Key Idea #9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... What do you want to be when you grow up? There are many important jobs that grown ups do to keep our world running smoothly. Whether doctors, teachers, builders, engineers, farmers, etc, everyone learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells spec ...
... What do you want to be when you grow up? There are many important jobs that grown ups do to keep our world running smoothly. Whether doctors, teachers, builders, engineers, farmers, etc, everyone learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells spec ...
INTRODUCTORY QUESTIONS
... 1. What are the common structures that make up all living things? -cells 2. What do you think are the basic materials involved in the metabolism of all cells? -Food, water, oxygen and carbon dioxide 3. What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to repl ...
... 1. What are the common structures that make up all living things? -cells 2. What do you think are the basic materials involved in the metabolism of all cells? -Food, water, oxygen and carbon dioxide 3. What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to repl ...
Life Processes and Living things
... • 1) The sperm cell - designed to fertilise eggs A sperm cell is very small and has a little tail which provides movement so it can swim and find an egg to fertilise Its head contains enzymes (in the vacuole) which allow it to digest its way through an egg membrane so the two nuclei can join It cont ...
... • 1) The sperm cell - designed to fertilise eggs A sperm cell is very small and has a little tail which provides movement so it can swim and find an egg to fertilise Its head contains enzymes (in the vacuole) which allow it to digest its way through an egg membrane so the two nuclei can join It cont ...
Life Processes and Living things
... • 1) The sperm cell - designed to fertilise eggs A sperm cell is very small and has a little tail which provides movement so it can swim and find an egg to fertilise Its head contains enzymes (in the vacuole) which allow it to digest its way through an egg membrane so the two nuclei can join It cont ...
... • 1) The sperm cell - designed to fertilise eggs A sperm cell is very small and has a little tail which provides movement so it can swim and find an egg to fertilise Its head contains enzymes (in the vacuole) which allow it to digest its way through an egg membrane so the two nuclei can join It cont ...
unit 1: the organisation of the human body
... When different types of tissue join together and form organs, their functions complement each other and produce more complex functions. Some examples of organs in our body are the heart, stomach, lung, kidney, liver, etc. Systems.They are formed by organs, and they are responsible for carrying out ...
... When different types of tissue join together and form organs, their functions complement each other and produce more complex functions. Some examples of organs in our body are the heart, stomach, lung, kidney, liver, etc. Systems.They are formed by organs, and they are responsible for carrying out ...
Unit 2 Exam Cell Cell organelles Plant and Animal Tissue
... When cells signal one another, some signals are long lived, reach distant organs by way of the circulatory system. These signals are called…. ...
... When cells signal one another, some signals are long lived, reach distant organs by way of the circulatory system. These signals are called…. ...
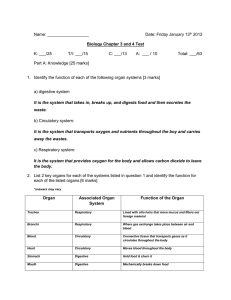
Name: Date: Friday January 13th 2012 Biology Chapter 3 and 4 Test
... 1. Describe the path an apple takes as it goes through your digestive system [5 marks] Food enters the body through the mouth and exits through the anus. In between, it undergoes digestion (from the mouth to the stomach), absorption (from the stomach to the small intestines), and elimination (from t ...
... 1. Describe the path an apple takes as it goes through your digestive system [5 marks] Food enters the body through the mouth and exits through the anus. In between, it undergoes digestion (from the mouth to the stomach), absorption (from the stomach to the small intestines), and elimination (from t ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
... In your body, a single skin cell or blood cell does not work alone. Cells work together in groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together carrying out a certain job. For example, skin cells work together as skin tissue that covers and protects your body. Other ...
... In your body, a single skin cell or blood cell does not work alone. Cells work together in groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together carrying out a certain job. For example, skin cells work together as skin tissue that covers and protects your body. Other ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
... In your body, a single skin cell or blood cell does not work alone. Cells work together in groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together carrying out a certain job. For example, skin cells work together as skin tissue that covers and protects your body. Other ...
... In your body, a single skin cell or blood cell does not work alone. Cells work together in groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together carrying out a certain job. For example, skin cells work together as skin tissue that covers and protects your body. Other ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
... In your body, a single skin cell or blood cell does not work alone. Cells work together in groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together carrying out a certain job. For example, skin cells work together as skin tissue that covers and protects your body. Other ...
... In your body, a single skin cell or blood cell does not work alone. Cells work together in groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together carrying out a certain job. For example, skin cells work together as skin tissue that covers and protects your body. Other ...
What`s So Cool About Cells?
... nucleus and has pores which allow RNA to pass through the cytoplasm Regulates protein messages to the rest of the cell ...
... nucleus and has pores which allow RNA to pass through the cytoplasm Regulates protein messages to the rest of the cell ...
Vertebrate Form and Function Homeostasis: The Foundation of
... function of subcellular organelles, proteins etc. ...
... function of subcellular organelles, proteins etc. ...
Cells and Basketball
... When you shoot a basketball many parts of your body work together to help you make the shot! These different parts are made up of different tissues and cells. Each type of cell is specialized to perform its job in shooting a basketball. Cells can be specialized in their shape and the organelles that ...
... When you shoot a basketball many parts of your body work together to help you make the shot! These different parts are made up of different tissues and cells. Each type of cell is specialized to perform its job in shooting a basketball. Cells can be specialized in their shape and the organelles that ...
Check In: WHAT ARE CELLS?
... Why do you think larger organisms need more cells instead of just bigger cells? Record What You See Record which pond organisms were made of a single cell. Record which pond organisms were made of many cells. One cell (single-celled organism) ...
... Why do you think larger organisms need more cells instead of just bigger cells? Record What You See Record which pond organisms were made of a single cell. Record which pond organisms were made of many cells. One cell (single-celled organism) ...
Cell
... different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can grow into any type of cell found in the body. They are found in organisms at all stages of their lives, not just adults e.g. skin, blood & bone marrow stem cells ...
... different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can grow into any type of cell found in the body. They are found in organisms at all stages of their lives, not just adults e.g. skin, blood & bone marrow stem cells ...
Cells_and_Chemical_Changes_Background_Info_
... Cells and Chemical Changes Background Informataion Cells differentiate in both plants and animals. Although the groups of cells that form muscle tissue are different from the groups that form bone or blood, and cells that form roots of plants are different from those that form leaves. The protoplasm ...
... Cells and Chemical Changes Background Informataion Cells differentiate in both plants and animals. Although the groups of cells that form muscle tissue are different from the groups that form bone or blood, and cells that form roots of plants are different from those that form leaves. The protoplasm ...
File
... Scientists insert genes (DNA) into organisms. Transformation. DNA Replication: DNA makes an exact copy of itself before cell division. chromatin chromatids (S phase of cell cycle) o DNA unwinds and unzips: helicase o Free nucleotides pair up according to the base pair rule: A-T G-C o DNA polyermas ...
... Scientists insert genes (DNA) into organisms. Transformation. DNA Replication: DNA makes an exact copy of itself before cell division. chromatin chromatids (S phase of cell cycle) o DNA unwinds and unzips: helicase o Free nucleotides pair up according to the base pair rule: A-T G-C o DNA polyermas ...
class_objective_2 student
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
Name
... 20. Some cells, such as human nerve and muscle cells, contain many more mitochondria than do other cells, such as skin cells. Why do some cells have more mitochondria than others? A. The cells use more energy. B. The cells store more nutrients. C. The cells degrade more proteins. D. The cells divid ...
... 20. Some cells, such as human nerve and muscle cells, contain many more mitochondria than do other cells, such as skin cells. Why do some cells have more mitochondria than others? A. The cells use more energy. B. The cells store more nutrients. C. The cells degrade more proteins. D. The cells divid ...
Cells to Body Systems
... Has two parts: central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. It receives and interprets signals from your body. It controls ...
... Has two parts: central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. It receives and interprets signals from your body. It controls ...
UNIT 2 CELLS AND SYSTEMS
... hollow disc shaped to increase surface area to pick up oxygen Advantage of being unicellular – reproduce quickly advantages of being multicellular – can grow large – don’t have to live in watery, food-rich environment – can obtain energy from wide variety of foods – cells specialize and can do jobs ...
... hollow disc shaped to increase surface area to pick up oxygen Advantage of being unicellular – reproduce quickly advantages of being multicellular – can grow large – don’t have to live in watery, food-rich environment – can obtain energy from wide variety of foods – cells specialize and can do jobs ...
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
... Process of renewal, restoration, and growth that makes cells able to repair themselves after damage. ...
... Process of renewal, restoration, and growth that makes cells able to repair themselves after damage. ...
Laboratory 4: Cells Structure and Function
... through it while slowing or stopping others. The cytoplasm is protected from the environment, yet still can exchange materials with it. Within the cytoplasm, cells differ in the type and number of organelles. Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) have the simplest structure with each independent cell lacking ...
... through it while slowing or stopping others. The cytoplasm is protected from the environment, yet still can exchange materials with it. Within the cytoplasm, cells differ in the type and number of organelles. Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) have the simplest structure with each independent cell lacking ...
Cells - College of Science | Oregon State University
... __________________________ cells (choose from the list above). When you view the model from the side, the muscle cells look long and tubular in shape. When you view the model from above, what shape does each muscle cell seem to have? ____________________ This difference in appearance from different ...
... __________________________ cells (choose from the list above). When you view the model from the side, the muscle cells look long and tubular in shape. When you view the model from above, what shape does each muscle cell seem to have? ____________________ This difference in appearance from different ...
Embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ES cells) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage preimplantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the embryoblast or inner cell mass (ICM) results in destruction of the blastocyst, which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage should be considered to have the same moral or legal status as more developed human beings.Human ES cells measure approximately 14 μm while mouse ES cells are closer to 8 μm.