Exam 3 Study Guide
... The Milky Way is a _________ type galaxy. The Solar System is located in the ___________ spur. The Sun is located ________ away from the center of the Milky Way. The mass of the Milky Way is ________________ solar masses. The closest galaxy to the Milky Way is the ________________. Leavitt’s Law rel ...
... The Milky Way is a _________ type galaxy. The Solar System is located in the ___________ spur. The Sun is located ________ away from the center of the Milky Way. The mass of the Milky Way is ________________ solar masses. The closest galaxy to the Milky Way is the ________________. Leavitt’s Law rel ...
2014 Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. 1 Astro 113 Final Exam Review 1. What
... 23. What is the role of collisions between galaxies in the formation and evolution of galaxies? 24. What is cosmological redshift? 25. An object at room temperature (T = 300 degrees Kelvin) emits ...
... 23. What is the role of collisions between galaxies in the formation and evolution of galaxies? 24. What is cosmological redshift? 25. An object at room temperature (T = 300 degrees Kelvin) emits ...
Welcome to the Milky Way Galaxy: Student Notes
... • According to astronomers, their best estimate predicts there are at least ______ _____________ galaxies in the ___________________ universe. ...
... • According to astronomers, their best estimate predicts there are at least ______ _____________ galaxies in the ___________________ universe. ...
Document
... theory of Galactic stellar kinematics, including an explanation of High Velocity Stars in the Sun’s vicinity - slow moving stars with apparent high velocities due to the Sun’s motions around the MW center. These drift towards the center of the galaxy explaining the central bulges that had been obser ...
... theory of Galactic stellar kinematics, including an explanation of High Velocity Stars in the Sun’s vicinity - slow moving stars with apparent high velocities due to the Sun’s motions around the MW center. These drift towards the center of the galaxy explaining the central bulges that had been obser ...
Stars and Galaxies
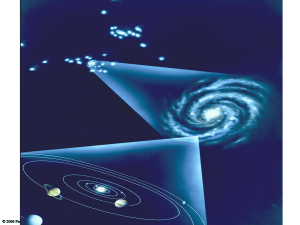
... can get a glimpse of it. Every time we look at the Moon, for example, we see it as it was a little more than a second ago. That’s because sunlight reflected from the Moon’s surface takes a little more than a second to reach Earth. We see the Sun as it looked about eight minutes ago, and the other st ...
... can get a glimpse of it. Every time we look at the Moon, for example, we see it as it was a little more than a second ago. That’s because sunlight reflected from the Moon’s surface takes a little more than a second to reach Earth. We see the Sun as it looked about eight minutes ago, and the other st ...
The Sun and Beyond - Valhalla High School
... subgroups around two massive spiral galaxies -the Milky Way, and the Andromeda Galaxy. In several billion years it is possible that the Milky Way and Andromeda will collide and merge to form one huge elliptical galaxy.(Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss) ...
... subgroups around two massive spiral galaxies -the Milky Way, and the Andromeda Galaxy. In several billion years it is possible that the Milky Way and Andromeda will collide and merge to form one huge elliptical galaxy.(Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss) ...
2010_02_04 LP08 Our Galactic Home
... R R Lyrae variable stars (M=0.5) Cepheid variable stars Brightest supergiants (M=-8) “Normal” novae Globular clusters (brightest at M=-10) H II Regions (doesn’t work perfectly) Planetary nebulae Hydrogen clouds (measure the angular size) Type 1 supernovae (M=-20) Brightest galaxies in a cluster Hubb ...
... R R Lyrae variable stars (M=0.5) Cepheid variable stars Brightest supergiants (M=-8) “Normal” novae Globular clusters (brightest at M=-10) H II Regions (doesn’t work perfectly) Planetary nebulae Hydrogen clouds (measure the angular size) Type 1 supernovae (M=-20) Brightest galaxies in a cluster Hubb ...
Messier 87

Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, and generally abbreviated to M87) is a supergiant elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo. One of the most massive galaxies in the local universe, it is notable for its large population of globular clusters—M87 contains about 12,000 compared to the 150-200 orbiting the Milky Way—and its jet of energetic plasma that originates at the core and extends outward at least 1,500 parsecs (4,900 light-years), travelling at relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky, and is a popular target for both amateur astronomy observations and professional astronomy study.French astronomer Charles Messier discovered M87 in 1781, cataloguing it as a nebulous feature while searching for objects that would confuse comet hunters. The second brightest galaxy within the northern Virgo Cluster, M87 is located about 16.4 million parsecs (53.5 million light-years) from Earth. Unlike a disk-shaped spiral galaxy, M87 has no distinctive dust lanes. Instead, it has an almost featureless, ellipsoidal shape typical of most giant elliptical galaxies, diminishing in luminosity with distance from the centre. Forming around one sixth of M87's mass, the stars in this galaxy have a nearly spherically symmetric distribution, their density decreasing with increasing distance from the core. At the core is a supermassive black hole, which forms the primary component of an active galactic nucleus. This object is a strong source of multiwavelength radiation, particularly radio waves. M87's galactic envelope extends out to a radius of about 150 kiloparsecs (490,000 light-years), where it has been truncated—possibly by an encounter with another galaxy. Between the stars is a diffuse interstellar medium of gas that has been chemically enriched by elements emitted from evolved stars.