+, which we had reported previously.7 These are the first PKAr binding proteins identified i ...
... interact in this system (data not shown). This indicates that interactions of TcPKAr and these P-type ATPases are specific. One of the candidates turned out to be a Na+-ATPase mediating adaptation for high Na+, which we had reported previously.7 These are the first PKAr binding proteins identified i ...
Pentose P Path
... NADPH, a product of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway, functions as a reductant in anabolic (synthetic) pathways, e.g., fatty acid synthesis. NAD+ serves as electron acceptor in catabolic pathways, in which metabolites are oxidized. ...
... NADPH, a product of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway, functions as a reductant in anabolic (synthetic) pathways, e.g., fatty acid synthesis. NAD+ serves as electron acceptor in catabolic pathways, in which metabolites are oxidized. ...
Presentation
... What are the Rules? • Cancer is associated with deregulation of the same signaling pathways as determine intrinsic cellular radiosensitivity • Activation of cell survival/cell cycle progression pathways generally result in increased radioresistance • Activation of pro-apoptotic/cell cycle arrest pa ...
... What are the Rules? • Cancer is associated with deregulation of the same signaling pathways as determine intrinsic cellular radiosensitivity • Activation of cell survival/cell cycle progression pathways generally result in increased radioresistance • Activation of pro-apoptotic/cell cycle arrest pa ...