MCAT Fluid dynamics
... 8:-At terminal velocity the net force acting on the body is zero. 9:-Terminal velocity of the body is directly proportional to its mass & density. 10:-Strokes law holds good for objects having spherical symmetry. 11:-Ideal fluid is also ir-rotational so it has zero angular momentum. 12:- Above criti ...
... 8:-At terminal velocity the net force acting on the body is zero. 9:-Terminal velocity of the body is directly proportional to its mass & density. 10:-Strokes law holds good for objects having spherical symmetry. 11:-Ideal fluid is also ir-rotational so it has zero angular momentum. 12:- Above criti ...
Section_36_Turbulenc..
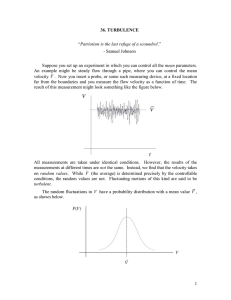
... concentrated on the mean flow, based on this we might anticipate that there would be very little dissipation in the system. However, we know that, in steady state, all of the energy that is input at the large scales must be dissipated, and at the same rate that it is input; it is just dissipated at ...
... concentrated on the mean flow, based on this we might anticipate that there would be very little dissipation in the system. However, we know that, in steady state, all of the energy that is input at the large scales must be dissipated, and at the same rate that it is input; it is just dissipated at ...
Fluid Dynamics
... The flow rate is inversely proportional to… • the length of the tube • the coefficient of viscosity ...
... The flow rate is inversely proportional to… • the length of the tube • the coefficient of viscosity ...
Relationship between Obukhov and Ozmidov length scales in the
... Abstract Measurements of atmospheric small-scale turbulence made at five levels on a 20-m tower during the Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic Ocean experiment (SHEBA) are used to examine different aspects of the stable boundary layer (SBL); e.g., the existence of Kolmogorov’s cascade, critical Richar ...
... Abstract Measurements of atmospheric small-scale turbulence made at five levels on a 20-m tower during the Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic Ocean experiment (SHEBA) are used to examine different aspects of the stable boundary layer (SBL); e.g., the existence of Kolmogorov’s cascade, critical Richar ...
Fluids - Dynamics - Physics of Papaleo
... So far, our discussion about fluids has been when they are at rest. We will Now talk about fluids that are in MOTION. An IDEAL FLUID is non-viscous No internal friction is incompressible Density R.T.S. is when its motion is steady A fluid's motion can be said to be STREAMLINE, or LAMINAR. ...
... So far, our discussion about fluids has been when they are at rest. We will Now talk about fluids that are in MOTION. An IDEAL FLUID is non-viscous No internal friction is incompressible Density R.T.S. is when its motion is steady A fluid's motion can be said to be STREAMLINE, or LAMINAR. ...
1. Introduction - Louisiana Tech University College of
... The primary role of drop structures is to direct flow from shallow surface sewers to deeper collection tunnels via a vertical shaft. There are thousands of drop structures across North America, some 300 feet tall, which convey billions of gallons per day. We are developing an innovative method for h ...
... The primary role of drop structures is to direct flow from shallow surface sewers to deeper collection tunnels via a vertical shaft. There are thousands of drop structures across North America, some 300 feet tall, which convey billions of gallons per day. We are developing an innovative method for h ...
Derive from first principles the Poiseuille equation for
... will move in bulk. However in viscous fluids, there will be a resistance to the fluid motion as shear force is induced between adjacent layers of fluid. In the figure, the shear force retarding the motion is acting on the surface of the fluid element and given by FT = τ2πrL In fully-developed steady ...
... will move in bulk. However in viscous fluids, there will be a resistance to the fluid motion as shear force is induced between adjacent layers of fluid. In the figure, the shear force retarding the motion is acting on the surface of the fluid element and given by FT = τ2πrL In fully-developed steady ...
http://redshift.vif.com/JournalFiles/V13NO2PDF/V13N2DMI.pdf
... Let V ∗ be the volume of the turbulent fluid evaporated into the bubble. The kinetic energy K ∗ transferred with the fluid into the gas phase can be found if we know the volume density of the turbulence energy ...
... Let V ∗ be the volume of the turbulent fluid evaporated into the bubble. The kinetic energy K ∗ transferred with the fluid into the gas phase can be found if we know the volume density of the turbulence energy ...
Standard atmosphere data
... 3. Nozzle flow: Consider a straight line CD nozzle with area ratio 10 (both inlet and outlet) and half-angle of 45o(conv) and 15o(div). The stagnation temperature for the flow is 3500K. Assume the flow to be perfectly expanded. Solve the flow for the first two cases mentioned in problem 1. Calculate ...
... 3. Nozzle flow: Consider a straight line CD nozzle with area ratio 10 (both inlet and outlet) and half-angle of 45o(conv) and 15o(div). The stagnation temperature for the flow is 3500K. Assume the flow to be perfectly expanded. Solve the flow for the first two cases mentioned in problem 1. Calculate ...
File - The Physics Doctor
... Write a small list of factors that would affect flow through a pipe In low speed fluids or high viscosity fluids, flow tends to be laminar through a pipe. ...
... Write a small list of factors that would affect flow through a pipe In low speed fluids or high viscosity fluids, flow tends to be laminar through a pipe. ...
APPH 4200 Physics of Fluids
... Continuity (incompressible flow and the Boussinesq approximation) ...
... Continuity (incompressible flow and the Boussinesq approximation) ...
Dragedit - Physics Forums
... very accurate as modelling the drag force is an incredibly complex procedure that is usually dependent on two complex factors; drag pressure and drag friction. We can however say “As the size and/or speed of the body increases, in due course the flow of fluid past the body becomes disorderly and tur ...
... very accurate as modelling the drag force is an incredibly complex procedure that is usually dependent on two complex factors; drag pressure and drag friction. We can however say “As the size and/or speed of the body increases, in due course the flow of fluid past the body becomes disorderly and tur ...
Chapter 9
... Friction in laminar flow is called viscosity Turbulent flow Irregular paths Sets in for high gradients (large velocities or small pipes) ...
... Friction in laminar flow is called viscosity Turbulent flow Irregular paths Sets in for high gradients (large velocities or small pipes) ...
Turbulence

In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and flow velocity in space and time.Flow in which the kinetic energy dies out due to the action of fluid molecular viscosity is called laminar flow. While there is no theorem relating the non-dimensional Reynolds number (Re) to turbulence, flows at Reynolds numbers larger than 5000 are typically (but not necessarily) turbulent, while those at low Reynolds numbers usually remain laminar. In Poiseuille flow, for example, turbulence can first be sustained if the Reynolds number is larger than a critical value of about 2040; moreover, the turbulence is generally interspersed with laminar flow until a larger Reynolds number of about 4000.In turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear on many scales and interact with each other. Drag due to boundary layer skin friction increases. The structure and location of boundary layer separation often changes, sometimes resulting in a reduction of overall drag. Although laminar-turbulent transition is not governed by Reynolds number, the same transition occurs if the size of the object is gradually increased, or the viscosity of the fluid is decreased, or if the density of the fluid is increased. Nobel Laureate Richard Feynman described turbulence as ""the most important unsolved problem of classical physics.""