PLANETS
... transit across its surface from the perspective of Earth (1.7% dimming). Subsequent spectroscopic studies with the Hubble Space Telescope have even indicated that the exoplanet's atmosphere must have sodium vapor in it. The planet of HD 209458, unofficially named Osiris, is so close to its star that ...
... transit across its surface from the perspective of Earth (1.7% dimming). Subsequent spectroscopic studies with the Hubble Space Telescope have even indicated that the exoplanet's atmosphere must have sodium vapor in it. The planet of HD 209458, unofficially named Osiris, is so close to its star that ...
Explores Angular Size - Chandra X
... how big something is in kilometers, instead of how big it appears to be in angular measure. To get this information, all we need to know is how far away the object is from us. The moon is 324,000 kilometers away, and Venus is about 40 million kilometers away from Earth at its closest distance. The f ...
... how big something is in kilometers, instead of how big it appears to be in angular measure. To get this information, all we need to know is how far away the object is from us. The moon is 324,000 kilometers away, and Venus is about 40 million kilometers away from Earth at its closest distance. The f ...
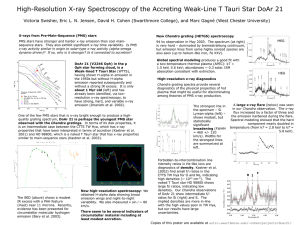
DoAr21_AAS2005 - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... emission reported subsequently and without a strong IR excess. It is only about 1 Myr old (left) and has already been identified, via lowresolution x-ray spectroscopy, to have strong, hard, and variable x-ray emission (Imanishi et al. 2002). One of the few PMS stars that is x-ray bright enough to pr ...
... emission reported subsequently and without a strong IR excess. It is only about 1 Myr old (left) and has already been identified, via lowresolution x-ray spectroscopy, to have strong, hard, and variable x-ray emission (Imanishi et al. 2002). One of the few PMS stars that is x-ray bright enough to pr ...
X-ray Emission from Massive Stars
... Massive stars have very strong radiationdriven stellar winds What is a stellar wind? It is the steady loss of mass from the surface of a star into interstellar space The Sun has a wind (the “solar wind”) but the winds of hot stars can be a billion times as strong as the Sun’s ...
... Massive stars have very strong radiationdriven stellar winds What is a stellar wind? It is the steady loss of mass from the surface of a star into interstellar space The Sun has a wind (the “solar wind”) but the winds of hot stars can be a billion times as strong as the Sun’s ...
Cepheus (constellation)
... between 3.5m and 4.4m over a period of 5 days and 9 hours. The Cepheids are a class of pulsating variable stars; Delta Cephei has a minimum size of 40 solar diameters and a maximum size of 46 solar diameters. It is also a double star; the yellow star also has a wide-set blue-hued companion of magnit ...
... between 3.5m and 4.4m over a period of 5 days and 9 hours. The Cepheids are a class of pulsating variable stars; Delta Cephei has a minimum size of 40 solar diameters and a maximum size of 46 solar diameters. It is also a double star; the yellow star also has a wide-set blue-hued companion of magnit ...
Is there life outside of Earth? Activity 2: Moving Stars and Their Planets
... In this model, students will change the mass of planet using the “planet-diameter” slider and the “Rocky-planet” switch. A rocky planet is denser than a gaseous planet, so the mass of the rocky planet will be higher than a gaseous planet of the same size. The mass of the student-created planet is gi ...
... In this model, students will change the mass of planet using the “planet-diameter” slider and the “Rocky-planet” switch. A rocky planet is denser than a gaseous planet, so the mass of the rocky planet will be higher than a gaseous planet of the same size. The mass of the student-created planet is gi ...
New product range (an implementation plan for business expansion)
... There will be some investment in new personnel — two part-time production workers, one new Production Supervisor and one dedicated Product Manager. At eighteen months a review is scheduled which will address any changes or additions that may be necessary. This review will focus particularly on addit ...
... There will be some investment in new personnel — two part-time production workers, one new Production Supervisor and one dedicated Product Manager. At eighteen months a review is scheduled which will address any changes or additions that may be necessary. This review will focus particularly on addit ...
Multiple Choice, continued Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe
... The diagrams show that the individual stars move at different rates and in different directions from one another; constellations are arbitrary human distinctions; the stars within constellations move along individual paths, not as a group; the familiar patterns that stars form in the Earth’s sky cha ...
... The diagrams show that the individual stars move at different rates and in different directions from one another; constellations are arbitrary human distinctions; the stars within constellations move along individual paths, not as a group; the familiar patterns that stars form in the Earth’s sky cha ...
Life Cycle of the Stars
... This H–R diagram shows the evolution of stars somewhat more and somewhat less massive than the Sun. The shape of the paths is similar, but they wind up in different places on the main sequence. ...
... This H–R diagram shows the evolution of stars somewhat more and somewhat less massive than the Sun. The shape of the paths is similar, but they wind up in different places on the main sequence. ...
Brown et al. 2008 Studying Resolved Stellar
... S/N=10 at the distance of the Virgo Cluster. Similar exposure times can reach K(AB) = 1 at a distance of 4 Mpc, getting beyond the RGB bump and providing more stars and greater color leverage for constraining the metallicity distribution. These observations can only be carried out in low-surface-bri ...
... S/N=10 at the distance of the Virgo Cluster. Similar exposure times can reach K(AB) = 1 at a distance of 4 Mpc, getting beyond the RGB bump and providing more stars and greater color leverage for constraining the metallicity distribution. These observations can only be carried out in low-surface-bri ...
Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... 2. White dwarfs and neutron stars are both end products of stellar evolution. White dwarfs are composed of mostly carbon, oxygen, and electrons, whereas neutron stars are composed of mostly neutrons. What happens to the protons in the atomic nuclei and the degenerate electrons that were inside the s ...
... 2. White dwarfs and neutron stars are both end products of stellar evolution. White dwarfs are composed of mostly carbon, oxygen, and electrons, whereas neutron stars are composed of mostly neutrons. What happens to the protons in the atomic nuclei and the degenerate electrons that were inside the s ...
PLANETS
... transit across its surface from the perspective of Earth (1.7% dimming). Subsequent spectroscopic studies with the Hubble Space Telescope have even indicated that the exoplanet's atmosphere must have sodium vapor in it. The planet of HD 209458, unofficially named Osiris, is so close to its star that ...
... transit across its surface from the perspective of Earth (1.7% dimming). Subsequent spectroscopic studies with the Hubble Space Telescope have even indicated that the exoplanet's atmosphere must have sodium vapor in it. The planet of HD 209458, unofficially named Osiris, is so close to its star that ...
Determination of kinetic energies of stars using Hipparcos data *
... Abstract. It is well known that the stars of late spectral types from the main sequence of the HR diagram have larger proper motions than the stars of earlier types. This is due to two reasons: firstly, these stars are generally closer because of the observational selection, and secondly, there is a ...
... Abstract. It is well known that the stars of late spectral types from the main sequence of the HR diagram have larger proper motions than the stars of earlier types. This is due to two reasons: firstly, these stars are generally closer because of the observational selection, and secondly, there is a ...
celestial sphere
... PURPOSE: To compare the horizon and equatorial coordinate systems and to learn how to determine sidereal time. To make use of a celestial globe in understanding the basic coordinate systems. PROCEDURE: Making use of the celestial globe, answer the questions in this lab pertaining to the horizon and ...
... PURPOSE: To compare the horizon and equatorial coordinate systems and to learn how to determine sidereal time. To make use of a celestial globe in understanding the basic coordinate systems. PROCEDURE: Making use of the celestial globe, answer the questions in this lab pertaining to the horizon and ...
Ecosystems, from life, to the Earth, to the Galaxy
... and, in some cases, planetary systems and life. Further star formation in a molecular cloud is self-regulated by the massive stars already forming, and by the cooling agents which are already present in it. These agents gradually change as the elemental abundances, particularly of carbon, increase a ...
... and, in some cases, planetary systems and life. Further star formation in a molecular cloud is self-regulated by the massive stars already forming, and by the cooling agents which are already present in it. These agents gradually change as the elemental abundances, particularly of carbon, increase a ...
Document
... Use the ecliptic and the celestial sphere to explain the positions that lead to lunar and solar eclipses. Match cycles of the moon to corresponding positions of Earth, moon, and sun. Explain why the constellations visible in the night sky change throughout the year. As.1.2 Use scientific not ...
... Use the ecliptic and the celestial sphere to explain the positions that lead to lunar and solar eclipses. Match cycles of the moon to corresponding positions of Earth, moon, and sun. Explain why the constellations visible in the night sky change throughout the year. As.1.2 Use scientific not ...
Differential Rotation in A stars
... There is a trade off between rotation and macroturbulent velocities. You can compensate a decrease in rotation by increasing the macroturbulent velocity. At low rotational velocities it is difficult to distinguish the two. Above the red line represents V = 3 km/s, M = 0 km/s. The blue line represent ...
... There is a trade off between rotation and macroturbulent velocities. You can compensate a decrease in rotation by increasing the macroturbulent velocity. At low rotational velocities it is difficult to distinguish the two. Above the red line represents V = 3 km/s, M = 0 km/s. The blue line represent ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.