How many molecules?
... (a string of these reactions is a decay chain) • The rates of each decay are variable – some are extremely slow • If a system is closed (no elements escape) then the proportion of parent (original) and daughter (product of a radioactive decay reaction) can yield a date. • Radioactive isotopes are al ...
... (a string of these reactions is a decay chain) • The rates of each decay are variable – some are extremely slow • If a system is closed (no elements escape) then the proportion of parent (original) and daughter (product of a radioactive decay reaction) can yield a date. • Radioactive isotopes are al ...
Proposal Title
... geometries. Because the field of commercial MEMS is still in its infancy, reliability is an important issue which still requires advanced research. Reliability directly influences the acceptance, competitivity and reputation of a technology. Reliability is a fundamental argument of cost which influe ...
... geometries. Because the field of commercial MEMS is still in its infancy, reliability is an important issue which still requires advanced research. Reliability directly influences the acceptance, competitivity and reputation of a technology. Reliability is a fundamental argument of cost which influe ...
Section 3.2 Atoms and Compounds
... • A given compound always contains the same proportion by mass of the elements of which it is composed. A mixture can have variable composition but the composition of a compound is fixed Does this give us a clue about the nature of matter? ...
... • A given compound always contains the same proportion by mass of the elements of which it is composed. A mixture can have variable composition but the composition of a compound is fixed Does this give us a clue about the nature of matter? ...
Synthesis and Characterization of Amorphous and Hybrid Materials
... are considered as biphasic materials, where the organic and inorganic phase is mixed at the nm to sub-µm scales. Nevertheless, it is obvious that the properties of these materials are not just the sum of the individual contributions from both phases; the role of the inner interfaces could be predomi ...
... are considered as biphasic materials, where the organic and inorganic phase is mixed at the nm to sub-µm scales. Nevertheless, it is obvious that the properties of these materials are not just the sum of the individual contributions from both phases; the role of the inner interfaces could be predomi ...
1 MATTER: Anything which occupies space , has volume and can
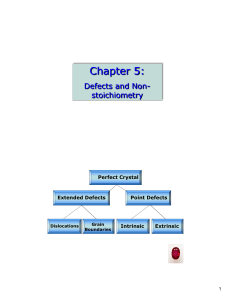
... Coordination number is the number of nearest neighbours of any particle. CN for simple cubic (SCC) =6, BCC =8, FCC (hcp or ccp) = 12. Q1. A compound formed by elements A and B has a cubic structure in which A atoms are at the corners of the cube and B atoms are at the face centres. Derive the formul ...
... Coordination number is the number of nearest neighbours of any particle. CN for simple cubic (SCC) =6, BCC =8, FCC (hcp or ccp) = 12. Q1. A compound formed by elements A and B has a cubic structure in which A atoms are at the corners of the cube and B atoms are at the face centres. Derive the formul ...
synthesis and potentiometric analysis of - G
... The IR spectra of the synthesized compounds were recorded by means of the spectrometer «Nicolet Avatar-360" (KBr tablets, measurement error is 0.2 cm-1). 1H NMR spectra were recorded by the spectrometer «Bruker DRX500» of operating frequency of 500 MHz in DMSO-d6 solution relatively to internal stan ...
... The IR spectra of the synthesized compounds were recorded by means of the spectrometer «Nicolet Avatar-360" (KBr tablets, measurement error is 0.2 cm-1). 1H NMR spectra were recorded by the spectrometer «Bruker DRX500» of operating frequency of 500 MHz in DMSO-d6 solution relatively to internal stan ...
Physical or Chemical Property?
... together, but not chemically combined. Each component in a mixture keeps its individual properties. Example: salt water contains water molecules (H2O) and ...
... together, but not chemically combined. Each component in a mixture keeps its individual properties. Example: salt water contains water molecules (H2O) and ...
abstract
... Here, Ψbulk and Ψs are the Helmholtz energy of the bulk and the surface energy associated with the formation of new cracks. Obviously, the total energy depends on the unknown topology of the crack surface Γc . According to Eq. (1), crack propagation is understood as a competition between surface ene ...
... Here, Ψbulk and Ψs are the Helmholtz energy of the bulk and the surface energy associated with the formation of new cracks. Obviously, the total energy depends on the unknown topology of the crack surface Γc . According to Eq. (1), crack propagation is understood as a competition between surface ene ...
Matter Anything that has mass and takes up space (volume).
... substance is created and the original matter can be recovered. Physical change does not change the composition of the matter. The original matter is still present. The substance may seem different, but the way the atoms are linked up are the same. ...
... substance is created and the original matter can be recovered. Physical change does not change the composition of the matter. The original matter is still present. The substance may seem different, but the way the atoms are linked up are the same. ...
Solid

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a gas does. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice) or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass).The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science is primarily concerned with the physical and chemical properties of solids. Solid-state chemistry is especially concerned with the synthesis of novel materials, as well as the science of identification and chemical composition.