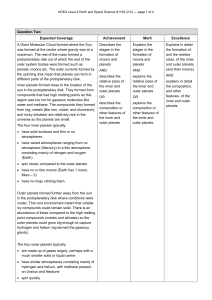
Great Migrations & other natural history tales
... fuels a black hole (BH). 300 light-years across, the disk is tipped by 60 deg, to provide a clear view of the bright inner disk. The dark, dusty disk represents a cold outer region which extends inwards to an ultra-hot accretion disk with a few AU from the BH. This disk feeds matter into the BH, whe ...
... fuels a black hole (BH). 300 light-years across, the disk is tipped by 60 deg, to provide a clear view of the bright inner disk. The dark, dusty disk represents a cold outer region which extends inwards to an ultra-hot accretion disk with a few AU from the BH. This disk feeds matter into the BH, whe ...
Sample Schedule 2012
... the surface is low compared to the high luminosity and the star sits in an area on the HR diagram that is unusual with high luminosity but low temperature. White Dwarfs are the leftover hot core of planetary nebula. They do not have any nuclear fuel so cool down over time. This core is extremely den ...
... the surface is low compared to the high luminosity and the star sits in an area on the HR diagram that is unusual with high luminosity but low temperature. White Dwarfs are the leftover hot core of planetary nebula. They do not have any nuclear fuel so cool down over time. This core is extremely den ...
Signatures of planets and of planet formation in debris disks Mark
... Explains 24 and 70m stats 24 and 70μm statistics explained using a population model (Wyatt et al. 2007; Lohne et al. 2008): • All stars have one planetesimal belt that evolves in steady state from t=0 • Distribution of initial mass is that of protoplanetary disks, and of radii is n(r) r-0.8 ...
... Explains 24 and 70m stats 24 and 70μm statistics explained using a population model (Wyatt et al. 2007; Lohne et al. 2008): • All stars have one planetesimal belt that evolves in steady state from t=0 • Distribution of initial mass is that of protoplanetary disks, and of radii is n(r) r-0.8 ...
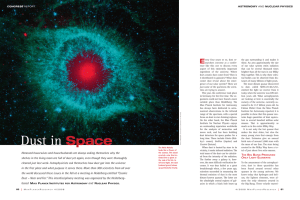
Dust in Space - Max-Planck
... does cosmic dust come from? How is it distributed in galaxies? What does comet dust reveal about the emergence of our solar system? These are just some of the questions the scientists are trying to answer. This year, the conference took place in Germany for the first time. The organizers could not h ...
... does cosmic dust come from? How is it distributed in galaxies? What does comet dust reveal about the emergence of our solar system? These are just some of the questions the scientists are trying to answer. This year, the conference took place in Germany for the first time. The organizers could not h ...
Chromospherically young, kinematically old stars
... interpreted as a sign of its youth. Young dwarfs show high rotation rates, and the interaction between rotation and outer envelope convection is expected to drive the chromospheric activity. Nevertheless, not only young single stars present high rotation rates. Close and contact binaries can keep hi ...
... interpreted as a sign of its youth. Young dwarfs show high rotation rates, and the interaction between rotation and outer envelope convection is expected to drive the chromospheric activity. Nevertheless, not only young single stars present high rotation rates. Close and contact binaries can keep hi ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... typical HR-diagram: Stars plotted according to their surface temperature (or color) and absolute magnitude. The y-axis shows both the luminosity and the absolute magnitude M of the stars (remember: these are just two different measures of the same property, check that you understand this). Note that ...
... typical HR-diagram: Stars plotted according to their surface temperature (or color) and absolute magnitude. The y-axis shows both the luminosity and the absolute magnitude M of the stars (remember: these are just two different measures of the same property, check that you understand this). Note that ...
arXiv:1502.04693v1 [gr
... As confusion with lensing B-modes begins to limit experiments that search for primordial B-mode polarization, robust methods for delensing the CMB polarization sky are becoming increasingly important. We investigate in detail the possibility of delensing the CMB with the cosmic infrared background ( ...
... As confusion with lensing B-modes begins to limit experiments that search for primordial B-mode polarization, robust methods for delensing the CMB polarization sky are becoming increasingly important. We investigate in detail the possibility of delensing the CMB with the cosmic infrared background ( ...
PLANETS
... planetary system. The disk does not start at the star. Rather, its inner edge begins around 25 AU away, farther than the average orbital distance of Uranus in the Solar System. Its outer edge appears to extend as far out as 550 AUs away from the star. Analysis of Hubble Space Telescope data indicate ...
... planetary system. The disk does not start at the star. Rather, its inner edge begins around 25 AU away, farther than the average orbital distance of Uranus in the Solar System. Its outer edge appears to extend as far out as 550 AUs away from the star. Analysis of Hubble Space Telescope data indicate ...
The negative equivalent mass of gravitational fields
... The negative equivalent mass of gravitational fields by Phillips V. Bradford, Sc.D. Ratios of negative gravitational mass to ordinary mass for known objects: To get some idea about the amount of equivalent mass associated with the negative energy in the gravitational fields, it may be instructive to ...
... The negative equivalent mass of gravitational fields by Phillips V. Bradford, Sc.D. Ratios of negative gravitational mass to ordinary mass for known objects: To get some idea about the amount of equivalent mass associated with the negative energy in the gravitational fields, it may be instructive to ...
... around 280 parts per million (ppm) to around 380 ppm now. Studies of ice core show that concentrations of CO2 have not been so high for nearly half a million years. At the current rate of increase, they will have reached 800 ppm by the end of the 21st century! Beyond 550 ppm it would not be liveable ...
Chapter 12: Stars and Galaxies
... based on luminosity and temperature. Two of these star groupings lie above the main sequence line. The group closest to the main sequence has large-diameter stars with lower temperatures. They are called red giants. The stars in the group at the top of an H-R diagram are very large and have varying ...
... based on luminosity and temperature. Two of these star groupings lie above the main sequence line. The group closest to the main sequence has large-diameter stars with lower temperatures. They are called red giants. The stars in the group at the top of an H-R diagram are very large and have varying ...
Determining Distances to Other Galaxies
... If stars in the disk of a spiral galaxy are on slightly eccentric orbits, and the position angle of these ellipses vary with radius, a spiral-shaped density wave can be formed from a set of nested ovals. Density wave theory is really based on the premise that mutual gravitational attraction of stars ...
... If stars in the disk of a spiral galaxy are on slightly eccentric orbits, and the position angle of these ellipses vary with radius, a spiral-shaped density wave can be formed from a set of nested ovals. Density wave theory is really based on the premise that mutual gravitational attraction of stars ...
Draco: The Dragon - Courtney Stookey
... distant. While Eltanin is the brightest star in the constellation, Thuban, or 3445 alpha Draconis, is not very noticeable in comparison. This star is referred to as ‘the basilisk’. Thuban is a binary star that includes a white giant and a red or white dwarf. These stars are more than 300 light years ...
... distant. While Eltanin is the brightest star in the constellation, Thuban, or 3445 alpha Draconis, is not very noticeable in comparison. This star is referred to as ‘the basilisk’. Thuban is a binary star that includes a white giant and a red or white dwarf. These stars are more than 300 light years ...
The Mighty Hunter in the Winter Sky By Shannon Jackson
... Five constellations are always in our northern sky. Other groupings appear seasonally, and then disappear as they fall below the horizon. There are five constellations, however, which seem to circle Polaris (po LAR us), also known as the North Star. The North Star always stays put while the other st ...
... Five constellations are always in our northern sky. Other groupings appear seasonally, and then disappear as they fall below the horizon. There are five constellations, however, which seem to circle Polaris (po LAR us), also known as the North Star. The North Star always stays put while the other st ...
3.2 Black body Radiation
... An electron orbits a nucleus in a stable energy level. If a photon of a specific frequency interacts with the electron, it can gain sufficient energy to "jump up" one or more levels. The photon is absorbed by the electron so cannot continue on to be detected by an observer. The electron then "de-exc ...
... An electron orbits a nucleus in a stable energy level. If a photon of a specific frequency interacts with the electron, it can gain sufficient energy to "jump up" one or more levels. The photon is absorbed by the electron so cannot continue on to be detected by an observer. The electron then "de-exc ...
Unit 13―The “Fixed” Stars
... luminosity decreases with increasing magnitude, generally speaking, the distance to a star increases with increasing magnitude. We cannot be certain that it will be true in every case until we know more about how stars actually produce their light. In the meantime, the scale has a few convenient fea ...
... luminosity decreases with increasing magnitude, generally speaking, the distance to a star increases with increasing magnitude. We cannot be certain that it will be true in every case until we know more about how stars actually produce their light. In the meantime, the scale has a few convenient fea ...
topics and terms sheet
... 15. Drag force: proportional to Area * v**2 (cross-sectional area times velocity squared). Increases with increasing speed, so at some point the drag force equals the gravity force. At that point no more acceleration occurs (since there is no more “net force”), so the falling object reaches “termina ...
... 15. Drag force: proportional to Area * v**2 (cross-sectional area times velocity squared). Increases with increasing speed, so at some point the drag force equals the gravity force. At that point no more acceleration occurs (since there is no more “net force”), so the falling object reaches “termina ...
Spagna
... The Chamaeleon region is one of the most active SFR near the Sun, including 3 large dark clouds (Cha I, Cha II and Cha III) and several small isolated clouds with 100
... The Chamaeleon region is one of the most active SFR near the Sun, including 3 large dark clouds (Cha I, Cha II and Cha III) and several small isolated clouds with 100
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.