Space Vocabulary - Primary Grades Class Page
... It is a large ball of rock or gas that follows a path around the sun (An object moving around a star.) ...
... It is a large ball of rock or gas that follows a path around the sun (An object moving around a star.) ...
Spectral Class and Colour index
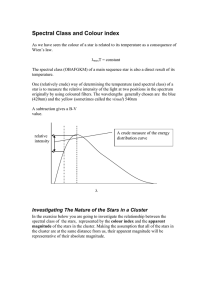
... Spectral Class and Colour index As we have seen the colour of a star is related to its temperature as a consequence of Wien’s law. λmaxT = constant The spectral class (OBAFGKM) of a main sequence star is also a direct result of its temperature. One (relatively crude) way of determining the temperatu ...
... Spectral Class and Colour index As we have seen the colour of a star is related to its temperature as a consequence of Wien’s law. λmaxT = constant The spectral class (OBAFGKM) of a main sequence star is also a direct result of its temperature. One (relatively crude) way of determining the temperatu ...
9ol.ASTRONOMY 1 ... Identify Terms - Matching (20 @ 1 point each =...
... 33. Would parallax be easier to measure if the Earth’s orbit were larger? Why or why not? 34. What is absolute visual magnitude? 35. What does a star’s luminosity depend on? 36. What can you deduce from the spectral lines in the solar spectrum? 37. How can the temperature of a star be determined? ...
... 33. Would parallax be easier to measure if the Earth’s orbit were larger? Why or why not? 34. What is absolute visual magnitude? 35. What does a star’s luminosity depend on? 36. What can you deduce from the spectral lines in the solar spectrum? 37. How can the temperature of a star be determined? ...
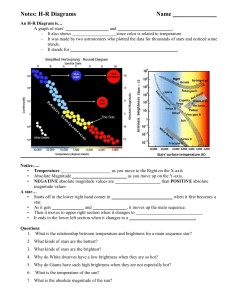
H-R Diagram Notes
... • Temperature ______________________ as you move to the Right on the X-axis • Absolute Magnitude ________________________ as you move up on the Y-axis. • NEGATIVE absolute magnitude values are ____________________ than POSITIVE absolute magnitude values A star… • Starts off in the lower right hand c ...
... • Temperature ______________________ as you move to the Right on the X-axis • Absolute Magnitude ________________________ as you move up on the Y-axis. • NEGATIVE absolute magnitude values are ____________________ than POSITIVE absolute magnitude values A star… • Starts off in the lower right hand c ...
doc
... These two explosive phenomena are both thought to be triggered by matter from a nearby star accreting onto a white dwarf. -> Novae, and Type I-a supernovae. --- Type II supernovae are caused by core-collapse and explosion of a supergiant star. ...
... These two explosive phenomena are both thought to be triggered by matter from a nearby star accreting onto a white dwarf. -> Novae, and Type I-a supernovae. --- Type II supernovae are caused by core-collapse and explosion of a supergiant star. ...
PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Syllabus: Phys 200 (3 cr
... Stellar Evolution and the Death of Stars Birth of stars. Evolution from the main-sequence to Red Giants. Testing stellar evolution using observed star clusters. Evolution to white Dwarfs, Neutron Stars or Black Holes. ...
... Stellar Evolution and the Death of Stars Birth of stars. Evolution from the main-sequence to Red Giants. Testing stellar evolution using observed star clusters. Evolution to white Dwarfs, Neutron Stars or Black Holes. ...
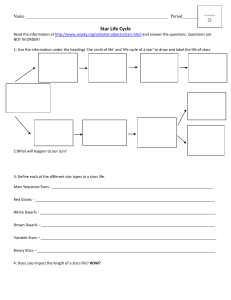
Characteristics of Stars WS Questions 1-20
... 6. Describe in detail how parallax is used to measure the distances to nearby stars. ...
... 6. Describe in detail how parallax is used to measure the distances to nearby stars. ...
Gravitation Worksheet
... 4. Discuss the variation in ‘g’ with altitude and depth. 5. Derive expression for escape velocity. 6. State and prove Kepler’s second and third law of planetary motion 7. How much faster than its present rate should earth rotate about its axis so that the weight of a body at equator becomes zero? 8. ...
... 4. Discuss the variation in ‘g’ with altitude and depth. 5. Derive expression for escape velocity. 6. State and prove Kepler’s second and third law of planetary motion 7. How much faster than its present rate should earth rotate about its axis so that the weight of a body at equator becomes zero? 8. ...
Some facts and concepts to have at your fingertips.
... wavelengths if the object is moving away from the observer. These are called redshifts. • An object that shows emission or absorption lines will have lines shifted toward shorter wavelengths if the object is moving towards the observer. These are called blueshifts. • Cold atomic hydrogen gas (e.g., ...
... wavelengths if the object is moving away from the observer. These are called redshifts. • An object that shows emission or absorption lines will have lines shifted toward shorter wavelengths if the object is moving towards the observer. These are called blueshifts. • Cold atomic hydrogen gas (e.g., ...
Life: Definition, Origin, Criteria
... • Planets should form naturally out of stellar ‘debris’ in the disk • We can now detect many planets, from Jupiter to Earth size ...
... • Planets should form naturally out of stellar ‘debris’ in the disk • We can now detect many planets, from Jupiter to Earth size ...
Life: Definition, Origin, Criteria
... • Planets should form naturally out of stellar ‘debris’ in the disk • We can now detect many planets, from Jupiter to Earth size ...
... • Planets should form naturally out of stellar ‘debris’ in the disk • We can now detect many planets, from Jupiter to Earth size ...
07 May: Omnis In Exitu Eius Pulchrima
... reflected light from a planet is tiny compared with the light emitted by a star ...
... reflected light from a planet is tiny compared with the light emitted by a star ...
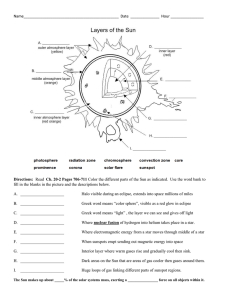
Ch. 20-2 Sun Study Gd. Revised
... Halo visible during an eclipse, extends into space millions of miles ...
... Halo visible during an eclipse, extends into space millions of miles ...
Astro 101-001 Summer 2013 (Howard) Assignment #3 Due: Wed
... 1. Adams and Leverrier both predicted the position of Neptune, based on its effects on: (a) the Sun; (b) Jupiter; (c) Saturn; (d) Uranus; (e) Pluto. 2. Which of these is the most unusual feature of Pluto's orbit? (a) It lies exactly on the ecliptic; (b) It has the lowest eccentricity of any planet's ...
... 1. Adams and Leverrier both predicted the position of Neptune, based on its effects on: (a) the Sun; (b) Jupiter; (c) Saturn; (d) Uranus; (e) Pluto. 2. Which of these is the most unusual feature of Pluto's orbit? (a) It lies exactly on the ecliptic; (b) It has the lowest eccentricity of any planet's ...
Name Date Period ______ 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions
... 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions: Define the following terms IN COMPLETE SENTENCES. 1. star: ...
... 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions: Define the following terms IN COMPLETE SENTENCES. 1. star: ...
SNC 1PW - TeacherWeb
... 23. ___________ are huge clouds of dust and gases that are the birthplace of stars. 24. A _______________ is an enormous explosion at the end of a large star’s life. By this stage, the star has used up all of its fuel needed to continue nuclear fusion. 25. A __________ ________ is a small, very dens ...
... 23. ___________ are huge clouds of dust and gases that are the birthplace of stars. 24. A _______________ is an enormous explosion at the end of a large star’s life. By this stage, the star has used up all of its fuel needed to continue nuclear fusion. 25. A __________ ________ is a small, very dens ...
Stars are classified according to their color
... between the stars. • Distance that light travels in one year. Its about 9.5 million million kilometers. That is not a typo! ...
... between the stars. • Distance that light travels in one year. Its about 9.5 million million kilometers. That is not a typo! ...
File
... Large natural objects which revolve around a planet many planets have more than one moon Earth’s moon has no atmosphere and has hills/valleys/craters after the invention of the telescope Galileo saw 4 moons of Jupiter Moons can come in a variety of size and with a variety of surfaces ...
... Large natural objects which revolve around a planet many planets have more than one moon Earth’s moon has no atmosphere and has hills/valleys/craters after the invention of the telescope Galileo saw 4 moons of Jupiter Moons can come in a variety of size and with a variety of surfaces ...
The Planet with Three Suns
... star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But despite this, this planet is not ...
... star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But despite this, this planet is not ...
Sun, Earth and Moon Model
... is a planet orbiting a distant star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But de ...
... is a planet orbiting a distant star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But de ...
Solar System - U
... The four inner or terrestrial planets have dense, rocky compositions, few or no moons, and no ring systems. They are composed largely of refractory minerals, such as the silicates, which form their crusts and mantles, and metals, such as iron and nickel, which form their cores. Three of the four in ...
... The four inner or terrestrial planets have dense, rocky compositions, few or no moons, and no ring systems. They are composed largely of refractory minerals, such as the silicates, which form their crusts and mantles, and metals, such as iron and nickel, which form their cores. Three of the four in ...
The genesis and characteristics of black holes
... Different phases: ◦ hydrogen burning ◦ helium burning ◦ carbon, neon, oxygen, silicate burning ...
... Different phases: ◦ hydrogen burning ◦ helium burning ◦ carbon, neon, oxygen, silicate burning ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.