CONSTELLATIONS
... Locate and identify the following constellations. The myth of Andromeda claims that her mother, Queen Cassiopeia, was so proud of her daughter's beauty that she boasted it surpassed even that of the nymphs of the sea. Such arrogance offended the gods, who released floods in retribution and threatene ...
... Locate and identify the following constellations. The myth of Andromeda claims that her mother, Queen Cassiopeia, was so proud of her daughter's beauty that she boasted it surpassed even that of the nymphs of the sea. Such arrogance offended the gods, who released floods in retribution and threatene ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Since a galaxy is a system of stars, one way is to just count fainter and fainter stars in all directions. Once I reach the most distant stars (which appear as the faintest) at the edge of the system, I find no more fainter stars. By repeating this procedure along all directions, I can get an idea o ...
... Since a galaxy is a system of stars, one way is to just count fainter and fainter stars in all directions. Once I reach the most distant stars (which appear as the faintest) at the edge of the system, I find no more fainter stars. By repeating this procedure along all directions, I can get an idea o ...
The ultra-luminous x-ray sources near center of M82
... Best Candidate of IMBH – M82 X-1 has luminosity ~ 1041 erg/sec not at the center of the galaxy => Not an AGN has a period of 62 days very close to a young star cluster MGG-11 ...
... Best Candidate of IMBH – M82 X-1 has luminosity ~ 1041 erg/sec not at the center of the galaxy => Not an AGN has a period of 62 days very close to a young star cluster MGG-11 ...
7 Structure of Distorted Stars
... quantity, the radiative flux, and an additional term that anticipates some results from later in the chapter. The quantity S is the entropy of the gas, and in Chapter 4 [see equation (4.6.9)] we saw that this term had to be included when the models were changing rapidly in time. In this case, the te ...
... quantity, the radiative flux, and an additional term that anticipates some results from later in the chapter. The quantity S is the entropy of the gas, and in Chapter 4 [see equation (4.6.9)] we saw that this term had to be included when the models were changing rapidly in time. In this case, the te ...
A Hero`s Little Horse: Discovery of a Dissolving Star Cluster in
... profile of the stellar number density, i.e. star counts in elliptical annuli around Kim 1, where r is the elliptical radius. For the center of the overdensity we adopted the centre of mass calculated in terms of the normalised signals on the array into which the stars were binned and smoothed as des ...
... profile of the stellar number density, i.e. star counts in elliptical annuli around Kim 1, where r is the elliptical radius. For the center of the overdensity we adopted the centre of mass calculated in terms of the normalised signals on the array into which the stars were binned and smoothed as des ...
November - LVAstronomy.com
... monthly summary. We also accept digital imaging. Visual astronomy depends on what’s seen through the eyepiece. Not only does it satisfy an innate curiosity, but it allows the visual observer to discover the beauty and the wonderment of the night sky. Before photography, all observations depended on ...
... monthly summary. We also accept digital imaging. Visual astronomy depends on what’s seen through the eyepiece. Not only does it satisfy an innate curiosity, but it allows the visual observer to discover the beauty and the wonderment of the night sky. Before photography, all observations depended on ...
PSC100 Summary Chapters 10 to Chapter 20
... temperatures and densities in the core that push the outer layers of the star outward. These outer layers cool so that the star not only appears much larger but also takes on a reddish coloration. This period of a star's life is called the RED GIANT phase. Meanwhile the core is really much hotter du ...
... temperatures and densities in the core that push the outer layers of the star outward. These outer layers cool so that the star not only appears much larger but also takes on a reddish coloration. This period of a star's life is called the RED GIANT phase. Meanwhile the core is really much hotter du ...
Nuclear Powerhouse
... estimated to be above the 8 million K needed to fuse hydrogen nuclei together Calculations have shown that the observed power output of the Sun is consistent with the power produced by the fusion of hydrogen nuclei The observed neutrinos from the Sun produced are expected as one of the byproducts of ...
... estimated to be above the 8 million K needed to fuse hydrogen nuclei together Calculations have shown that the observed power output of the Sun is consistent with the power produced by the fusion of hydrogen nuclei The observed neutrinos from the Sun produced are expected as one of the byproducts of ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... by the Sun, not the planets. The total mass of the planets only make up about one part in 1000 of the total mass of the solar system. If this is the normal ratio, and we have no reason to believe otherwise, then the planets can only explain a tiny part of the invisible matter. Brown dwarf stars (mor ...
... by the Sun, not the planets. The total mass of the planets only make up about one part in 1000 of the total mass of the solar system. If this is the normal ratio, and we have no reason to believe otherwise, then the planets can only explain a tiny part of the invisible matter. Brown dwarf stars (mor ...
species which remained immutable and unchanged thereafter. An
... changed into that of another when its nucleus changed its positive charge, and the electronic structure made a secondary adjustment in gaining or losing negatively charged electrons. In 1911, the identification of isotopes by Soddy led to the revival of Prout's hypothesis. Those elements which did n ...
... changed into that of another when its nucleus changed its positive charge, and the electronic structure made a secondary adjustment in gaining or losing negatively charged electrons. In 1911, the identification of isotopes by Soddy led to the revival of Prout's hypothesis. Those elements which did n ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... Hertzsprung-Russell diagram • Parts of an Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram • Main-sequence stars • 90 percent of all stars • Band through the center of the H-R diagram • Sun is in the main-sequence ...
... Hertzsprung-Russell diagram • Parts of an Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram • Main-sequence stars • 90 percent of all stars • Band through the center of the H-R diagram • Sun is in the main-sequence ...
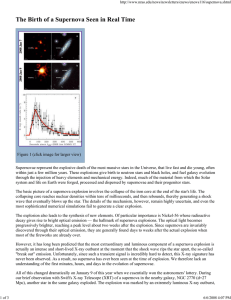
The Birth of a Supernova Seen in Real Time
... Supernovae represent the explosive death of the most massive stars in the Universe, that live fast and die young, often within just a few million years. These explosions give birth to neutron stars and black holes, and fuel galaxy evolution through the injection of heavy elements and mechanical ener ...
... Supernovae represent the explosive death of the most massive stars in the Universe, that live fast and die young, often within just a few million years. These explosions give birth to neutron stars and black holes, and fuel galaxy evolution through the injection of heavy elements and mechanical ener ...
The Galactic Halo The Galactic Disk Height and Thickness of MW
... each cluster using RR Lyrae stars and produced a three dimensional plot of the clusters’ positions. The center of the Galaxy was then identified by the average position of the clusters. " We now know that Shapley’s distance to the Galactic center was ~ three times too large because of calibration er ...
... each cluster using RR Lyrae stars and produced a three dimensional plot of the clusters’ positions. The center of the Galaxy was then identified by the average position of the clusters. " We now know that Shapley’s distance to the Galactic center was ~ three times too large because of calibration er ...
Short-Period Comets
... Short-Period Comets Short-period comets from the ___________________ come from _________________ between objects. Short-period comets take less than _________ years to orbit the sun. Short-period comets have a _____________ life span as they lose layers each time they pass the ____________. ...
... Short-Period Comets Short-period comets from the ___________________ come from _________________ between objects. Short-period comets take less than _________ years to orbit the sun. Short-period comets have a _____________ life span as they lose layers each time they pass the ____________. ...
Star-D_Teacher_Guide - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Discuss the distances of the planets from the Sun in comparison with the distances between stars. Earth, as discussed earlier, is only 15 meters from the Sun on this scale model. Compared with ...
... Discuss the distances of the planets from the Sun in comparison with the distances between stars. Earth, as discussed earlier, is only 15 meters from the Sun on this scale model. Compared with ...
ASTR2100 - Saint Mary's University | Astronomy & Physics
... function of the age of the stars, there appears to be a net metallicity growth with age amounting to: Δ<[Fe/H]> ≈ 0.5–0.7/1010 years, i.e. an increase of Fe/H by 4 ±1 every 1010 years. The relationship is not zeroed to the Sun, since solar metallicity is calculated to have been reached at an age of ...
... function of the age of the stars, there appears to be a net metallicity growth with age amounting to: Δ<[Fe/H]> ≈ 0.5–0.7/1010 years, i.e. an increase of Fe/H by 4 ±1 every 1010 years. The relationship is not zeroed to the Sun, since solar metallicity is calculated to have been reached at an age of ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.