Sponges and Cnidarians
... The body of the simplest sponges takes the shape of a cylinder with a large central cavity, the spongocoel. Water enters the spongocoel from numerous pores in the body wall. Water ows out through a large opening called the osculum (Figure 3). However, sponges exhibit a diversity of body forms, whic ...
... The body of the simplest sponges takes the shape of a cylinder with a large central cavity, the spongocoel. Water enters the spongocoel from numerous pores in the body wall. Water ows out through a large opening called the osculum (Figure 3). However, sponges exhibit a diversity of body forms, whic ...
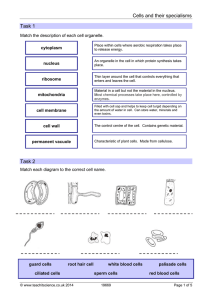
Cells and their specialisms Task 1 Task 2
... Cells and their specialisms Teaching notes and answers For the first three tasks students could be asked to cut and paste or simply draw a line to match up the correct statements. ...
... Cells and their specialisms Teaching notes and answers For the first three tasks students could be asked to cut and paste or simply draw a line to match up the correct statements. ...
Structure and - DANYAL`S NOTES AND RESOURCES
... Tissues are made up of the same type of cells which carry out a special function. Some types of tissues contain several types of cells, but the whole tissue performs one function. Connective tissue, for example, connects different parts of an organ or organs together.This kind of tissue is called co ...
... Tissues are made up of the same type of cells which carry out a special function. Some types of tissues contain several types of cells, but the whole tissue performs one function. Connective tissue, for example, connects different parts of an organ or organs together.This kind of tissue is called co ...
- Google Sites
... pseudostratified ciliated columnar: These cells appear layered but really are not. Why do they look layered? Nuclei in varying position within the cells ...
... pseudostratified ciliated columnar: These cells appear layered but really are not. Why do they look layered? Nuclei in varying position within the cells ...
3 - Environmental Intermediate
... As we have seen, organisms are genetically different thus producing inherited variation. However, the environment also causes variation. In both cases, these forms of variation may cause a survival advantage (the particular individual survives better and competes in a more efficient manner) and ulti ...
... As we have seen, organisms are genetically different thus producing inherited variation. However, the environment also causes variation. In both cases, these forms of variation may cause a survival advantage (the particular individual survives better and competes in a more efficient manner) and ulti ...
Implantation
... A teratogen is any infectious agent, drug, chemical, or irradiation that alters fetal morphology or fetal function if the fetus is exposed during a critical stage of development. 1. The resistant period (week 1 of development) the “all-ornone” phenomenon (i.e., the conceptus will either die as a ...
... A teratogen is any infectious agent, drug, chemical, or irradiation that alters fetal morphology or fetal function if the fetus is exposed during a critical stage of development. 1. The resistant period (week 1 of development) the “all-ornone” phenomenon (i.e., the conceptus will either die as a ...
Chapter 7. The Cell: Cytoskeleton
... Cytoskeleton Structure network of fibers extending throughout cytoplasm 3 main protein fibers ...
... Cytoskeleton Structure network of fibers extending throughout cytoplasm 3 main protein fibers ...
EB AP Cytoskeleton
... Cytoskeleton Structure network of fibers extending throughout cytoplasm 3 main protein fibers ...
... Cytoskeleton Structure network of fibers extending throughout cytoplasm 3 main protein fibers ...
Cells and Reproduction
... oxygen in the lungs and carry it to all the other cells in the body, from our brain to our leg muscle. Red blood cells are very, very tiny to let them squeeze through small blood vessels to get to every part of our body and deliver the oxygen. In our brain are millions of nerve cells. Although many ...
... oxygen in the lungs and carry it to all the other cells in the body, from our brain to our leg muscle. Red blood cells are very, very tiny to let them squeeze through small blood vessels to get to every part of our body and deliver the oxygen. In our brain are millions of nerve cells. Although many ...
3.1: The Hierarchy of Structure in Animals pg. 73 Hierarchy – an
... Tissue – a collection of similar cells that perform a particular, but limited, function. Organ – a structure composed of different tissues working together to perform a complex body function. Organ System – a system of one or more organs and structures that work together to perform a major vital bod ...
... Tissue – a collection of similar cells that perform a particular, but limited, function. Organ – a structure composed of different tissues working together to perform a complex body function. Organ System – a system of one or more organs and structures that work together to perform a major vital bod ...
Cells and Systems
... Multicellular: made up of two or more cells Multicellular organisms have specialized cells. This means that there are various kinds of cells and each kind carries out a specific function or functions needed to support life. Specialization means that the cells of a multicellular organism must work ...
... Multicellular: made up of two or more cells Multicellular organisms have specialized cells. This means that there are various kinds of cells and each kind carries out a specific function or functions needed to support life. Specialization means that the cells of a multicellular organism must work ...
Lab 2: Cells and Tissues Pre Lab 2 Test
... The nervous system is composed of the brain, the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system! ...
... The nervous system is composed of the brain, the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system! ...
Unit 8A
... They are anchored to B cells by the bottom of the Y shape in a transmembrane region. The tips of the Y are varied between B cells Binding of the antigen to the receptor allows B cells to recognize the antigen in its natural state and begin to mount a response with antibody production ...
... They are anchored to B cells by the bottom of the Y shape in a transmembrane region. The tips of the Y are varied between B cells Binding of the antigen to the receptor allows B cells to recognize the antigen in its natural state and begin to mount a response with antibody production ...
File - Intervention
... Mutations can cause abnormal patterns of growth and division. A mass of rapidly growing, abnormal cells is called a tumor. Some tumors are benign, or harmless, because their cells do not spread beyond the tumor. Some tumors are malignant, or cancerous, because they have cells that can spread ...
... Mutations can cause abnormal patterns of growth and division. A mass of rapidly growing, abnormal cells is called a tumor. Some tumors are benign, or harmless, because their cells do not spread beyond the tumor. Some tumors are malignant, or cancerous, because they have cells that can spread ...
m5zn_a2ee964dc9b908b
... • This leads to sloughing of the surface epithelial cells and then they undergo physiologic cell death (apoptotic cell death) to expose basal epithelial cells. • These basal cells have an extra cellular surface substances particularly glycopoteins that enhance adhesion between the shelf edges as wel ...
... • This leads to sloughing of the surface epithelial cells and then they undergo physiologic cell death (apoptotic cell death) to expose basal epithelial cells. • These basal cells have an extra cellular surface substances particularly glycopoteins that enhance adhesion between the shelf edges as wel ...
SelfAssessment 1 – Cells
... State that the plasmid is now called a recombinant plasmid and acts as a VECTOR since it carries the genetic material of one organism to another. State that the recombinant plasmid is inserted back inside the host bacterial cell where it is made into many copies. Describe the process of genetic engi ...
... State that the plasmid is now called a recombinant plasmid and acts as a VECTOR since it carries the genetic material of one organism to another. State that the recombinant plasmid is inserted back inside the host bacterial cell where it is made into many copies. Describe the process of genetic engi ...
Histology
... 4. stains for basement membrane a. PAS - stains carbohydrates in proteoglycans b. silver stain - stains type III collagen ( reticular fibers ) and is therefore called argyrophilic Hematoxolyn and Eosin do not show the basement membrane 5. hemidesmosomes – a site of adhesion between 2 epithelial cell ...
... 4. stains for basement membrane a. PAS - stains carbohydrates in proteoglycans b. silver stain - stains type III collagen ( reticular fibers ) and is therefore called argyrophilic Hematoxolyn and Eosin do not show the basement membrane 5. hemidesmosomes – a site of adhesion between 2 epithelial cell ...
Biology EOCT Practice Questions Part 2
... protection from predatory birds. Based on your knowledge of natural selection and the information above, which of the following conclusions can be drawn? A. Only the speckled crabs will survive and all of the offspring will be speckled. B. The allele for light brown color will be lost because of pre ...
... protection from predatory birds. Based on your knowledge of natural selection and the information above, which of the following conclusions can be drawn? A. Only the speckled crabs will survive and all of the offspring will be speckled. B. The allele for light brown color will be lost because of pre ...
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
... – Absence of cartilage from the wall of bronchioles is a potential hazard, since these airways can constrict to a point of closing if the tone of their muscles is increased. This is the problem of asthma which is an allergic condition to non-specific lung irritant. Wheezing noises and difficulty in ...
... – Absence of cartilage from the wall of bronchioles is a potential hazard, since these airways can constrict to a point of closing if the tone of their muscles is increased. This is the problem of asthma which is an allergic condition to non-specific lung irritant. Wheezing noises and difficulty in ...
Cells Human organs/Organisation
... Something used to carry seeds. Can be fleshy or dry. Controls what a cell does. Part of the carpel. It contains ovules, each of which contains an egg cell. Contains egg cells. Is found in the ovary. The male sex cell in plants. Tube that grows from a pollen grain down through the stigma and style an ...
... Something used to carry seeds. Can be fleshy or dry. Controls what a cell does. Part of the carpel. It contains ovules, each of which contains an egg cell. Contains egg cells. Is found in the ovary. The male sex cell in plants. Tube that grows from a pollen grain down through the stigma and style an ...
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
... ancestry of domestic dogs to wolves. However, they have recently found that the Sabre-tooth tiger is not the ancestor of the domestic cat. ...
... ancestry of domestic dogs to wolves. However, they have recently found that the Sabre-tooth tiger is not the ancestor of the domestic cat. ...
UNIT 1
... part of an organism. Cells keep the organism alive. That is why cells are called the basic units of life. Cells have different structures. Some structures make food. Some structures give the cell energy. Other structures move material from one place to another. Different organisms have different kin ...
... part of an organism. Cells keep the organism alive. That is why cells are called the basic units of life. Cells have different structures. Some structures make food. Some structures give the cell energy. Other structures move material from one place to another. Different organisms have different kin ...
CELL BIOLOGY: BIOLOGY HSA REVIEW
... development, the cells begin to differentiate and form specialized regions of the body. Each organ or type of tissue is formed from a group of cells that have a similar structure and function. The four main types of tissues are epithelial tissue, connective tissue (including cartilage and bone), mus ...
... development, the cells begin to differentiate and form specialized regions of the body. Each organ or type of tissue is formed from a group of cells that have a similar structure and function. The four main types of tissues are epithelial tissue, connective tissue (including cartilage and bone), mus ...
Embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ES cells) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage preimplantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the embryoblast or inner cell mass (ICM) results in destruction of the blastocyst, which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage should be considered to have the same moral or legal status as more developed human beings.Human ES cells measure approximately 14 μm while mouse ES cells are closer to 8 μm.