Phase Rule
... Along this curve two phases, ice and water are in equilibrium. The inclination of OC line towards the pressure axis indicates that the melting point of ice is slightly lowered by increase of pressure. (According to Le Chatelier's principle the increase in pressure causes the water - ice equilibrium ...
... Along this curve two phases, ice and water are in equilibrium. The inclination of OC line towards the pressure axis indicates that the melting point of ice is slightly lowered by increase of pressure. (According to Le Chatelier's principle the increase in pressure causes the water - ice equilibrium ...
Analysis of thermal diffusivity in aluminum (particle)
... The material used in this research was solid atactic PMMA and aluminum powder of a mean diameter between 10 and 40 mm. The molecular weight distribution of the PMMA was measured by GPC using a Shimadzu L-6A liquid chromatogram system with a RID-6A refractive index detector and a Shimpack GPC 802-803 ...
... The material used in this research was solid atactic PMMA and aluminum powder of a mean diameter between 10 and 40 mm. The molecular weight distribution of the PMMA was measured by GPC using a Shimadzu L-6A liquid chromatogram system with a RID-6A refractive index detector and a Shimpack GPC 802-803 ...
Reduction and Oxidation
... 4. For atoms of group 13/ III (except B), the ON is + III (EX3) or + I (EX). And for atoms of group 14/ IV (except C, Si), the ON is + IV (EX4) or + II (EX2) 5. In compounds which are made up of non‐metals, the ON of the more electronegative element is equal to the charge of ...
... 4. For atoms of group 13/ III (except B), the ON is + III (EX3) or + I (EX). And for atoms of group 14/ IV (except C, Si), the ON is + IV (EX4) or + II (EX2) 5. In compounds which are made up of non‐metals, the ON of the more electronegative element is equal to the charge of ...
Book of Abstracts
... solution are perspective at application in solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) [3], and NiFe2O4 can be used for the cathode production [4]. Elaboration of computer models of phase diagrams (PD) for oxide systems permit to expand the possibilities of their investigation. The dividing on two, one and zerodim ...
... solution are perspective at application in solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) [3], and NiFe2O4 can be used for the cathode production [4]. Elaboration of computer models of phase diagrams (PD) for oxide systems permit to expand the possibilities of their investigation. The dividing on two, one and zerodim ...
Molecular dynamics investigation of heat conductivity in monocrystal
... shown in Fig.8. The dependence is close to linear, but with additional noise, which becomes higher for higher values of t. The corresponding time-dependence of β is shown in Fig.9. The graph demonstrates much more irregular behavior then the previous one. In fact this graph is a derivative of the de ...
... shown in Fig.8. The dependence is close to linear, but with additional noise, which becomes higher for higher values of t. The corresponding time-dependence of β is shown in Fig.9. The graph demonstrates much more irregular behavior then the previous one. In fact this graph is a derivative of the de ...
L-5: Thermodynamics of Mixtures (Chapter 7)
... • For example, in NaCl there is one Na+ and one Cl- associated with each lattice site. • The factor of 2 comes about because there are two ions associated with each defect. ...
... • For example, in NaCl there is one Na+ and one Cl- associated with each lattice site. • The factor of 2 comes about because there are two ions associated with each defect. ...
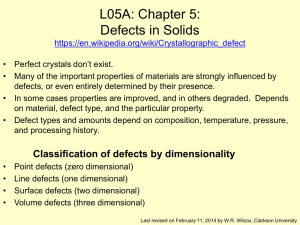
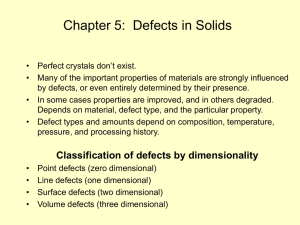
1 Introduction to Hybrid Materials
... Apart from the use of inorganic materials as fillers for organic polymers, such as rubber, it was a long time before much scientific activity was devoted to mixtures of inorganic and organic materials. One process changed this situation: the sol–gel process. This process, which will be discussed in mo ...
... Apart from the use of inorganic materials as fillers for organic polymers, such as rubber, it was a long time before much scientific activity was devoted to mixtures of inorganic and organic materials. One process changed this situation: the sol–gel process. This process, which will be discussed in mo ...
Single-Crystal Structure of a Covalent Organic
... 1,4-dioxane at 120 °C to produce a highly porous 9-fold interwoven diamond net. COF-320 exhibits permanent porosity with a Langmuir surface area of 2400 m2/g and a methane total uptake of 15.0 wt % (176 cm3/cm3) at 25 °C and 80 bar. The successful determination of the structure of COF-320 directly f ...
... 1,4-dioxane at 120 °C to produce a highly porous 9-fold interwoven diamond net. COF-320 exhibits permanent porosity with a Langmuir surface area of 2400 m2/g and a methane total uptake of 15.0 wt % (176 cm3/cm3) at 25 °C and 80 bar. The successful determination of the structure of COF-320 directly f ...
Identification - KHAZAR UNIVERSITY
... xxi. Henry’s law and solubility of gases(311) xxii. Distribution of a solute between two solvents(313) xxiii. Chemical equilibrium in the ideal solutions(313) ...
... xxi. Henry’s law and solubility of gases(311) xxii. Distribution of a solute between two solvents(313) xxiii. Chemical equilibrium in the ideal solutions(313) ...
Thermal conductivity of ordered molecular water
... with the experimental value. At lower field strengths the application of the electric field has a minor effect on . However, beyond 5.0 V / nm fields 共which are very large by experimental standards兲, there is a very significant increase of thermal conductivity. In order to understand this behavior ...
... with the experimental value. At lower field strengths the application of the electric field has a minor effect on . However, beyond 5.0 V / nm fields 共which are very large by experimental standards兲, there is a very significant increase of thermal conductivity. In order to understand this behavior ...
Thermal Transport Measurements of Individual Multiwalled Nanotubes
... The thermal properties of carbon nanotubes are of fundamental interest and also play a critical role in controlling the performance and stability of nanotube devices [1]. Unlike electrical and mechanical properties, which have been studied at a single nanotube level [2], the thermal properties of ca ...
... The thermal properties of carbon nanotubes are of fundamental interest and also play a critical role in controlling the performance and stability of nanotube devices [1]. Unlike electrical and mechanical properties, which have been studied at a single nanotube level [2], the thermal properties of ca ...
Latent Heat of Vaporization and Speci c Heat - Physlab
... We know that molecules are always on the move as they have kinetic energy, but the question is, how is this energy shared? James Clerk Maxwell solved this problem for a large number of molecules. He said that energy is equally divided in all the directions a molecule is free to move. The average ene ...
... We know that molecules are always on the move as they have kinetic energy, but the question is, how is this energy shared? James Clerk Maxwell solved this problem for a large number of molecules. He said that energy is equally divided in all the directions a molecule is free to move. The average ene ...
Large-strain time-temperature equivalence in high density
... Abstract. Time-temperature equivalence is a widely recognized property of many time-dependent material systems, where there is a clear predictive link relating the deformation response at a nominal temperature and a high strain-rate to an equivalent response at a depressed temperature and nominal st ...
... Abstract. Time-temperature equivalence is a widely recognized property of many time-dependent material systems, where there is a clear predictive link relating the deformation response at a nominal temperature and a high strain-rate to an equivalent response at a depressed temperature and nominal st ...
Crystal structure
... at one of the unit cell corners; each of the x, y, and z axes coincides with one of the three parallelepiped edges that extend from this corner, as illustrated in Figure 1.2. The unit cell geometry is completely defined in terms of six parameters: the three edge lengths a, b, and c, and the three in ...
... at one of the unit cell corners; each of the x, y, and z axes coincides with one of the three parallelepiped edges that extend from this corner, as illustrated in Figure 1.2. The unit cell geometry is completely defined in terms of six parameters: the three edge lengths a, b, and c, and the three in ...
Solid

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a gas does. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice) or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass).The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science is primarily concerned with the physical and chemical properties of solids. Solid-state chemistry is especially concerned with the synthesis of novel materials, as well as the science of identification and chemical composition.