1327004619.
... this type 0of movement is called locomotion. Plants and other organisms that are fixed in one place do not loco mote but can move parts of their bodies. Movements of living things involve expenditure of energy derived from respiration. ...
... this type 0of movement is called locomotion. Plants and other organisms that are fixed in one place do not loco mote but can move parts of their bodies. Movements of living things involve expenditure of energy derived from respiration. ...
Review 1 - misshoughton.net
... Cell Parts and Function _______________________________ — the outer boundary of the cell that controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell. Found in both plant and animal cells. _______________________________ — the fluid within the cell that contains organelles and aids in moving thin ...
... Cell Parts and Function _______________________________ — the outer boundary of the cell that controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell. Found in both plant and animal cells. _______________________________ — the fluid within the cell that contains organelles and aids in moving thin ...
cells
... skin. -Information goes to the brain. -brain sends signals to muscles, skin and blood vessels. - they all work together to help your body perform properly. this system consists of the brain, spinal cord and the nerves. Diet, exercise, drugs, injury, and disease can affect body systems and disrup ...
... skin. -Information goes to the brain. -brain sends signals to muscles, skin and blood vessels. - they all work together to help your body perform properly. this system consists of the brain, spinal cord and the nerves. Diet, exercise, drugs, injury, and disease can affect body systems and disrup ...
Product Datasheet for ab15830
... At Abcam, we have one centralized database to hold all of our product information, so that everything we know about this SOX2 antibody - Embryonic Stem Cell Marker is on this datasheet. But please do contact us if you would like any reassurance! See below for SOX2 antibody - Embryonic Stem Cell Mark ...
... At Abcam, we have one centralized database to hold all of our product information, so that everything we know about this SOX2 antibody - Embryonic Stem Cell Marker is on this datasheet. But please do contact us if you would like any reassurance! See below for SOX2 antibody - Embryonic Stem Cell Mark ...
are all made up of specialized nerve cells called neurons. Neurons
... Red blood cells deliver oxygen to the tissues and return carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. They are released from the bone marrow with a life span of 120 days. Unlike most cells of the body, mature red cells do not contain a nucleus. There are three reasons for the. 1. The main function ...
... Red blood cells deliver oxygen to the tissues and return carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. They are released from the bone marrow with a life span of 120 days. Unlike most cells of the body, mature red cells do not contain a nucleus. There are three reasons for the. 1. The main function ...
connective tissue
... and relays commands for response • Consists of excitable neurons and supporting neuroglial cells ...
... and relays commands for response • Consists of excitable neurons and supporting neuroglial cells ...
Body Organization
... • Different body tissues and organs are made up of different kinds of cells. • The cells in similar tissues and organs in other animals are similar to those in human beings but differ somewhat from cells found in plants. • Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multi-cellular organisms. ...
... • Different body tissues and organs are made up of different kinds of cells. • The cells in similar tissues and organs in other animals are similar to those in human beings but differ somewhat from cells found in plants. • Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multi-cellular organisms. ...
Student Packet 16 Plant Animal Cells L.14.3
... The purpose of this document is to provide students with enhancement tutorial sessions that will enrich the depth of content knowledge of the Biology 1 course. Each tutorial session is aligned to Biology Annually Assessed Benchmarks of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards (NGSSS) as describe ...
... The purpose of this document is to provide students with enhancement tutorial sessions that will enrich the depth of content knowledge of the Biology 1 course. Each tutorial session is aligned to Biology Annually Assessed Benchmarks of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards (NGSSS) as describe ...
Slide 1
... •Growth - increase in cellular mass, and/or increase in number of cells •Reproduction - formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as living organisms. ...
... •Growth - increase in cellular mass, and/or increase in number of cells •Reproduction - formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as living organisms. ...
Biology Review PPT
... •Growth - increase in cellular mass, and/or increase in number of cells •Reproduction - formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as living organisms. ...
... •Growth - increase in cellular mass, and/or increase in number of cells •Reproduction - formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as living organisms. ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell - GMCbiology
... states cells are produced only from preexisting cells. What does this mean? What does it make you think about? ...
... states cells are produced only from preexisting cells. What does this mean? What does it make you think about? ...
Plants and Pollinators
... Type 3: Muscle Tissue • Cells contract when stimulated • Moves body and specific body ...
... Type 3: Muscle Tissue • Cells contract when stimulated • Moves body and specific body ...
LAB 16 - Stuyvesant High School
... openings called STOMATES. The size of the stoma (stoma is singular, stomates is plural) opening is regulated by the chloroplast containing GUARD CELLS which surround it. Gas exchange through the stomates is advantageous because the amount of exchange can be controlled by the opening and closing of t ...
... openings called STOMATES. The size of the stoma (stoma is singular, stomates is plural) opening is regulated by the chloroplast containing GUARD CELLS which surround it. Gas exchange through the stomates is advantageous because the amount of exchange can be controlled by the opening and closing of t ...
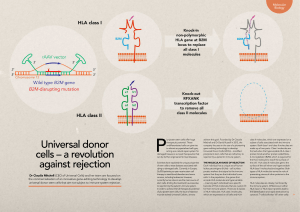
Universal donor cells – a revolution against rejection
... class II molecules, which are expressed on a subset of cells associated with the immune system. Both class I and class II molecules are made up of two parts. Class I molecules are formed when the hypervariable HLA class I protein binds another protein called Beta2-microglobulin (B2M), which is requi ...
... class II molecules, which are expressed on a subset of cells associated with the immune system. Both class I and class II molecules are made up of two parts. Class I molecules are formed when the hypervariable HLA class I protein binds another protein called Beta2-microglobulin (B2M), which is requi ...
File - Loris High School Medical Magnet Program
... 11. Vacuole: containers F. Cell reproduction 1. Mitosis: replaces dead/injured cells; divide into 2 identical cells; form of asexual reproduction; some cells do not reproduce after birth i.e. nerve cells in brain and spinal cord, muscle cells 2. Meiosis: reduction division; 23 chromosomes = ovum; 23 ...
... 11. Vacuole: containers F. Cell reproduction 1. Mitosis: replaces dead/injured cells; divide into 2 identical cells; form of asexual reproduction; some cells do not reproduce after birth i.e. nerve cells in brain and spinal cord, muscle cells 2. Meiosis: reduction division; 23 chromosomes = ovum; 23 ...
Study guide packet part 1
... D. Mitochondria- “powerhouse” of the cell. Provides energy by Cellular respiration. E. Cell wall- this is not in animals. Provides protection and support for the cell F. Chloroplast- this is only in plants and protists. This is where photosynthesis happens. It contains a pigment called chlorophyll w ...
... D. Mitochondria- “powerhouse” of the cell. Provides energy by Cellular respiration. E. Cell wall- this is not in animals. Provides protection and support for the cell F. Chloroplast- this is only in plants and protists. This is where photosynthesis happens. It contains a pigment called chlorophyll w ...
The Basic Unit of Life.
... Similarly, there are different kinds of cells in animals, including humans, that have different kinds of functions. For example, skin cells are flat and wide to protect other cells that are underneath them. Muscles are made of long, thread-like cells that let the body move. Nerve cells transport mes ...
... Similarly, there are different kinds of cells in animals, including humans, that have different kinds of functions. For example, skin cells are flat and wide to protect other cells that are underneath them. Muscles are made of long, thread-like cells that let the body move. Nerve cells transport mes ...
Unit 1 – Biology – Cells PowerPoint
... Information that results in plants and animals having similar characteristics to their parents is carried by ________________, which are passed on in the __________________________ from which the offspring ...
... Information that results in plants and animals having similar characteristics to their parents is carried by ________________, which are passed on in the __________________________ from which the offspring ...
doc
... All of the autosomal cells of a given organism share the same genetic material (the organism’s genome) Differentiation and morphogenesis result from differences in gene expression among cells, i.e., different portions of the common genome are expressed in different cells Differentiation occurs as ti ...
... All of the autosomal cells of a given organism share the same genetic material (the organism’s genome) Differentiation and morphogenesis result from differences in gene expression among cells, i.e., different portions of the common genome are expressed in different cells Differentiation occurs as ti ...
Cell Theory
... In organisms, structure and function are related. Structure is the arrangement of parts in an organism. It includes the shape of a part and the material of which the part is made. Function is the job the part does. For example, the structure of the lungs is a large, spongy sac. In the lungs, there a ...
... In organisms, structure and function are related. Structure is the arrangement of parts in an organism. It includes the shape of a part and the material of which the part is made. Function is the job the part does. For example, the structure of the lungs is a large, spongy sac. In the lungs, there a ...
Cells
... • Flagella – a whip-like ‘tail’ some cells have for movement • Golgi – membrane sacs that receive and repackage proteins • Mitochondria – organelle that produces energy for the cell by breaking down glucose (sugar) ...
... • Flagella – a whip-like ‘tail’ some cells have for movement • Golgi – membrane sacs that receive and repackage proteins • Mitochondria – organelle that produces energy for the cell by breaking down glucose (sugar) ...
10. Use a different colour for each stage of
... Use the terms in the vocabulary box to fill in the blanks. Each term may be used as often as necessary. 1.____________________________________________________ refers to the amount of a substance in a given space. 2.______________is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an ...
... Use the terms in the vocabulary box to fill in the blanks. Each term may be used as often as necessary. 1.____________________________________________________ refers to the amount of a substance in a given space. 2.______________is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an ...
Embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ES cells) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage preimplantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the embryoblast or inner cell mass (ICM) results in destruction of the blastocyst, which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage should be considered to have the same moral or legal status as more developed human beings.Human ES cells measure approximately 14 μm while mouse ES cells are closer to 8 μm.