Electrokinetics
... to indirect driving force • Electroosmotic driven flow is more uniform due to a direct driving force on each atom ...
... to indirect driving force • Electroosmotic driven flow is more uniform due to a direct driving force on each atom ...
Lecture Notes for First Quiz - Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences
... pressure increasing downstream favors boundary layer growth and separation airplane wings introduce paired vorticity into flow, related to lift and contrail formation Sports balls curve when the spin drags the boundary layer with medium pressure to one side, but low pressure remains on the other sid ...
... pressure increasing downstream favors boundary layer growth and separation airplane wings introduce paired vorticity into flow, related to lift and contrail formation Sports balls curve when the spin drags the boundary layer with medium pressure to one side, but low pressure remains on the other sid ...
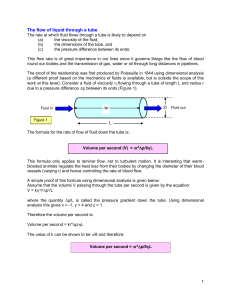
Flow of liquid through a tube
... The proof of the relationship was first produced by Poiseuille in 1844 using dimensional analysis (a different proof based on the mechanics of fluids is available, but is outside the scope of this work at this level). Consider a fluid of viscosity flowing through a tube of length L and radius r du ...
... The proof of the relationship was first produced by Poiseuille in 1844 using dimensional analysis (a different proof based on the mechanics of fluids is available, but is outside the scope of this work at this level). Consider a fluid of viscosity flowing through a tube of length L and radius r du ...
Fully Developed Couette Flow - Pharos University in Alexandria
... • Step 6: Verify solution by back-substituting into differential equations – Given the solution (u,v,w)=(Vy/h, 0, 0) ...
... • Step 6: Verify solution by back-substituting into differential equations – Given the solution (u,v,w)=(Vy/h, 0, 0) ...
MMV211, March 9, 2005 P1. The figure below shows a vane with a
... exit plane there must be a shock wave upstream of the Pitot-static tube. There are two possibilities, either there is (i) a normal shock wave standing in the diverging section, or there is (ii) a curved shock wave just upstream of the Pitot-static tube (supersonic outlet). Assume that it is alternat ...
... exit plane there must be a shock wave upstream of the Pitot-static tube. There are two possibilities, either there is (i) a normal shock wave standing in the diverging section, or there is (ii) a curved shock wave just upstream of the Pitot-static tube (supersonic outlet). Assume that it is alternat ...
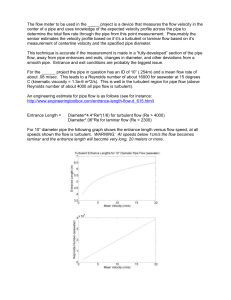
The flow meter to be used in the _____ project is a device that
... flow, away from pipe entrances and exits, changes in diameter, and other deviations from a smooth pipe. Entrance and exit conditions are probably the biggest issue. For the ______ project the pipe in question has an ID of 10” (.254m) and a mean flow rate of about .08 m/sec. This leads to a Reynolds ...
... flow, away from pipe entrances and exits, changes in diameter, and other deviations from a smooth pipe. Entrance and exit conditions are probably the biggest issue. For the ______ project the pipe in question has an ID of 10” (.254m) and a mean flow rate of about .08 m/sec. This leads to a Reynolds ...
Problem 1. Water flows steadily from a large closed tank as shown in
... a.) Calculate the volumetric flow rate in µl/min if glass has a zeta potential of -60mV at this condition. b.) For flows through tubes in the presence of both electric field and pressure gradient, the total flow rate can be calculated by adding flow rates caused by electric field and pressure gradie ...
... a.) Calculate the volumetric flow rate in µl/min if glass has a zeta potential of -60mV at this condition. b.) For flows through tubes in the presence of both electric field and pressure gradient, the total flow rate can be calculated by adding flow rates caused by electric field and pressure gradie ...
B12a - damtp - University of Cambridge
... the fluid. Calculate the velocity profile and find the volume flux (per unit width) of fluid down the wall. 3. A long, horizontal, two-dimensional container of depth h, filled with viscous fluid, has rigid, stationary bottom and end walls and a rigid top wall that moves with velocity (U, 0) in Carte ...
... the fluid. Calculate the velocity profile and find the volume flux (per unit width) of fluid down the wall. 3. A long, horizontal, two-dimensional container of depth h, filled with viscous fluid, has rigid, stationary bottom and end walls and a rigid top wall that moves with velocity (U, 0) in Carte ...
Compressible Flow
... T10. An engineer wants to apply a numerical solution scheme for compressible flow. The flow he is interested in contains shocks. He has to choose between two different solution methods – one which is based on the conservation form of the governing equations and one which is based on the non-conserv ...
... T10. An engineer wants to apply a numerical solution scheme for compressible flow. The flow he is interested in contains shocks. He has to choose between two different solution methods – one which is based on the conservation form of the governing equations and one which is based on the non-conserv ...
AE 2350 Lecture Notes #5
... or if some external force is applied. – Example: A child squeezing a balloon ...
... or if some external force is applied. – Example: A child squeezing a balloon ...
MCAT Fluid dynamics
... 28:- Bernoulli’s equation is a special case of Euler’s equation. 29:- Viscous flow of a fluig is also called poiseuille flow. 30:- Founder of modern fluid dynamics are Ludwig Prandtl & G.I Taylor. 31:- Fluid mechanics is the branch of science which is concerned with moving & stationary fluids. 32:- ...
... 28:- Bernoulli’s equation is a special case of Euler’s equation. 29:- Viscous flow of a fluig is also called poiseuille flow. 30:- Founder of modern fluid dynamics are Ludwig Prandtl & G.I Taylor. 31:- Fluid mechanics is the branch of science which is concerned with moving & stationary fluids. 32:- ...
D23Lc - damtp - University of Cambridge
... where F(x, t) is the force per unit volume (called force density, e.g. gravity ρg) that acts on the fluid. This is Euler’s equation. ρ ...
... where F(x, t) is the force per unit volume (called force density, e.g. gravity ρg) that acts on the fluid. This is Euler’s equation. ρ ...
Motion with Air Resistance
... Motion with Air Resistance The dissipative force in air or other fluids can generally be expressed in the form: fdiss = α v + β v 2 . Either term on the right-hand side of this equation may be important, depending on circumstances. The first term is most likely to be important in low-speed, streamli ...
... Motion with Air Resistance The dissipative force in air or other fluids can generally be expressed in the form: fdiss = α v + β v 2 . Either term on the right-hand side of this equation may be important, depending on circumstances. The first term is most likely to be important in low-speed, streamli ...
There are several equations useful in understanding hydraulics and
... forces that act to stop that motion. The force of inertia express the distance traveled by a discrete portion of the fluid ...
... forces that act to stop that motion. The force of inertia express the distance traveled by a discrete portion of the fluid ...
study of dynamic loads on fabric car cover using coupled fluid
... transportation of vehicle to local showrooms is done by trucks or train. In order to prevent any damage on the vehicle body due to dust, small stones or hail a textile cover is often applied. The aerodynamic flow unsteadiness is amplified by the cover displacement while at the same time the fabric c ...
... transportation of vehicle to local showrooms is done by trucks or train. In order to prevent any damage on the vehicle body due to dust, small stones or hail a textile cover is often applied. The aerodynamic flow unsteadiness is amplified by the cover displacement while at the same time the fabric c ...
File
... Ideal Fluid ◦ Incompressible ◦ Nonviscous – lose no kinetic energy due to friction as they flow ◦ Steady Flow – velocity, density, and pressure at each point are constant ◦ Nonturbulent – no eddy currents in the moving liquid ...
... Ideal Fluid ◦ Incompressible ◦ Nonviscous – lose no kinetic energy due to friction as they flow ◦ Steady Flow – velocity, density, and pressure at each point are constant ◦ Nonturbulent – no eddy currents in the moving liquid ...
Chapter 2 - CP Physics
... An airplane’s wings each have an area of 4.0 m2. When flying level, the speed of the air over the wings is 245 m/s, while the speed of the air under the wings is 222 m/s. What is the mass of the plane? ...
... An airplane’s wings each have an area of 4.0 m2. When flying level, the speed of the air over the wings is 245 m/s, while the speed of the air under the wings is 222 m/s. What is the mass of the plane? ...
Chap 5 Instruments
... Smooth cone shaped As speeds increase in the throat the pressure is reduced according to Bernoulli ...
... Smooth cone shaped As speeds increase in the throat the pressure is reduced according to Bernoulli ...
CEE161A/264A: Rivers, Streams, and Canals Summer Quarter 2012
... Rivers, Streams, and Canals is a class dedicated to understanding a branch of fluid dynamics often referred to as Open Channel Flow/Hydraulics, i.e., the flow in channels with a free surface that is ...
... Rivers, Streams, and Canals is a class dedicated to understanding a branch of fluid dynamics often referred to as Open Channel Flow/Hydraulics, i.e., the flow in channels with a free surface that is ...
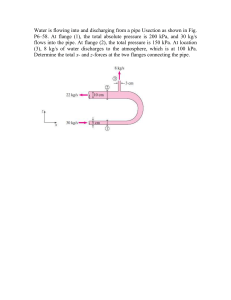
Water is flowing into and discharging from a pipe Usection as shown
... and gas absorption experiments. There is no applied pressure other than hydrostatic pressure due to gravity. Use the equations of motion in rectangular coordinates to derive expressions for: a) The velocity profile b) The pressure drop between the inlet and the exit points c) The total volumetric fl ...
... and gas absorption experiments. There is no applied pressure other than hydrostatic pressure due to gravity. Use the equations of motion in rectangular coordinates to derive expressions for: a) The velocity profile b) The pressure drop between the inlet and the exit points c) The total volumetric fl ...
Types of sediment load
... n Suspended load: Particulate sediment that is carried in the body of the flow o Suspended load moves at the same velocity as the flow. o A small particle (e.g. clay and fine silt), with a large relative surface area, is held in suspension more easily because of the electrostatic attraction between ...
... n Suspended load: Particulate sediment that is carried in the body of the flow o Suspended load moves at the same velocity as the flow. o A small particle (e.g. clay and fine silt), with a large relative surface area, is held in suspension more easily because of the electrostatic attraction between ...
ООО НПП «Электротех»
... • cement squeeze. System SKCS-01 may be used for various processes where fluids of different density are pumped. ...
... • cement squeeze. System SKCS-01 may be used for various processes where fluids of different density are pumped. ...
The influence of fluid inflow in the central hexagon on sperm
... In actual situation, the average speed of sperm from a healthy individual was around 35 m/s. What’s more, in actual situation, the flow velocity would become slower and slower as the hydrostatic pressure difference between the inlets and outlets were reduced. In the chemotaxis assay, the observatio ...
... In actual situation, the average speed of sperm from a healthy individual was around 35 m/s. What’s more, in actual situation, the flow velocity would become slower and slower as the hydrostatic pressure difference between the inlets and outlets were reduced. In the chemotaxis assay, the observatio ...
Isentropic and Ideal Gas Density Relationships
... solutions are again quite similar to each other and to the classical flow solution. ...
... solutions are again quite similar to each other and to the classical flow solution. ...
File - The Physics Doctor
... Write a small list of factors that would affect flow through a pipe In low speed fluids or high viscosity fluids, flow tends to be laminar through a pipe. ...
... Write a small list of factors that would affect flow through a pipe In low speed fluids or high viscosity fluids, flow tends to be laminar through a pipe. ...
Aerodynamics

Aerodynamics, from Greek ἀήρ aer (air) + δυναμική (dynamics), is a branch of Fluid dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a solid object, such as an airplane wing. Aerodynamics is a sub-field of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, and many aspects of aerodynamics theory are common to these fields. The term aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with the difference being that ""gas dynamics"" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, not limited to air.Formal aerodynamics study in the modern sense began in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag have been recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics worked towards achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Wilbur and Orville Wright in 1903. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed the scientific basis for ongoing developments in heavier-than-air flight and a number of other technologies. Recent work in aerodynamics has focused on issues related to compressible flow, turbulence, and boundary layers, and has become increasingly computational in nature.