PowerPoint Presentation - The Sun as a Power House
... to make more massive nuclei like Helium. • H-bomb, tokamak, internal confinement fusion • Sun has lots of Hydrogen!! ...
... to make more massive nuclei like Helium. • H-bomb, tokamak, internal confinement fusion • Sun has lots of Hydrogen!! ...
spectral lines as distant measurement tools
... and colleagues called the “luminosity classification” I–II–III–IV–V. Stars with luminosity class V are on the main sequence while stars with lower luminosity class (higher luminosity) are increasingly above it. The HRD is the most important diagram in astronomy, but when it was first plotted (in 190 ...
... and colleagues called the “luminosity classification” I–II–III–IV–V. Stars with luminosity class V are on the main sequence while stars with lower luminosity class (higher luminosity) are increasingly above it. The HRD is the most important diagram in astronomy, but when it was first plotted (in 190 ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Letter to the Editor Low
... The resulting net CMD for cluster stars within r ≤ 3300 of NGC 3603 is shown at the right in Fig. 2. We overlayed the theoretical isochrones of pre-main sequence stars from Palla & Stahler (1999) down to 0.1M . We assumed a distance modulus of (m − M )o = 13.9 based on the distance of 6 kpc (De Pre ...
... The resulting net CMD for cluster stars within r ≤ 3300 of NGC 3603 is shown at the right in Fig. 2. We overlayed the theoretical isochrones of pre-main sequence stars from Palla & Stahler (1999) down to 0.1M . We assumed a distance modulus of (m − M )o = 13.9 based on the distance of 6 kpc (De Pre ...
Hall Scorpius constellation (11) Jacob Hall Physics 1040, sec 002
... and at an estimated distance of 32,600 light-years, M80's spatial diameter is about 95 light-years. It contains several hundred thousand stars, and is among the more densely populated globular clusters in the Milky Way Galaxy. M80 contains a relatively large number of blue stragglers, stars that app ...
... and at an estimated distance of 32,600 light-years, M80's spatial diameter is about 95 light-years. It contains several hundred thousand stars, and is among the more densely populated globular clusters in the Milky Way Galaxy. M80 contains a relatively large number of blue stragglers, stars that app ...
Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Characterization of the
... range of a few tens μas for other sources – Intermediate resolution spectra for ~ 150 x 106 stars – Will greatly increase the accuracy of exoplanet host stars distances – Stars with distances larger than 50-100 pc will most greatly benefit with respect to the current measurements based on Hipparc ...
... range of a few tens μas for other sources – Intermediate resolution spectra for ~ 150 x 106 stars – Will greatly increase the accuracy of exoplanet host stars distances – Stars with distances larger than 50-100 pc will most greatly benefit with respect to the current measurements based on Hipparc ...
PLANETS
... Analysis of earlier pictures from the Hubble Space Telescope indicated that planets were only beginning to form around Beta Pictoris, a very young star at between 20 million and 100 million years old. Most dust grains in the disk are not agglomerating to form larger bodies; instead, they are eroding ...
... Analysis of earlier pictures from the Hubble Space Telescope indicated that planets were only beginning to form around Beta Pictoris, a very young star at between 20 million and 100 million years old. Most dust grains in the disk are not agglomerating to form larger bodies; instead, they are eroding ...
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades
... table of these values is located in Table 3 located below. Slide the plastic overlay up and down until the main sequence on the overlay best aligns with the main sequence on your paper graph. Keep the y axes precisely parallel and over top one another. Seek a best fit for the central portion of the ...
... table of these values is located in Table 3 located below. Slide the plastic overlay up and down until the main sequence on the overlay best aligns with the main sequence on your paper graph. Keep the y axes precisely parallel and over top one another. Seek a best fit for the central portion of the ...
Document
... that are outside the habitable zone but could still have liquid water. Like Europa. The major problem with the calculations for the habitable zone is that they don’t take any odd factors into account. Like tidal stretching, volcanic activity, or ultra-thick atmospheres. We have to keep in mind that ...
... that are outside the habitable zone but could still have liquid water. Like Europa. The major problem with the calculations for the habitable zone is that they don’t take any odd factors into account. Like tidal stretching, volcanic activity, or ultra-thick atmospheres. We have to keep in mind that ...
“Breakthroughs” of the 20th Century
... The fact that there is a variety of nuclear “fuels”, coupled with the possibility of simply utilizing potential energy, means that there are a range of different star types. So the second major “stellar” breakthrough concerns the division of the stellar population into dwarf stars, giant stars and w ...
... The fact that there is a variety of nuclear “fuels”, coupled with the possibility of simply utilizing potential energy, means that there are a range of different star types. So the second major “stellar” breakthrough concerns the division of the stellar population into dwarf stars, giant stars and w ...
The star and the colours
... Star: ‘Oh no! Pitter patter, pitter patter! There are raindrops on my head! I want a hat!’ Narrator 1: The star is cold and tired. Narrator 2: She falls asleep. ...
... Star: ‘Oh no! Pitter patter, pitter patter! There are raindrops on my head! I want a hat!’ Narrator 1: The star is cold and tired. Narrator 2: She falls asleep. ...
Tutor Marked Assignment
... (b) The estimated lifetime of the Sun on the main sequence is ~ 1010 years. Calculate the main sequence lifetime of a star of mass (i) 5 M and (ii) 0.2 M. ...
... (b) The estimated lifetime of the Sun on the main sequence is ~ 1010 years. Calculate the main sequence lifetime of a star of mass (i) 5 M and (ii) 0.2 M. ...
astronomy
... stones that are thought to have been aligned to track the movements of the Sun and Moon and to measure eclipses. Around 1300 BC, Chinese astronomers embarked on a long, precise study of eclipses, recording 900 solar eclipses and 600 lunar eclipses over the next 2600 years. In about 700 BC, the Babyl ...
... stones that are thought to have been aligned to track the movements of the Sun and Moon and to measure eclipses. Around 1300 BC, Chinese astronomers embarked on a long, precise study of eclipses, recording 900 solar eclipses and 600 lunar eclipses over the next 2600 years. In about 700 BC, the Babyl ...
Chapter 14 Neutron Stars and Black holes
... 2. White dwarfs and neutron stars are both end products of stellar evolution. White dwarfs are composed of mostly carbon, oxygen, and electrons, whereas neutron stars are composed of mostly neutrons. What happens to the protons in the atomic nuclei and the degenerate electrons that were inside the s ...
... 2. White dwarfs and neutron stars are both end products of stellar evolution. White dwarfs are composed of mostly carbon, oxygen, and electrons, whereas neutron stars are composed of mostly neutrons. What happens to the protons in the atomic nuclei and the degenerate electrons that were inside the s ...
D109-08x
... In Cycle 17 of HST we request a small amount of time to obtain high resolution imaging of this collection of knots in as many filters as practical. Having a better photometric characterization of the knots over a broader color baseline than obtainable from the ground coupled with higher resolution i ...
... In Cycle 17 of HST we request a small amount of time to obtain high resolution imaging of this collection of knots in as many filters as practical. Having a better photometric characterization of the knots over a broader color baseline than obtainable from the ground coupled with higher resolution i ...
*Studying Complex Star-Forming Fields: Rosette Nebula and Monoceros Loop by Chris Hathaway and Anthony Kuchera
... physical parameters indicated that the stellar content of the possible subgroups is similar. At the same time, the photometric diagrams related to stellar distance further supported the notion of subgroups at different distances. This finding of subgroups within the clusters, however, requires furth ...
... physical parameters indicated that the stellar content of the possible subgroups is similar. At the same time, the photometric diagrams related to stellar distance further supported the notion of subgroups at different distances. This finding of subgroups within the clusters, however, requires furth ...
Document
... them → know their distance (with ~6% uncertainty) • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
... them → know their distance (with ~6% uncertainty) • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... Of these sources, electromagnetic waves is by far the most important. Practical problems limit the amount of information we can obtain from other sources with current technology. Since electromagnetic radiation is almost the only source which we use to get information about the distant universe, it ...
... Of these sources, electromagnetic waves is by far the most important. Practical problems limit the amount of information we can obtain from other sources with current technology. Since electromagnetic radiation is almost the only source which we use to get information about the distant universe, it ...
Script Chapter 7 part 1
... The cooling time scale becomes shorter during the collapse because the particle density increases steadily. – the contraction is rapid in the optically thin case, because then the radiation can escape from the entire cloud volume, – the contraction is slow if the cloud is optically thick, because th ...
... The cooling time scale becomes shorter during the collapse because the particle density increases steadily. – the contraction is rapid in the optically thin case, because then the radiation can escape from the entire cloud volume, – the contraction is slow if the cloud is optically thick, because th ...
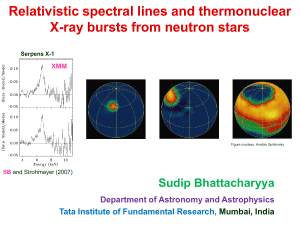
Broad Relativistic Iron Lines from Neutron Star LMXBs
... (4) observer’s inclination angle w.r.t. NS spin axis: i; (5) beaming (due to NS atmosphere) parameter: n [specific intensity as a function of angle (in emitter’s frame) from surface normal is given by I() cosn() ]; (6) background. ...
... (4) observer’s inclination angle w.r.t. NS spin axis: i; (5) beaming (due to NS atmosphere) parameter: n [specific intensity as a function of angle (in emitter’s frame) from surface normal is given by I() cosn() ]; (6) background. ...
Lesson Plan - ScienceA2Z.com
... to be grouped in the night sky. A star pattern may be widely known but may not be recognized by the International Astronomical Union; such a pattern of stars is called an asterism. An example is the grouping called the Big Dipper. The stars in a constellation or asterism rarely have any astrophysica ...
... to be grouped in the night sky. A star pattern may be widely known but may not be recognized by the International Astronomical Union; such a pattern of stars is called an asterism. An example is the grouping called the Big Dipper. The stars in a constellation or asterism rarely have any astrophysica ...
Galaxies - Indiana University Astronomy
... For Wednesday, April 8 Part 7: Supernova in M51 At least two supernovae have been detected in recent years in the nearby Whirlpool Galaxy, Messier 51. M51 is located at a distance of about 31 million light years (about 10 megaparsecs) in the direction of the constellation Canes Venatici. Stars can ...
... For Wednesday, April 8 Part 7: Supernova in M51 At least two supernovae have been detected in recent years in the nearby Whirlpool Galaxy, Messier 51. M51 is located at a distance of about 31 million light years (about 10 megaparsecs) in the direction of the constellation Canes Venatici. Stars can ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.