Deep Space (PDF: 224k)
... core collapses and the star releases more energy than the star produced during its entire lifetime! This is a supernova explosion that expels material at 10 percent the speed of light and leaves behind a black hole. Stars with initial masses between eight and 50 times that of the Sun do not evolve t ...
... core collapses and the star releases more energy than the star produced during its entire lifetime! This is a supernova explosion that expels material at 10 percent the speed of light and leaves behind a black hole. Stars with initial masses between eight and 50 times that of the Sun do not evolve t ...
Lecture Notes – Galaxies
... Discovered in the 1940s by Carl Seyfert and appear as normal spirals but with very bright nuclei and emit strong non-thermal spectrum. The visible spectrum contains broad (5 000–10 000 km/s) emission lines indicating clouds of gas moving at very high speeds in the nucleus of the galaxy. 1% of spiral ...
... Discovered in the 1940s by Carl Seyfert and appear as normal spirals but with very bright nuclei and emit strong non-thermal spectrum. The visible spectrum contains broad (5 000–10 000 km/s) emission lines indicating clouds of gas moving at very high speeds in the nucleus of the galaxy. 1% of spiral ...
ALMA_BoJun605_Gruppioni
... but also higher TCMB providing higher background levels for CO excitation. • Different models predict brighter or fainter higherorder transitions. Few measurements of CO rotational transitions exist for distant quasars and ULIRGs, but these are dominated by central regions. • → Assume L’co(3-2) / L’ ...
... but also higher TCMB providing higher background levels for CO excitation. • Different models predict brighter or fainter higherorder transitions. Few measurements of CO rotational transitions exist for distant quasars and ULIRGs, but these are dominated by central regions. • → Assume L’co(3-2) / L’ ...
Folie 1 - Pi of the Sky
... The first generation of stars. Early galaxy formation. The chemical enrichment of the universe. The reionizaion of the universe, all the way back to the ‘dark ages’. Soltan institute for Nuclear Studies Warsaw 14.01.2005 ...
... The first generation of stars. Early galaxy formation. The chemical enrichment of the universe. The reionizaion of the universe, all the way back to the ‘dark ages’. Soltan institute for Nuclear Studies Warsaw 14.01.2005 ...
Lecture21
... • An object dropped from a height of 1 m would hit the surface at a velocity 0.6% the speed of light. • Must use general relativity to model correctly ...
... • An object dropped from a height of 1 m would hit the surface at a velocity 0.6% the speed of light. • Must use general relativity to model correctly ...
PowerPoint - StarDate`s Black Hole Encyclopedia
... At the time, 3C 273 was known as a "radio star." Though astronomers could detect it with radio telescopes, they couldn't pinpoint its location well enough to SEE it with optical telescopes. But that changed the day the Moon passed between the radio star and Earth, blocking its radio signals and allo ...
... At the time, 3C 273 was known as a "radio star." Though astronomers could detect it with radio telescopes, they couldn't pinpoint its location well enough to SEE it with optical telescopes. But that changed the day the Moon passed between the radio star and Earth, blocking its radio signals and allo ...
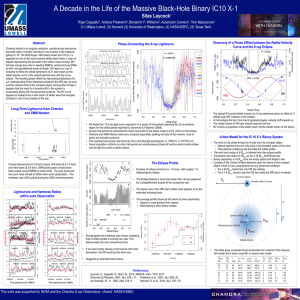
A Decade in the Life of the Massive Black-Hole Binary... Silas Laycock !
... • Companion star radius is 2Rsun as for a 35 Msun Wolf-Rayet star • Binary separation is 18 Rsun from the binary period and Kepler’s law. • Location of the Center of Mass depends upon the nature of the compact object, which is now unconstrained by any dynamical evidence. • For a 24 Msun black ho ...
... • Companion star radius is 2Rsun as for a 35 Msun Wolf-Rayet star • Binary separation is 18 Rsun from the binary period and Kepler’s law. • Location of the Center of Mass depends upon the nature of the compact object, which is now unconstrained by any dynamical evidence. • For a 24 Msun black ho ...
WEEK 8: CSI UCSC: ASTRO EDITION SOLUTIONS This week you
... (1) Compare Types I and II supernovae. What kinds of objects explode and what are their explosion mechanisms? There are two main types. The first one is Type Ia supernova, which comes from a white dwarf in a binary system with another star. A white dwarf may steal material from the companion star, a ...
... (1) Compare Types I and II supernovae. What kinds of objects explode and what are their explosion mechanisms? There are two main types. The first one is Type Ia supernova, which comes from a white dwarf in a binary system with another star. A white dwarf may steal material from the companion star, a ...
Cosmic Dawn A Hunting for the First Stars in the Universe
... where the emitted wavelength is measured in the lab or determined from theory. Typically we measure redshifts by comparing a whole suite of lines measured in the lab with the astronomical spectrum, to see that their wavelengths are all boosted by the same factor of (1+z). Because we live in an expan ...
... where the emitted wavelength is measured in the lab or determined from theory. Typically we measure redshifts by comparing a whole suite of lines measured in the lab with the astronomical spectrum, to see that their wavelengths are all boosted by the same factor of (1+z). Because we live in an expan ...
The Life Cycle of Spiral Arm Galaxies
... As a star goes supernova, it releases a great amount of energy (light) and also ejects a massive amount of matter (galactic cosmic rays), which are charged particles such as protons and pieces of ...
... As a star goes supernova, it releases a great amount of energy (light) and also ejects a massive amount of matter (galactic cosmic rays), which are charged particles such as protons and pieces of ...
The star Betelgeuse is about 500 light years away from us. If this star
... b) the photons received on Earth from the distant star have higher frequency c) the photons received on Earth are the same from both stars except there are many more from our sun d) the photons from the distant star are bluer e) not enough information to tell Infrared light waves have __________ co ...
... b) the photons received on Earth from the distant star have higher frequency c) the photons received on Earth are the same from both stars except there are many more from our sun d) the photons from the distant star are bluer e) not enough information to tell Infrared light waves have __________ co ...
G485 5.5.1 Structure of the Universe
... only appears when it is near the Sun and it always points directly away from the Sun. The solar wind, an emission of ions from the Sun’s surface, causes the comet’s gases to spread out, become ionised and therefore glow. ...
... only appears when it is near the Sun and it always points directly away from the Sun. The solar wind, an emission of ions from the Sun’s surface, causes the comet’s gases to spread out, become ionised and therefore glow. ...
Hubble`s Expansion of the Universe
... As we go further out into the Universe, eventually we are no longer able to use Cepheid variables as a distance indicator as they become too faint. At this point, we use another object known as type Ia supernovae. A supernova marks the end of a star’s life in an extremely energetic explosion. When a ...
... As we go further out into the Universe, eventually we are no longer able to use Cepheid variables as a distance indicator as they become too faint. At this point, we use another object known as type Ia supernovae. A supernova marks the end of a star’s life in an extremely energetic explosion. When a ...
Shocking Truth about Massive Stars Lidia Oskinova Chandra’s First Decade of Discovery
... ’’A very energetic explosion of a massive star is likely to create a ... fireball.... the inner core of a massive, rapidly rotating star collapses into a ~10 M Kerr black hole ... A superstrong ~10 15 G magnetic field is needed to make the object ... a microquasar. Such events must be vary rare...to ...
... ’’A very energetic explosion of a massive star is likely to create a ... fireball.... the inner core of a massive, rapidly rotating star collapses into a ~10 M Kerr black hole ... A superstrong ~10 15 G magnetic field is needed to make the object ... a microquasar. Such events must be vary rare...to ...
8.4 White Dwarfs
... Loose protons and electrons near the surface of the neutron star will be sweep up and stream along the magnetic field lines towards the north and south magnetic poles of the neutron star. The magnetic axis of the neutron star does not necessarily have to be aligned with the rotation axis (like the ...
... Loose protons and electrons near the surface of the neutron star will be sweep up and stream along the magnetic field lines towards the north and south magnetic poles of the neutron star. The magnetic axis of the neutron star does not necessarily have to be aligned with the rotation axis (like the ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
... • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars
... • Degenerate stars heavier than 1.4 solar masses collapse to become neutron stars • Formed in supernova explosions • Electrons are not separate – Combine with nuclei to form neutrons ...
... • Degenerate stars heavier than 1.4 solar masses collapse to become neutron stars • Formed in supernova explosions • Electrons are not separate – Combine with nuclei to form neutrons ...
White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars
... • Degenerate stars heavier than 1.4 solar masses collapse to become neutron stars • Formed in supernova explosions • Electrons are not separate – Combine with nuclei to form neutrons ...
... • Degenerate stars heavier than 1.4 solar masses collapse to become neutron stars • Formed in supernova explosions • Electrons are not separate – Combine with nuclei to form neutrons ...
HIERARCHICAL GALAXY ASSEMBLY AND ITS MANIFESTATIONS
... not originating from direct cooling of gas, which turns into stars The formation mechanism is going to be imprinted in the bulge distribution. The distribution of bulge types seem to indicate that secular and classical channels are well separated. ...
... not originating from direct cooling of gas, which turns into stars The formation mechanism is going to be imprinted in the bulge distribution. The distribution of bulge types seem to indicate that secular and classical channels are well separated. ...
Chapter 5 Galaxies and Star Systems
... Some galaxies do not have regular shapes, thus they are called irregular galaxies. These galaxies are typically smaller than other types of galaxies and generally have many bright, young stars. They contain a lot of gas a dust to from new stars. The Milky Way Galaxy Although it is difficult to know ...
... Some galaxies do not have regular shapes, thus they are called irregular galaxies. These galaxies are typically smaller than other types of galaxies and generally have many bright, young stars. They contain a lot of gas a dust to from new stars. The Milky Way Galaxy Although it is difficult to know ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • there are ~ 100 billion galaxies in the observable Universe • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
... • there are ~ 100 billion galaxies in the observable Universe • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
Chapter 24
... • First one discovered in early 1970s • Pulsar (pulsating radio source) • Found in the Crab nebula (remnant of an A.D. 1054 supernova) ...
... • First one discovered in early 1970s • Pulsar (pulsating radio source) • Found in the Crab nebula (remnant of an A.D. 1054 supernova) ...
Candles in the Dark
... that the Milky Way was the whole Universe, so M31 was presumably a relatively small and nearby object. Hubble calculated from the variation of his Andromeda Cepheid how far away it was and came up with the answer of more than 900 000 light years (better modern measurements give the accepted figure o ...
... that the Milky Way was the whole Universe, so M31 was presumably a relatively small and nearby object. Hubble calculated from the variation of his Andromeda Cepheid how far away it was and came up with the answer of more than 900 000 light years (better modern measurements give the accepted figure o ...
Gamma-ray burst

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the brightest electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. The initial burst is usually followed by a longer-lived ""afterglow"" emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).Most observed GRBs are believed to consist of a narrow beam of intense radiation released during a supernova or hypernova as a rapidly rotating, high-mass star collapses to form a neutron star, quark star, or black hole. A subclass of GRBs (the ""short"" bursts) appear to originate from a different process – this may be due to the merger of binary neutron stars. The cause of the precursor burst observed in some of these short events may be due to the development of a resonance between the crust and core of such stars as a result of the massive tidal forces experienced in the seconds leading up to their collision, causing the entire crust of the star to shatter.The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million years). All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way. It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.GRBs were first detected in 1967 by the Vela satellites, a series of satellites designed to detect covert nuclear weapons tests. Hundreds of theoretical models were proposed to explain these bursts in the years following their discovery, such as collisions between comets and neutron stars. Little information was available to verify these models until the 1997 detection of the first X-ray and optical afterglows and direct measurement of their redshifts using optical spectroscopy, and thus their distances and energy outputs. These discoveries, and subsequent studies of the galaxies and supernovae associated with the bursts, clarified the distance and luminosity of GRBs. These facts definitively placed them in distant galaxies and also connected long GRBs with the explosion of massive stars, the only possible source for the energy outputs observed.