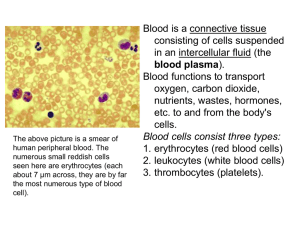
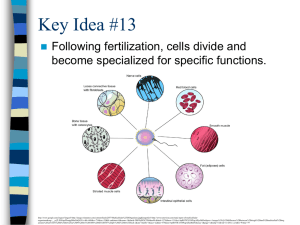
Cells - need help with revision notes?
... mother cell grows to a critical size at a time coinciding with DNA synthesis. There is a weakening of a small area of the cell wall and this, together with the turgor pressure of osmosis allows swelling of the plasma membrane and cytoplasm to form a bud. This process leaves a ring in the plasma memb ...
... mother cell grows to a critical size at a time coinciding with DNA synthesis. There is a weakening of a small area of the cell wall and this, together with the turgor pressure of osmosis allows swelling of the plasma membrane and cytoplasm to form a bud. This process leaves a ring in the plasma memb ...
Grade 8 Science Cells and Systems
... Include: primary defense system - skin, tears, ear wax, saliva, gastric juices, cilia hairs; secondary defense system - white blood cells, antibodies ...
... Include: primary defense system - skin, tears, ear wax, saliva, gastric juices, cilia hairs; secondary defense system - white blood cells, antibodies ...
Microbiology/Cells/Nutrition Vocabulary 1 Abiotic
... 24. Communicable- when an infectious disease can be passed from person to person by direct contact or with an affected person indirectly (sneezing, coughing, etc.) 25. Cytoplasm- the fluid that fills most of the space in a cell 26. Diabetes- due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin or ...
... 24. Communicable- when an infectious disease can be passed from person to person by direct contact or with an affected person indirectly (sneezing, coughing, etc.) 25. Cytoplasm- the fluid that fills most of the space in a cell 26. Diabetes- due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin or ...
PowerPoint - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web Pages
... Macrophages are one of many types of white blood cells (leukocytes) present in body tissues. Macrophages are important in immune response and cell stability because they mobilize in cell tissue to attack large foreign particles such as bacteria, yeast, and dead cells. Macrophages are derived from pr ...
... Macrophages are one of many types of white blood cells (leukocytes) present in body tissues. Macrophages are important in immune response and cell stability because they mobilize in cell tissue to attack large foreign particles such as bacteria, yeast, and dead cells. Macrophages are derived from pr ...
Intermediate Filaments
... Vimentins, being the common structural support of many cells. Type I and type II: acidic keratin and basic keratin, respectively.Produced by different types of epithelial cells ( bladder, skin,etc). Neurofilaments of neural cells . Lamin inside the inner nuclear envelope, lamins are vital to t ...
... Vimentins, being the common structural support of many cells. Type I and type II: acidic keratin and basic keratin, respectively.Produced by different types of epithelial cells ( bladder, skin,etc). Neurofilaments of neural cells . Lamin inside the inner nuclear envelope, lamins are vital to t ...
Objective 2 - Organization of Living Systems
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
File - Mr. Downing Science 10
... also includes contains photosynthetic organs that The root system: ...
... also includes contains photosynthetic organs that The root system: ...
ASK Biology Review
... • Predator/prey- predator is one who hunts/eats another organism, prey is the one who gets eaten. Ex- Shark is a predator, seal is the prey • Parasite/host- parasite is one that lives or feeds on another organism causing it harm, Host is who the parasite lives on and is hurt. Ex- A flea is a parasit ...
... • Predator/prey- predator is one who hunts/eats another organism, prey is the one who gets eaten. Ex- Shark is a predator, seal is the prey • Parasite/host- parasite is one that lives or feeds on another organism causing it harm, Host is who the parasite lives on and is hurt. Ex- A flea is a parasit ...
The Cell
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
Levels of Organization-Plants
... different systems C. A structure made up of a group of 2. Xylem is a tissue True or False? tissues that work together to perform a specific job 3.What is the function of a stem? D. A body structure, such as muscles and lungs ...
... different systems C. A structure made up of a group of 2. Xylem is a tissue True or False? tissues that work together to perform a specific job 3.What is the function of a stem? D. A body structure, such as muscles and lungs ...
Study Guide with Answers - Mrs. Rasmussen Science Class
... Non-living means it never had all 6 of the characteristics. Living means it has all 6. Dead means it used to have all 6 but no longer has all 6 and will never again have all 6. ...
... Non-living means it never had all 6 of the characteristics. Living means it has all 6. Dead means it used to have all 6 but no longer has all 6 and will never again have all 6. ...
Cell - centralmountainbiology
... • All living things detect changes in their environment. • Ex. You respond to stepping on a sharp rock. • A rock does not respond if you step on it. • Homeostasis: process of maintaining a stable internal environment. • Ex. Sweating or shivering when temperature changes. ...
... • All living things detect changes in their environment. • Ex. You respond to stepping on a sharp rock. • A rock does not respond if you step on it. • Homeostasis: process of maintaining a stable internal environment. • Ex. Sweating or shivering when temperature changes. ...
Cells are the
... Takes proteins from ER and ______________ to make them work; then sends them on their way (_____________ of the cell). ...
... Takes proteins from ER and ______________ to make them work; then sends them on their way (_____________ of the cell). ...
What is an animal?
... (a) Early organogenesis. The archenteron forms when lateral folds (b) pinch the embryo away from the yolk. The embryo remains open to the yolk, attached by the yolk stalk, about midway along its length, as shown in this cross section. The notochord, neural tube, and somites subsequently form much as ...
... (a) Early organogenesis. The archenteron forms when lateral folds (b) pinch the embryo away from the yolk. The embryo remains open to the yolk, attached by the yolk stalk, about midway along its length, as shown in this cross section. The notochord, neural tube, and somites subsequently form much as ...
Cells - Body Systems
... • cells work together to help your body function well • cells come in different shape and sizes ...
... • cells work together to help your body function well • cells come in different shape and sizes ...
Oct 2310:58 AM Comparing Cells Lab Analysis Questions
... 1. Describe 3 differences between the plant cells and the animal cells you looked at. 2. Thinking about how the structure and arrangement of cells contributes to the functioning of the organism, propose reasons for the differences you mentioned. 3. Why do you think we stained the cheek cells but ...
... 1. Describe 3 differences between the plant cells and the animal cells you looked at. 2. Thinking about how the structure and arrangement of cells contributes to the functioning of the organism, propose reasons for the differences you mentioned. 3. Why do you think we stained the cheek cells but ...
Cellular Structure and Function Web Research 100 pts
... cells divide during the process of mitosis. Next, students learn how cell specialization takes place in vertebrate embryos. They explore a gallery of different kinds of specialized cells and compare each cell's structure and function. After making drawings of these cells, they place their drawings i ...
... cells divide during the process of mitosis. Next, students learn how cell specialization takes place in vertebrate embryos. They explore a gallery of different kinds of specialized cells and compare each cell's structure and function. After making drawings of these cells, they place their drawings i ...
The respiratory system - Spark (e
... is formed by two different types of specialized cells. These cells are easily crossed by gases and that is why the exchange between blood and air is quite simple. ...
... is formed by two different types of specialized cells. These cells are easily crossed by gases and that is why the exchange between blood and air is quite simple. ...
Key Idea #9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... engineers, farmers, etc, everyone learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells specialize in important jobs. ...
... engineers, farmers, etc, everyone learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells specialize in important jobs. ...
Session 2 Presentation
... Different cells perform different functions in the body. Cells are specialized to best perform a particular job for a particular system. Blood cells are moved by the circulatory system to carry oxygen to cells. Muscle cells contract to move the body. Liver cells play a role in digestion and filterin ...
... Different cells perform different functions in the body. Cells are specialized to best perform a particular job for a particular system. Blood cells are moved by the circulatory system to carry oxygen to cells. Muscle cells contract to move the body. Liver cells play a role in digestion and filterin ...
Getting to Know: Cell Theory
... Unicellular organisms consist of just one cell. These cells go through life cycles just like more complex organisms. They grow and reproduce and then eventually die. Most one-celled organisms can’t be seen without a microscope, but they are very common. In fact, there are more living one-celled orga ...
... Unicellular organisms consist of just one cell. These cells go through life cycles just like more complex organisms. They grow and reproduce and then eventually die. Most one-celled organisms can’t be seen without a microscope, but they are very common. In fact, there are more living one-celled orga ...
Chapter 4 - Valhalla High School
... structural unit of life, they function in groups as tissues to carry out specialized activities 2. Properties of tissues are influenced by factors such as extracellular material and connections between cells 3. Tissues may be hard, semisolid, or liquid 4. Vary with kind of cells present, cellular ar ...
... structural unit of life, they function in groups as tissues to carry out specialized activities 2. Properties of tissues are influenced by factors such as extracellular material and connections between cells 3. Tissues may be hard, semisolid, or liquid 4. Vary with kind of cells present, cellular ar ...
File - Mr. Downing Science 10
... open system – exchanges both matter and energy with the environment (e.g. human body) closed system – exchanges energy but not matter (e.g. a sealed glass jar) isolated system – exchanges neither energy nor matter (does not exist in reality) ...
... open system – exchanges both matter and energy with the environment (e.g. human body) closed system – exchanges energy but not matter (e.g. a sealed glass jar) isolated system – exchanges neither energy nor matter (does not exist in reality) ...
Embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ES cells) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage preimplantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the embryoblast or inner cell mass (ICM) results in destruction of the blastocyst, which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage should be considered to have the same moral or legal status as more developed human beings.Human ES cells measure approximately 14 μm while mouse ES cells are closer to 8 μm.