6.1 Organizing the Periodic Table
... • High luster- reflect light • Solids at room temperature • Ductile ...
... • High luster- reflect light • Solids at room temperature • Ductile ...
Test Review Jeopardy
... the left end of the conductor, but do not touch it. What charge will the right end of the conductor have? ...
... the left end of the conductor, but do not touch it. What charge will the right end of the conductor have? ...
transparencies
... Br: 35), high density (7.5 g/cm3) and wide bandgap (2.7 eV). The photon stopping power of TlBr crystal is greater than any of the semiconductors discussed. Therefore this material is promising for Xand γ- ray detector applications. K.S.Shah et al. IEEE Trans.Nucl.Sci. (1989) v.39(1). ...
... Br: 35), high density (7.5 g/cm3) and wide bandgap (2.7 eV). The photon stopping power of TlBr crystal is greater than any of the semiconductors discussed. Therefore this material is promising for Xand γ- ray detector applications. K.S.Shah et al. IEEE Trans.Nucl.Sci. (1989) v.39(1). ...
TAP 518- 7: Fields in nature and in particle accelerators
... In questions 7 and 8 there are several stages in the calculation so excessive rounding in the earlier parts of the question would lead to errors in the final answer. All answers have been rounded to two significant figures, but three significant figures have been used for numerical values that have ...
... In questions 7 and 8 there are several stages in the calculation so excessive rounding in the earlier parts of the question would lead to errors in the final answer. All answers have been rounded to two significant figures, but three significant figures have been used for numerical values that have ...
January 2009 - University of Michigan
... a) Sketch the energy level diagram for the lowest five (exactly five) energy levels of helium, ignoring fine structure splitting (i.e., show all levels for n = 1 and n = 2). Identify each level using spectroscopic notation. The levels must be drawn in correct relative order. For each of the five lev ...
... a) Sketch the energy level diagram for the lowest five (exactly five) energy levels of helium, ignoring fine structure splitting (i.e., show all levels for n = 1 and n = 2). Identify each level using spectroscopic notation. The levels must be drawn in correct relative order. For each of the five lev ...
Chemical Change
... The chemical properties of elements are related to the energy changes that take place when atoms lose, gain or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. ...
... The chemical properties of elements are related to the energy changes that take place when atoms lose, gain or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. ...
2004-424-final
... (b) Indicate the type of electric current that is represented by each term on the right hand side of this equation. At a frequency f = 10 Hz, which term is larger? Simplify this equation by discarding the smaller term. (6 points) (c) Find a solution to this equation of the form Ex = Aekz. The wave h ...
... (b) Indicate the type of electric current that is represented by each term on the right hand side of this equation. At a frequency f = 10 Hz, which term is larger? Simplify this equation by discarding the smaller term. (6 points) (c) Find a solution to this equation of the form Ex = Aekz. The wave h ...
$doc.title
... 25) In an electric circuit driven by a battery, which of the following is true? a) the battery supplies the energy necessary for the current of electrons to flow b) the battery supplies the ele ...
... 25) In an electric circuit driven by a battery, which of the following is true? a) the battery supplies the energy necessary for the current of electrons to flow b) the battery supplies the ele ...
4. Atomic Structure
... • used a cathode ray tube to show smaller units that make up an atom. The ray was deflected a certain way by a magnetic field, so he concluded that the ray was formed by particles and that the particles were negatively charged. The only source available for the particles was the atoms present. ...
... • used a cathode ray tube to show smaller units that make up an atom. The ray was deflected a certain way by a magnetic field, so he concluded that the ray was formed by particles and that the particles were negatively charged. The only source available for the particles was the atoms present. ...
Semiconductors: Electrons and holes
... true conductors, (like metals) which are always highly conducting and insulators (like glass or plastic or common ceramics) which always ...
... true conductors, (like metals) which are always highly conducting and insulators (like glass or plastic or common ceramics) which always ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... Material that electric current can’t pass through. Material that resists but doesn’t stop the flow of current Circuit with one path for electric current. Circuit with more than one path for current. ...
... Material that electric current can’t pass through. Material that resists but doesn’t stop the flow of current Circuit with one path for electric current. Circuit with more than one path for current. ...
$doc.title
... a) water has a relatively high rate of heat conduction b) water is a good radiator c) water has a relatively high specific heat d) water is a poor heat conductor e) water is a poor electr ...
... a) water has a relatively high rate of heat conduction b) water is a good radiator c) water has a relatively high specific heat d) water is a poor heat conductor e) water is a poor electr ...
here
... Earth mass 5.972×1024 kg The gravitational acceleration perturbation due to an anomalous density layer with lay thickness t. ...
... Earth mass 5.972×1024 kg The gravitational acceleration perturbation due to an anomalous density layer with lay thickness t. ...
Solid State Physics and Semiconductors
... k is a vector of real numbers called the (crystal) wave vector. n is a discrete index, called the band index, which is present because there are many different Bloch waves with the same k (each has a different periodic component u). Within a band (i.e., for fixed n), nk varies continuously with k, ...
... k is a vector of real numbers called the (crystal) wave vector. n is a discrete index, called the band index, which is present because there are many different Bloch waves with the same k (each has a different periodic component u). Within a band (i.e., for fixed n), nk varies continuously with k, ...
Free electrons
... slightly into the fourth zones. The bands are filled up to the Fermi energy EF, and direct transitions can take place from any the states below the Fermi level to unoccupied bands directly above them on the E—k diagram. “parallel band effect” corresponding to the dip in the reflectivity at 1.5 eV or ...
... slightly into the fourth zones. The bands are filled up to the Fermi energy EF, and direct transitions can take place from any the states below the Fermi level to unoccupied bands directly above them on the E—k diagram. “parallel band effect” corresponding to the dip in the reflectivity at 1.5 eV or ...
Free electrons
... slightly into the fourth zones. The bands are filled up to the Fermi energy EF, and direct transitions can take place from any the states below the Fermi level to unoccupied bands directly above them on the E—k diagram. “parallel band effect” corresponding to the dip in the reflectivity at 1.5 eV or ...
... slightly into the fourth zones. The bands are filled up to the Fermi energy EF, and direct transitions can take place from any the states below the Fermi level to unoccupied bands directly above them on the E—k diagram. “parallel band effect” corresponding to the dip in the reflectivity at 1.5 eV or ...
TOPIC 4 STATIC ELECTRICITY
... the neutral metal sphere the (negatively) charged electrons in the sphere are repelled to the far side of the sphere, leaving the atoms on the near side positively charged owing to their missing electrons. If we then connect a copper wire to the negative side of the sphere and an electrical ground s ...
... the neutral metal sphere the (negatively) charged electrons in the sphere are repelled to the far side of the sphere, leaving the atoms on the near side positively charged owing to their missing electrons. If we then connect a copper wire to the negative side of the sphere and an electrical ground s ...
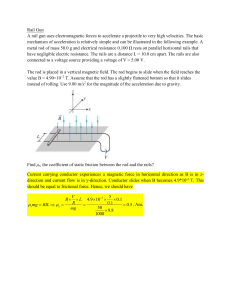
A rail gun uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate a projectile to
... A rail gun uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate a projectile to very high velocities. The basic mechanism of acceleration is relatively simple and can be illustrated in the following example. A metal rod of mass 50.0 g and electrical resistance 0.100 Ω rests on parallel horizontal rails that ha ...
... A rail gun uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate a projectile to very high velocities. The basic mechanism of acceleration is relatively simple and can be illustrated in the following example. A metal rod of mass 50.0 g and electrical resistance 0.100 Ω rests on parallel horizontal rails that ha ...