Chapter 2
... Fluid as a Continuum Fluid as a Continuum – disregard the behavior of individual molecules. (A less rigid assumption than that in solid mechanics – in some cases such as rarefied gas flow, we have to abandon this concept) As a consequence of the continuum assumption, each fluid property is assumed ...
... Fluid as a Continuum Fluid as a Continuum – disregard the behavior of individual molecules. (A less rigid assumption than that in solid mechanics – in some cases such as rarefied gas flow, we have to abandon this concept) As a consequence of the continuum assumption, each fluid property is assumed ...
1 - vnhsteachers
... BASIC LAW OF FLUID PRESSURE The pressure at the bottom of a fluid can be expressed as: p = gh ( = density of fluid) (h = depth of fluid) (g = 9.8 m/s2) The pressure at any point in a fluid depends only on its density and its depth. It acts equally in all directions. ABSOLUTE PRESSURE The absolute ...
... BASIC LAW OF FLUID PRESSURE The pressure at the bottom of a fluid can be expressed as: p = gh ( = density of fluid) (h = depth of fluid) (g = 9.8 m/s2) The pressure at any point in a fluid depends only on its density and its depth. It acts equally in all directions. ABSOLUTE PRESSURE The absolute ...
Methodological Travails: Taling
... Much of Tantra is concerned with worship in a ritualistic form, using the three basic tools of mantra, yantra and mandala. ...
... Much of Tantra is concerned with worship in a ritualistic form, using the three basic tools of mantra, yantra and mandala. ...
p = F /A - Derry Area School District
... the perpendicular force per unit area or p = F┴/A; Pascal (Pa) 2)What is gauge pressure? the difference between the pressure you are measuring and atmospheric pressure 3) What is density? What is the density of water? the mass per unit volume or ρ = m/V; 1000 kg/m3 4) Why does pressure increase as y ...
... the perpendicular force per unit area or p = F┴/A; Pascal (Pa) 2)What is gauge pressure? the difference between the pressure you are measuring and atmospheric pressure 3) What is density? What is the density of water? the mass per unit volume or ρ = m/V; 1000 kg/m3 4) Why does pressure increase as y ...
CIEG-306 Fluid Mechanics Laboratory 5. HYDRAULIC JUMP
... The purpose of this experiment is to observe the hydraulic jump phenomenon and to compare measured flow depths with theoretical results based on the application of continuity and momentum principles. In the laboratory flume, the flow is regulated from the upstream end by a sluice gate so that a shal ...
... The purpose of this experiment is to observe the hydraulic jump phenomenon and to compare measured flow depths with theoretical results based on the application of continuity and momentum principles. In the laboratory flume, the flow is regulated from the upstream end by a sluice gate so that a shal ...
Fluid Mechanics
... • Fluid Mechanics: the study of forces that develop when an object moves through a fluid medium. • Two fluids of interest – Water – Air ...
... • Fluid Mechanics: the study of forces that develop when an object moves through a fluid medium. • Two fluids of interest – Water – Air ...
Flow Measurement
... a pipe per unit of time. This form of measurement is most frequently achieved by measuring the velocity of a fluid with a DP sensor as it travels through a pipe of known cross sectional area. Mass flow rates: Mass flow is a measure of the actual amount of mass of the fluid that passes some point per ...
... a pipe per unit of time. This form of measurement is most frequently achieved by measuring the velocity of a fluid with a DP sensor as it travels through a pipe of known cross sectional area. Mass flow rates: Mass flow is a measure of the actual amount of mass of the fluid that passes some point per ...
L15 - University of Iowa Physics
... • so far we have considered only “ideal” liquids liquids that can flow without any resistance to the flow • “real” liquids (like ketchup) have a property called viscosity which is a tendency for the liquid to resist flowing ...
... • so far we have considered only “ideal” liquids liquids that can flow without any resistance to the flow • “real” liquids (like ketchup) have a property called viscosity which is a tendency for the liquid to resist flowing ...
Properties of Fluids
... • A property of fluids (gases and liquids) that states: –Pressure applied to a fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid ...
... • A property of fluids (gases and liquids) that states: –Pressure applied to a fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid ...
chapter14 - People Server at UNCW
... the day at the lake. They are each sitting on a beach ball that is just submerged beneath the water (see Figure). Ignoring the weight of the air within the balls and the parts of their legs that are underwater, find the radius of each ball. ...
... the day at the lake. They are each sitting on a beach ball that is just submerged beneath the water (see Figure). Ignoring the weight of the air within the balls and the parts of their legs that are underwater, find the radius of each ball. ...
L-14 Fluids [3] - University of Iowa Physics
... earth is also one of the most unusual in its behavior in that it expands when it freezes. • Since it expands, the density of ice is slightly less than the density of water (917 kg/ m3 as compared to 1000 kg/ m3 for water). So the part of the iceberg above the surface is less than 10% of the total ...
... earth is also one of the most unusual in its behavior in that it expands when it freezes. • Since it expands, the density of ice is slightly less than the density of water (917 kg/ m3 as compared to 1000 kg/ m3 for water). So the part of the iceberg above the surface is less than 10% of the total ...
Chapter 16 Section 2
... displaced by the object If you place an object in water, it will push water out of the way as it sinks If the weight of the water displaced = the block’s weight, it floats If the weight of the water displaced < the block’s weight, it sinks ...
... displaced by the object If you place an object in water, it will push water out of the way as it sinks If the weight of the water displaced = the block’s weight, it floats If the weight of the water displaced < the block’s weight, it sinks ...
FLUID MECHANICS FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS
... organisms, atmospheric circulation, oceanic currents, flows in rivers, windand water loads on buildings and structures, gas motion in flames and explosions, aero- and hydrodynamic forces acting on airplanes and ships, flows in water and gas turbines, pumps, engines, pipes, valves, bearings, hydrauli ...
... organisms, atmospheric circulation, oceanic currents, flows in rivers, windand water loads on buildings and structures, gas motion in flames and explosions, aero- and hydrodynamic forces acting on airplanes and ships, flows in water and gas turbines, pumps, engines, pipes, valves, bearings, hydrauli ...
FLUID MECHANICS FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS
... organisms, atmospheric circulation, oceanic currents, flows in rivers, windand water loads on buildings and structures, gas motion in flames and explosions, aero- and hydrodynamic forces acting on airplanes and ships, flows in water and gas turbines, pumps, engines, pipes, valves, bearings, hydrauli ...
... organisms, atmospheric circulation, oceanic currents, flows in rivers, windand water loads on buildings and structures, gas motion in flames and explosions, aero- and hydrodynamic forces acting on airplanes and ships, flows in water and gas turbines, pumps, engines, pipes, valves, bearings, hydrauli ...
Where is the blood?
... Flow = CO (mL/min) CO at rest ~5000 mL/min (~5 L/min) Aortic flow at rest ~5000 mL/min (~5 L/min) Blood flows from high pressure to low pressure – Down the pressure gradient ...
... Flow = CO (mL/min) CO at rest ~5000 mL/min (~5 L/min) Aortic flow at rest ~5000 mL/min (~5 L/min) Blood flows from high pressure to low pressure – Down the pressure gradient ...
Slides from the lecture
... Becomes important for wind velocity v > √2gh (≈ 10 m/s for h ≈ 5 m). ...
... Becomes important for wind velocity v > √2gh (≈ 10 m/s for h ≈ 5 m). ...
2. Patterned Microfluidic Channel
... polarity with respect to its neighbors. In the presence of an electric field, these mobile ion layers will flow against each other. This gives rise to vortex-like flow near the boundaries, but when the channel is sufficiently thick (thickness > 10 x pattern period), no net flow is coupled to the bul ...
... polarity with respect to its neighbors. In the presence of an electric field, these mobile ion layers will flow against each other. This gives rise to vortex-like flow near the boundaries, but when the channel is sufficiently thick (thickness > 10 x pattern period), no net flow is coupled to the bul ...
MECHANISM CLUSTER First Year B.Eng/M.Eng 2007 Solutions to
... of height 3d. The cylinder is placed across the flow in the middle of the test section. The reading of a Pitot-static tube in a uniform flow at the inlet of the test section is 150mm of water. A velocity profile is measured at the outlet of the test section. It consists of a viscous wake which thick ...
... of height 3d. The cylinder is placed across the flow in the middle of the test section. The reading of a Pitot-static tube in a uniform flow at the inlet of the test section is 150mm of water. A velocity profile is measured at the outlet of the test section. It consists of a viscous wake which thick ...
Fluid Flow
... the particles in the adjacent lower layer, which then drag the particles in the next lowest layer, and so on—thus giving rise to momentum transfer ...
... the particles in the adjacent lower layer, which then drag the particles in the next lowest layer, and so on—thus giving rise to momentum transfer ...
Chap09c - MSU Physics
... There is no internal friction between adjacent layers The fluid is incompressible Its density is constant The flow is in steady state Its velocity, density and pressure do not change in time The flow is without turbulence No eddy currents are present ...
... There is no internal friction between adjacent layers The fluid is incompressible Its density is constant The flow is in steady state Its velocity, density and pressure do not change in time The flow is without turbulence No eddy currents are present ...
V‐NLH‐048 (Revision 1, Nov 18‐14) 2013 NLH General Rate Application Page 1 of 2 Reference: Section 4: Rates and Regulation, Section 4.6 Rate Stabilization Plan,
... Reference: Section 4: Rates and Regulation, Section 4.6 Rate Stabilization Plan, ...
... Reference: Section 4: Rates and Regulation, Section 4.6 Rate Stabilization Plan, ...
Here
... The saltwater oscillator denotes a non-linear phenomenon that can be observed when vertically neighboring liquids of different densities are periodically exchanged in a small orifice. For a conventional saltwater oscillator, a liquid with a larger density is placed above another liquid with a smalle ...
... The saltwater oscillator denotes a non-linear phenomenon that can be observed when vertically neighboring liquids of different densities are periodically exchanged in a small orifice. For a conventional saltwater oscillator, a liquid with a larger density is placed above another liquid with a smalle ...
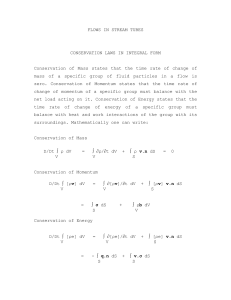
FLOWS IN STREAM TUBES CONSERVATION LAWS IN INTEGRAL
... This equation is known as the Bernoulli Equation. It can also be derived from conservation of momentum. For a short stream tube, a force balance gives: DC/Dt ...
... This equation is known as the Bernoulli Equation. It can also be derived from conservation of momentum. For a short stream tube, a force balance gives: DC/Dt ...
Aerodynamics

Aerodynamics, from Greek ἀήρ aer (air) + δυναμική (dynamics), is a branch of Fluid dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a solid object, such as an airplane wing. Aerodynamics is a sub-field of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, and many aspects of aerodynamics theory are common to these fields. The term aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with the difference being that ""gas dynamics"" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, not limited to air.Formal aerodynamics study in the modern sense began in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag have been recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics worked towards achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Wilbur and Orville Wright in 1903. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed the scientific basis for ongoing developments in heavier-than-air flight and a number of other technologies. Recent work in aerodynamics has focused on issues related to compressible flow, turbulence, and boundary layers, and has become increasingly computational in nature.









![L-14 Fluids [3] - University of Iowa Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015391226_1-fdc5124b593c632cc9a0ec2ed3f4cea6-300x300.png)