The Unified Theory of Stellar Evolution
... and electrons combine and form hydrogen, the lowest element on the periodic table. [In many cases, the plasmas of elementary particles were ejected during past supernova explosions.] A new star is ...
... and electrons combine and form hydrogen, the lowest element on the periodic table. [In many cases, the plasmas of elementary particles were ejected during past supernova explosions.] A new star is ...
Teaching Text Structure with Understanding the Scale of the Universe
... By 1920, many scientists began to think that some of the objects they were seeing must be other galaxies like the Milky Way but separate from the Milky Way. They spoke of these separate clusters of stars as island universes. ...
... By 1920, many scientists began to think that some of the objects they were seeing must be other galaxies like the Milky Way but separate from the Milky Way. They spoke of these separate clusters of stars as island universes. ...
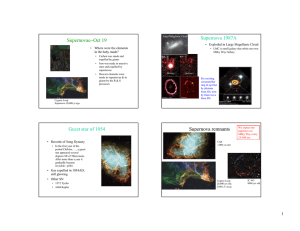
26.Meikle.Supernova_2002hh
... ejecta. Supernovae are suspected to be a major source of dust in the universe and the presence of new dust in SN 2002hh is expected to be observed at a later stage. This is only the second time for which a spectrum has been obtained of a supernova in 2.9-4.1 micron range (the other was SN 1987A whic ...
... ejecta. Supernovae are suspected to be a major source of dust in the universe and the presence of new dust in SN 2002hh is expected to be observed at a later stage. This is only the second time for which a spectrum has been obtained of a supernova in 2.9-4.1 micron range (the other was SN 1987A whic ...
An analogy
... – distant galaxies are younger than those used to define the Hubble Sequence – more peculiar galaxies are observed: could be due to patchy star formation (younger age) or to interactions being more frequent (denser Universe) – resolution is poor compared to local galaxies and usually limited to a fe ...
... – distant galaxies are younger than those used to define the Hubble Sequence – more peculiar galaxies are observed: could be due to patchy star formation (younger age) or to interactions being more frequent (denser Universe) – resolution is poor compared to local galaxies and usually limited to a fe ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... Radial velocities are nearly all positive with values up to several hundred km/s - later to be determined to be due to the expansion of the Universe. Curtis believed that the spiral nebulae are galaxies like our own lying at distances ranging from 150 kpc (M31) to 3,000 kpc for the most distant syst ...
... Radial velocities are nearly all positive with values up to several hundred km/s - later to be determined to be due to the expansion of the Universe. Curtis believed that the spiral nebulae are galaxies like our own lying at distances ranging from 150 kpc (M31) to 3,000 kpc for the most distant syst ...
The Origin of the Milky Way
... • 1976: The British astronomer Patrick Moore announced on BBC Radio 2 that at 9:47 AM a once-in-a-lifetime astronomical event was going to occur that listeners could experience in their very own homes. The planet Pluto would pass behind Jupiter, temporarily causing a gravitational alignment that wou ...
... • 1976: The British astronomer Patrick Moore announced on BBC Radio 2 that at 9:47 AM a once-in-a-lifetime astronomical event was going to occur that listeners could experience in their very own homes. The planet Pluto would pass behind Jupiter, temporarily causing a gravitational alignment that wou ...
Name - CLC Charter School
... When the supernova is done exploding, as an effect of the large transfer of matter and energy, there is a very different kind of star left. This star is called a spinning neutron star. Neutron stars produce radio waves in a steady stream or in random bursts. But if a star is massive enough, it can l ...
... When the supernova is done exploding, as an effect of the large transfer of matter and energy, there is a very different kind of star left. This star is called a spinning neutron star. Neutron stars produce radio waves in a steady stream or in random bursts. But if a star is massive enough, it can l ...
Galaxies - Mike Brotherton
... M87 = Central, giant elliptical galaxy in the Virgo cluster of galaxies Optical and radio observations detect a jet with velocities up to ~ 1/2 c. ...
... M87 = Central, giant elliptical galaxy in the Virgo cluster of galaxies Optical and radio observations detect a jet with velocities up to ~ 1/2 c. ...
Supernovae Oct 19 − Supernova 1987A
... expelled by giants • Iron was made in massive stars and expelled by supernovae • Heavier elements were made in supernovae & in giants by the R & S processes ...
... expelled by giants • Iron was made in massive stars and expelled by supernovae • Heavier elements were made in supernovae & in giants by the R & S processes ...
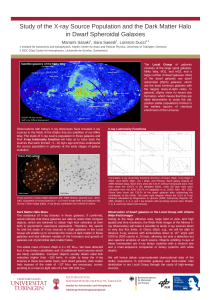
Study of the X-ray Source Population and the Dark Matter
... spatial and time resolution, the Wide Field Imager of the Athena Xray Observatory will make it possible to study X-ray sources down to very low flux limits. In Draco dSph, e.g., we will be able to observe X-ray sources with luminosities down to 1031 erg/s with 1000 to 2000 counts in 10 ksec, allowin ...
... spatial and time resolution, the Wide Field Imager of the Athena Xray Observatory will make it possible to study X-ray sources down to very low flux limits. In Draco dSph, e.g., we will be able to observe X-ray sources with luminosities down to 1031 erg/s with 1000 to 2000 counts in 10 ksec, allowin ...
Beyond the Solar System By Patti Hutchison ANSWER THE
... As a galaxy, the Milky Way is actually a giant. Its diameter is about 100,000 light years. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. A light year is about 9.5 trillion kilometers or about 6 trillion miles. Our solar system is about 4.6 billion years old. Our sun is a young star. S ...
... As a galaxy, the Milky Way is actually a giant. Its diameter is about 100,000 light years. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. A light year is about 9.5 trillion kilometers or about 6 trillion miles. Our solar system is about 4.6 billion years old. Our sun is a young star. S ...
OCR Physics A Refer to the Physics A datasheet for data, formulae
... A binary star system consists of two stars, A and B, rotating about their common centre of mass. Figure 3 shows three absorption lines in the spectra from the binary system measured over a period of time. The diagram is not drawn to ...
... A binary star system consists of two stars, A and B, rotating about their common centre of mass. Figure 3 shows three absorption lines in the spectra from the binary system measured over a period of time. The diagram is not drawn to ...
Exploring The Universe
... • Quasars may be infant galaxies. • In 1960, a faint object was matched with a strong radio signal. This object was called a quasar. • quasar quasi-stellar radio sources; very luminous objects that produce energy at a high rate and that are thought to be the most distant objects in the universe • Ea ...
... • Quasars may be infant galaxies. • In 1960, a faint object was matched with a strong radio signal. This object was called a quasar. • quasar quasi-stellar radio sources; very luminous objects that produce energy at a high rate and that are thought to be the most distant objects in the universe • Ea ...
Gamma-Ray Bursts as Sources of Strong Magnetic Fields
... new t0 . Overall such a model requires a the magnetic field that is extremely large initially, leading to the prompt emission and then it decreases, just at the right time (and before all the rotational energy is exhausted) to a lower level in which the weaker magnetar powers (using the remaining ro ...
... new t0 . Overall such a model requires a the magnetic field that is extremely large initially, leading to the prompt emission and then it decreases, just at the right time (and before all the rotational energy is exhausted) to a lower level in which the weaker magnetar powers (using the remaining ro ...
Galaxies Galaxies M81
... bright, point-like nucleus from which a jet of material emanates. The jet is seen in great detail from an HST image at right. ...
... bright, point-like nucleus from which a jet of material emanates. The jet is seen in great detail from an HST image at right. ...
Final review - Physics and Astronomy
... fl = The fraction of suitable planets on which life actually appears. fi = The fraction of life bearing planets on which intelligent life emerges. fc = The fraction of civilizations that develop a technology that releases detectable signs of their existence into space. L = The length of time such ci ...
... fl = The fraction of suitable planets on which life actually appears. fi = The fraction of life bearing planets on which intelligent life emerges. fc = The fraction of civilizations that develop a technology that releases detectable signs of their existence into space. L = The length of time such ci ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Composition unknown. Probably mostly exotic particles that don't interact with ordinary matter at all (except gravity). Some may be brown dwarfs, dead white dwarfs … Most likely it's a dark halo surrounding the Milky Way. ...
... Composition unknown. Probably mostly exotic particles that don't interact with ordinary matter at all (except gravity). Some may be brown dwarfs, dead white dwarfs … Most likely it's a dark halo surrounding the Milky Way. ...
Astrophysics Outline—Option E
... E.1.5 Describe the apparent motion of the stars/constellations over a period of a night and over a period of a year, and explain these observations in terms of the rotation and revolution of the Earth E.2 Stellar Radiation and Stellar types Assessment Statement Energy Source E.2.1 State that fusion ...
... E.1.5 Describe the apparent motion of the stars/constellations over a period of a night and over a period of a year, and explain these observations in terms of the rotation and revolution of the Earth E.2 Stellar Radiation and Stellar types Assessment Statement Energy Source E.2.1 State that fusion ...
Topic Outline - Physics Rocks!
... E.6.3 Solve problems involving red-shift and the recession speed of galaxies Hubble’s Law E.6.4 State Hubble’s Law E.6.5 Discuss the limitations of Hubble’s law E.6.6 Explain how the Hubble constant may be determined E.6.7 Explain how the Hubble constant may be used to estimate the age of the univer ...
... E.6.3 Solve problems involving red-shift and the recession speed of galaxies Hubble’s Law E.6.4 State Hubble’s Law E.6.5 Discuss the limitations of Hubble’s law E.6.6 Explain how the Hubble constant may be determined E.6.7 Explain how the Hubble constant may be used to estimate the age of the univer ...
Review Sheet and Study Hints - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... In what sense is the formation of ellipticals different from that of spirals? In what sense was Hubble correct/incorrect with this evolutionary proposal? How do galaxies in the past look different from galaxies today? Be able to look at pictures of field galaxies and clusters and comment B ...
... In what sense is the formation of ellipticals different from that of spirals? In what sense was Hubble correct/incorrect with this evolutionary proposal? How do galaxies in the past look different from galaxies today? Be able to look at pictures of field galaxies and clusters and comment B ...
Astrophysics - Mr Priest`s Physics Notes
... Radio astronomy is unaffected by cloud cover and can be performed during the daytime, two significant advantages over visible light telescopes. Disadvantages are discussed below, but this “transparency” of radio waves is the reason why it continues to be widely used, since it allows us to probe the ...
... Radio astronomy is unaffected by cloud cover and can be performed during the daytime, two significant advantages over visible light telescopes. Disadvantages are discussed below, but this “transparency” of radio waves is the reason why it continues to be widely used, since it allows us to probe the ...
essay - Caltech Astronomy
... It is my deep conviction that all phenomena in nature are interesting. The key to appreciate Nature is to discover phenomena. For this reason I list my best four discoveries: the first millisecond pulsar, the first brown dwarf, the discovery that gamma-ray bursts (GRB) are of extra-galactic origin a ...
... It is my deep conviction that all phenomena in nature are interesting. The key to appreciate Nature is to discover phenomena. For this reason I list my best four discoveries: the first millisecond pulsar, the first brown dwarf, the discovery that gamma-ray bursts (GRB) are of extra-galactic origin a ...
Gamma-ray burst

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the brightest electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. The initial burst is usually followed by a longer-lived ""afterglow"" emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).Most observed GRBs are believed to consist of a narrow beam of intense radiation released during a supernova or hypernova as a rapidly rotating, high-mass star collapses to form a neutron star, quark star, or black hole. A subclass of GRBs (the ""short"" bursts) appear to originate from a different process – this may be due to the merger of binary neutron stars. The cause of the precursor burst observed in some of these short events may be due to the development of a resonance between the crust and core of such stars as a result of the massive tidal forces experienced in the seconds leading up to their collision, causing the entire crust of the star to shatter.The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million years). All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way. It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.GRBs were first detected in 1967 by the Vela satellites, a series of satellites designed to detect covert nuclear weapons tests. Hundreds of theoretical models were proposed to explain these bursts in the years following their discovery, such as collisions between comets and neutron stars. Little information was available to verify these models until the 1997 detection of the first X-ray and optical afterglows and direct measurement of their redshifts using optical spectroscopy, and thus their distances and energy outputs. These discoveries, and subsequent studies of the galaxies and supernovae associated with the bursts, clarified the distance and luminosity of GRBs. These facts definitively placed them in distant galaxies and also connected long GRBs with the explosion of massive stars, the only possible source for the energy outputs observed.