4.2 Fluid Friction Notes
... The fluid pressure in the wake is less than the fluid pressure in the flow. The lower pressure in the wake causes a force to act on the object (boat or car) in the opposite direction to its velocity. This pressure difference in a wake is called pressure drag. Frictional drag and pressure drag b ...
... The fluid pressure in the wake is less than the fluid pressure in the flow. The lower pressure in the wake causes a force to act on the object (boat or car) in the opposite direction to its velocity. This pressure difference in a wake is called pressure drag. Frictional drag and pressure drag b ...
afmflow2 - Royal Society of Chemistry
... Note that a graded mesh was used to minimise the number of nodes, with the highest density being used near the sample surface and in regions of high gradients. The nodes in the files lie on a rectangular grid of 71 × 21 × 31 nodes with non-uniform spacing in the x and y directions. Simulations of ch ...
... Note that a graded mesh was used to minimise the number of nodes, with the highest density being used near the sample surface and in regions of high gradients. The nodes in the files lie on a rectangular grid of 71 × 21 × 31 nodes with non-uniform spacing in the x and y directions. Simulations of ch ...
CE 3372 Water Systems Design
... Hydraulics Definition Hydraulics is a topic in applied science and ...
... Hydraulics Definition Hydraulics is a topic in applied science and ...
Exam2 - Purdue Engineering
... 5) An airplane flies through sea level air. Its pitot tube reads a gage pressure of 0.2 atm. The air speed (in m/s) is closest to a. 10 b. 50 c. 100 d. 200 e. 400 ...
... 5) An airplane flies through sea level air. Its pitot tube reads a gage pressure of 0.2 atm. The air speed (in m/s) is closest to a. 10 b. 50 c. 100 d. 200 e. 400 ...
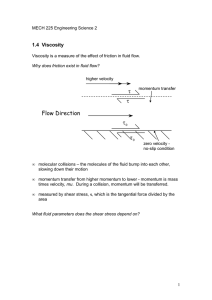
Viscosity
... The shear stress is proportional to the rate of change of velocity, also called du the velocity gradient. We can write this as: τ ∝ dy So near the surface, the shear stress is high, while on moving further into the stream the shear stress gets smaller. ...
... The shear stress is proportional to the rate of change of velocity, also called du the velocity gradient. We can write this as: τ ∝ dy So near the surface, the shear stress is high, while on moving further into the stream the shear stress gets smaller. ...
CHAPTER 14
... The region of flow over which the thermal boundary layer develops and reaches the tube center is called the thermal entry region, and the length of this region is called the thermal entry length. The region in which the flow is both hydrodynamically (the velocity profile is fully developed and remai ...
... The region of flow over which the thermal boundary layer develops and reaches the tube center is called the thermal entry region, and the length of this region is called the thermal entry length. The region in which the flow is both hydrodynamically (the velocity profile is fully developed and remai ...
Flow label for equal cost multipath routing in tunnels
... For foo-in-IPv6 tunnels, the source TEP sets a flow label per user flow in the outer packet ...
... For foo-in-IPv6 tunnels, the source TEP sets a flow label per user flow in the outer packet ...
The combined forced and free convection heat transfer from
... Along the path of the air flow, we then measured the velocity profiles in the vertical direction at the outlet surface by adjusted the free stream nozzle at different location. With each location, the pressure can be measure by reading off the different height from the manometers. Figure 1 The press ...
... Along the path of the air flow, we then measured the velocity profiles in the vertical direction at the outlet surface by adjusted the free stream nozzle at different location. With each location, the pressure can be measure by reading off the different height from the manometers. Figure 1 The press ...
Fully Developed Couette Flow - Pharos University in Alexandria
... pressure fields, and estimate the shear force per unit area acting on the bottom plate • Step 1: Geometry, dimensions, and properties ...
... pressure fields, and estimate the shear force per unit area acting on the bottom plate • Step 1: Geometry, dimensions, and properties ...
Abstract-Sumer PEKER - ic-rmm1
... emulsions to exhibit different rheological behavior under different flow conditions. The continuous phase is usually a polymer or a surfactant in solution. Surfactants with a linear hydrophobic chain and a small hydrophilic group with approximately the same cross sectional area as the hydrocarbon ch ...
... emulsions to exhibit different rheological behavior under different flow conditions. The continuous phase is usually a polymer or a surfactant in solution. Surfactants with a linear hydrophobic chain and a small hydrophilic group with approximately the same cross sectional area as the hydrocarbon ch ...
flowing fluids and pressure variation!
... Lagrangian and Eulerian Descriptions of Fluid Motion! Eulerian: Observer stays at a fixed point in space.! Lagrangian: Observer moves along with a given fluid particle.! We consider first the Lagrangian case. The position of a fluid particle at a given time t can be written as a Cartesian ...
... Lagrangian and Eulerian Descriptions of Fluid Motion! Eulerian: Observer stays at a fixed point in space.! Lagrangian: Observer moves along with a given fluid particle.! We consider first the Lagrangian case. The position of a fluid particle at a given time t can be written as a Cartesian ...
Aula Teórica 17
... Adverse pressure gradient • In case of the adverse pressure gradient pressure force decreases the velocity and can invert the sense of the flow. • For layers close to the wall the forward shear stress (above) is larger that the backward shear (below) and thus friction contribute to keep the forward ...
... Adverse pressure gradient • In case of the adverse pressure gradient pressure force decreases the velocity and can invert the sense of the flow. • For layers close to the wall the forward shear stress (above) is larger that the backward shear (below) and thus friction contribute to keep the forward ...
Extreme fluctuations and the finite lifetime of the turbulent state
... The fundamental nature and stability of the turbulent state of fluids remains an open and challenging question. Fluid flow is characterized by a dimensionless number Re, which depends on the characteristic length L, velocity U, and kinematic viscosity of the fluid through the relation Re ⬅ UL / . ...
... The fundamental nature and stability of the turbulent state of fluids remains an open and challenging question. Fluid flow is characterized by a dimensionless number Re, which depends on the characteristic length L, velocity U, and kinematic viscosity of the fluid through the relation Re ⬅ UL / . ...