... The temperature range over which the growth occurred is about 100 oC, so Meibom was able to calculate a cooling rate for the portion of the nebula in which the metal grains grew. By dividing the temperature interval (100 oC) by the growth time (19 days, or 456 hours), he found a cooling rate of 0.2 ...
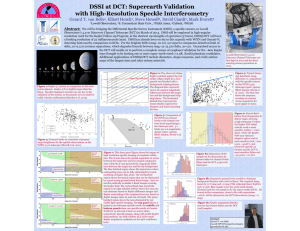
DSSI at DCT: Superearth Validation with High
... delta_m=5.5 at 200mas separations, which degrades linearly between mag~12-15.5 to delta_m=3.0. Guaranteed access to the DCT will enable us to perform a complete census of exoplanet validation for the ~600 Kepler stars thought to be hosting one or more super-earth-sized (>2.5R_Earth) planetary candid ...
... delta_m=5.5 at 200mas separations, which degrades linearly between mag~12-15.5 to delta_m=3.0. Guaranteed access to the DCT will enable us to perform a complete census of exoplanet validation for the ~600 Kepler stars thought to be hosting one or more super-earth-sized (>2.5R_Earth) planetary candid ...
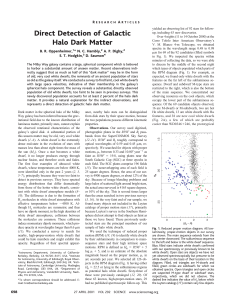
Direct Detection of Galactic Halo Dark Matter
... to harbor a substantial amount of unseen matter. Recent observations indirectly suggest that as much as half of this “dark matter” may be in the form of old, very cool white dwarfs, the remnants of an ancient population of stars as old as the galaxy itself. We conducted a survey to find faint, cool ...
... to harbor a substantial amount of unseen matter. Recent observations indirectly suggest that as much as half of this “dark matter” may be in the form of old, very cool white dwarfs, the remnants of an ancient population of stars as old as the galaxy itself. We conducted a survey to find faint, cool ...
AUI CA science talk - National Radio Astronomy Observatory
... • [Even SKA project office admits full SKA is not realizable in next decade.] • Near term: Narrow focus to quantify how NRAO facilities will make major strides in addressing the SKA KSP goals, as well as delineate the requisite upgrades, or development work on plausible new facilities. • Naturally p ...
... • [Even SKA project office admits full SKA is not realizable in next decade.] • Near term: Narrow focus to quantify how NRAO facilities will make major strides in addressing the SKA KSP goals, as well as delineate the requisite upgrades, or development work on plausible new facilities. • Naturally p ...
Notes - Bill Wolf
... and luminosity to denote how much light the star is actually giving off. These two words have analogous magnitude scales. The magnitude scale that measures brightness is the one that Hipparchus thought up. We call it Apparent Magnitude, often denoted m. The scale corresponding to luminosity is calle ...
... and luminosity to denote how much light the star is actually giving off. These two words have analogous magnitude scales. The magnitude scale that measures brightness is the one that Hipparchus thought up. We call it Apparent Magnitude, often denoted m. The scale corresponding to luminosity is calle ...
The cosmic distance scale
... Since r1 = r0 + ∆ r, if we measure T0 and T1, and ∆ r using the lineshifts in the spectrum, we can solve for r0, and thereby derive its total luminosity and so its distance. We may choose to compare two epochs when the colour of the star is the same, that is when T0 = T1. In that case, the above equ ...
... Since r1 = r0 + ∆ r, if we measure T0 and T1, and ∆ r using the lineshifts in the spectrum, we can solve for r0, and thereby derive its total luminosity and so its distance. We may choose to compare two epochs when the colour of the star is the same, that is when T0 = T1. In that case, the above equ ...
Exam 2
... structures. This diversity holds clues about stellar evolution and about numerous ways in which stars interact with their environments. For example, some of the heavy elements (such as carbon, nitrogen and oxygen) that form in a star’s core move into its outer layers. The abundance of these elements ...
... structures. This diversity holds clues about stellar evolution and about numerous ways in which stars interact with their environments. For example, some of the heavy elements (such as carbon, nitrogen and oxygen) that form in a star’s core move into its outer layers. The abundance of these elements ...
81 KB - CSIRO Publishing
... may initially be based on appearance to the human eye (e.g. Hubble 1926), but to make progress this taxonomy may need to have some basis in the underlying nature or physics of the objects being examined. With this mind, astronomers need a working definition so as to divide objects into different cat ...
... may initially be based on appearance to the human eye (e.g. Hubble 1926), but to make progress this taxonomy may need to have some basis in the underlying nature or physics of the objects being examined. With this mind, astronomers need a working definition so as to divide objects into different cat ...
The Milky Way
... 7. With the 100-inch telescope, Harlow Shapley could not resolve variable stars in the more distant globular clusters of the Milky Way. What basic assumption did Shapley make about the faraway globular clusters that allowed their distances to be ...
... 7. With the 100-inch telescope, Harlow Shapley could not resolve variable stars in the more distant globular clusters of the Milky Way. What basic assumption did Shapley make about the faraway globular clusters that allowed their distances to be ...
VESPA`s bins
... HWT12 forms fewer stars at early times (ie high redshift) but a higher starformation rate at all subsequent times. ...
... HWT12 forms fewer stars at early times (ie high redshift) but a higher starformation rate at all subsequent times. ...
The Sun, Our Star
... (A) Photograph of the Zeeman effect in a sunspot. Notice that the line is split over the spot where the magnetic field is strong but that the line is unsplit outside the spot where the field is weak or absent. (B) Magnetogram of the Sun. Yellow indicates regions with north polarity and dark blue in ...
... (A) Photograph of the Zeeman effect in a sunspot. Notice that the line is split over the spot where the magnetic field is strong but that the line is unsplit outside the spot where the field is weak or absent. (B) Magnetogram of the Sun. Yellow indicates regions with north polarity and dark blue in ...
Black Hole Accretion
... Blackbody emission from optically thick gas at temperature T TB > 1010 K would peak in -rays (and would outshine the universe!!): L = 4R2T4 ~ 1062 erg/s Sgr A* is definitely not doing this!! Therefore, the radiation from Sgr A* must be emitted by gas that is optically thin in IR/X-rays/-rays ...
... Blackbody emission from optically thick gas at temperature T TB > 1010 K would peak in -rays (and would outshine the universe!!): L = 4R2T4 ~ 1062 erg/s Sgr A* is definitely not doing this!! Therefore, the radiation from Sgr A* must be emitted by gas that is optically thin in IR/X-rays/-rays ...
Document
... while the disk is home to stars of all ages. In addition, halo stars have a much smaller proportion of heavy elements than stars in the disk. • What does the environment around hot stars look like? • High-mass, hot stars energize spectacular ionization and reflection nebulae in the gas and dust arou ...
... while the disk is home to stars of all ages. In addition, halo stars have a much smaller proportion of heavy elements than stars in the disk. • What does the environment around hot stars look like? • High-mass, hot stars energize spectacular ionization and reflection nebulae in the gas and dust arou ...
Spectral Variations of Three RV Tauri Stars Donald K. Walter
... UZ Oph, TT Oph and AD Aql are classified as RV Tauri stars in the General Catalog of Variable Stars (GCVS). We present preliminary results of our study of the spectral variations of these stars including observations from 2003 to the present. Changes on the order of several spectral types and lumino ...
... UZ Oph, TT Oph and AD Aql are classified as RV Tauri stars in the General Catalog of Variable Stars (GCVS). We present preliminary results of our study of the spectral variations of these stars including observations from 2003 to the present. Changes on the order of several spectral types and lumino ...
compound sentences
... 2. Dad brought a pair of binoculars, and Nate used them to look for animals. 3. He saw his first live bear, and the hair stood up on his arms. 4. It was an exciting moment, but it only lasted a second. ...
... 2. Dad brought a pair of binoculars, and Nate used them to look for animals. 3. He saw his first live bear, and the hair stood up on his arms. 4. It was an exciting moment, but it only lasted a second. ...
The Sun Section 1 The Sun`s Energy, continued
... • In the second step, another proton combines with this proton-neutron pair to produce a nucleus made up of two protons and one neutron. • In the third step, two nuclei made up of two protons and one neutron collide and fuse. • As this fusion happens, two protons are released. The remaining two prot ...
... • In the second step, another proton combines with this proton-neutron pair to produce a nucleus made up of two protons and one neutron. • In the third step, two nuclei made up of two protons and one neutron collide and fuse. • As this fusion happens, two protons are released. The remaining two prot ...
ParalStellarDist.V2doc
... Parallax is defined as the apparent motion of a nearby object relative to a more distant background due to the observer changing position. There is a definite relationship between the amount of parallax observed and the distance to the object: the greater the distance, the smaller the parallax. Also ...
... Parallax is defined as the apparent motion of a nearby object relative to a more distant background due to the observer changing position. There is a definite relationship between the amount of parallax observed and the distance to the object: the greater the distance, the smaller the parallax. Also ...
Temperate Earth-sized planets transiting a nearby ultracool
... Earth6, favouring instead compositions dominated by ice-rich material originating from beyond the ice line7. Confirming this hypothesis will require precise mass measurements so as to break the degeneracy between the relative amounts of iron, silicates and ice22. This should be made possible by next ...
... Earth6, favouring instead compositions dominated by ice-rich material originating from beyond the ice line7. Confirming this hypothesis will require precise mass measurements so as to break the degeneracy between the relative amounts of iron, silicates and ice22. This should be made possible by next ...
Cygnus X-1
... Cygnus X1 Cygnus X-1 is one of the most likely candidates as being a black hole. Cygnus X-1 is about 14,000 light years away from earth. So this means that what we are seeing, is many, many, years old. It is a very inconsistent source for X-ray emissions. The emissions of X-rays for Cygnus X-1 flic ...
... Cygnus X1 Cygnus X-1 is one of the most likely candidates as being a black hole. Cygnus X-1 is about 14,000 light years away from earth. So this means that what we are seeing, is many, many, years old. It is a very inconsistent source for X-ray emissions. The emissions of X-rays for Cygnus X-1 flic ...
Astro-MilkyWay
... 7. With the 100-inch telescope, Harlow Shapley could not resolve variable stars in the more distant globular clusters of the Milky Way. What basic assumption did Shapley make about the faraway globular clusters that allowed their distances to be ...
... 7. With the 100-inch telescope, Harlow Shapley could not resolve variable stars in the more distant globular clusters of the Milky Way. What basic assumption did Shapley make about the faraway globular clusters that allowed their distances to be ...
Chapter 15
... 7. With the 100-inch telescope, Harlow Shapley could not resolve variable stars in the more distant globular clusters of the Milky Way. What basic assumption did Shapley make about the faraway globular clusters that allowed their distances to be ...
... 7. With the 100-inch telescope, Harlow Shapley could not resolve variable stars in the more distant globular clusters of the Milky Way. What basic assumption did Shapley make about the faraway globular clusters that allowed their distances to be ...
26.2 Stars - Clinton Public Schools
... is much closer than other stars. The brightness of a star as it appears from Earth is called its apparent magnitude. The apparent brightness of a star decreases as its distance from you increases. ...
... is much closer than other stars. The brightness of a star as it appears from Earth is called its apparent magnitude. The apparent brightness of a star decreases as its distance from you increases. ...
Facilitator`s Guide
... There are many “measuring sticks” that are used to measure distance in astronomy. They are placed in order on what is called the Distance Ladder. Some of the “rungs” on this ladder are named as follows: Parallax, Spectroscopic parallax, star clusters, Cepheid Variable Stars, Type Ia Supernovae The p ...
... There are many “measuring sticks” that are used to measure distance in astronomy. They are placed in order on what is called the Distance Ladder. Some of the “rungs” on this ladder are named as follows: Parallax, Spectroscopic parallax, star clusters, Cepheid Variable Stars, Type Ia Supernovae The p ...
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy
... There are other stars whose luminosity varies in a regular way, but much more subtly. These are called intrinsic variables. Two types of intrinsic variables have been found: RR Lyrae stars and Cepheids. ...
... There are other stars whose luminosity varies in a regular way, but much more subtly. These are called intrinsic variables. Two types of intrinsic variables have been found: RR Lyrae stars and Cepheids. ...
Supernova Neutrinos
... for astronomers. SNEWS exists to alert astronomers of a nearby supernova. ...
... for astronomers. SNEWS exists to alert astronomers of a nearby supernova. ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.