Astro-MilkyWay
... 13. How are Population II stars different than the Sun? a. The orbits of Population II stars are more circular than Population I stars. b. Population II stars are lower in metals than Population I stars. c. Population II stars are located only in the disk of the Galaxy. d. All of the above. e. The S ...
... 13. How are Population II stars different than the Sun? a. The orbits of Population II stars are more circular than Population I stars. b. Population II stars are lower in metals than Population I stars. c. Population II stars are located only in the disk of the Galaxy. d. All of the above. e. The S ...
Chapter 15
... 13. How are Population II stars different than the Sun? a. The orbits of Population II stars are more circular than Population I stars. b. Population II stars are lower in metals than Population I stars. c. Population II stars are located only in the disk of the Galaxy. d. All of the above. e. The S ...
... 13. How are Population II stars different than the Sun? a. The orbits of Population II stars are more circular than Population I stars. b. Population II stars are lower in metals than Population I stars. c. Population II stars are located only in the disk of the Galaxy. d. All of the above. e. The S ...
Presentation
... Stellar mass within the red galaxy population doubles. Star forming blue galaxies are being transformed. The most luminous galaxies were assembled at z>1. Some simulations overestimate z<1 galaxy assembly. ...
... Stellar mass within the red galaxy population doubles. Star forming blue galaxies are being transformed. The most luminous galaxies were assembled at z>1. Some simulations overestimate z<1 galaxy assembly. ...
ASTR2100 - Saint Mary's University | Astronomy & Physics
... the distance to the Andromeda Nebula using Cepheid variables. Somewhat less well-known is Lindblad’s 1926 development of a mathematical model for Galactic rotation. Lindblad’s model was developed further in 1927-28 by Oort, who demonstrated its applicability to the radial velocity data for stars. Fi ...
... the distance to the Andromeda Nebula using Cepheid variables. Somewhat less well-known is Lindblad’s 1926 development of a mathematical model for Galactic rotation. Lindblad’s model was developed further in 1927-28 by Oort, who demonstrated its applicability to the radial velocity data for stars. Fi ...
The Milky Way
... • The gravitational field of this spiral pattern causes stars and gas to slow down near the arm • This compresses the interstellar clouds, triggering the formation of stars • The entire arm pattern rotates around the Milky Way once every 500 million years ...
... • The gravitational field of this spiral pattern causes stars and gas to slow down near the arm • This compresses the interstellar clouds, triggering the formation of stars • The entire arm pattern rotates around the Milky Way once every 500 million years ...
15-3 Notes: Galaxies
... 15-3 Notes: Galaxies Large groups of stars, dust, and gas are called galaxies. Galaxies come in a variety of sizes and shapes. The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Astronomers classify a galaxy as a spiral, elliptical, or irregular galaxy according to its shape. Spiral galaxies, ...
... 15-3 Notes: Galaxies Large groups of stars, dust, and gas are called galaxies. Galaxies come in a variety of sizes and shapes. The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Astronomers classify a galaxy as a spiral, elliptical, or irregular galaxy according to its shape. Spiral galaxies, ...
22 pm - Starmap
... As a starting point, face North, holding the map in your eyesight direction, with its North down. As you change the direction, rotate the map accordingly. The objects listed on the first page can be observed with naked eyes, in clear skies, with moderate light pollution. Close your eyes one minute a ...
... As a starting point, face North, holding the map in your eyesight direction, with its North down. As you change the direction, rotate the map accordingly. The objects listed on the first page can be observed with naked eyes, in clear skies, with moderate light pollution. Close your eyes one minute a ...
The Marathon
... M102. Many believe that M102 was originally a duplicate of M101, but many feel that NGC 5866 was the galaxy that Messier and Méchain meant to catalog. We haven't got time to debate the issue, so just check it off and move on! We now take a break from galaxies and look for some more globular clusters ...
... M102. Many believe that M102 was originally a duplicate of M101, but many feel that NGC 5866 was the galaxy that Messier and Méchain meant to catalog. We haven't got time to debate the issue, so just check it off and move on! We now take a break from galaxies and look for some more globular clusters ...
Stellarium Night Sky Search Key Commands Constellations buttons
... Move your view to due North. Find Polaris. Click on it and hit the space bar to center it in your view. The constellations that circle the North Star are visible to us all year long and are called the circumpolar constellations. List them here. After you quit Stellarium, find the common name for eac ...
... Move your view to due North. Find Polaris. Click on it and hit the space bar to center it in your view. The constellations that circle the North Star are visible to us all year long and are called the circumpolar constellations. List them here. After you quit Stellarium, find the common name for eac ...
astrocoursespring2012lec5-1-1
... While M65 is almost edge-on in appearance, M66 is angles so that we see more of its face, including one spiral arm that hangs more limply tha the other, as if the galaxy had suffered some cosmic fall that injured its shoulder – David Levy, p. 193 http://www.asod.info/?p=1699 (image asod – Dale Holt ...
... While M65 is almost edge-on in appearance, M66 is angles so that we see more of its face, including one spiral arm that hangs more limply tha the other, as if the galaxy had suffered some cosmic fall that injured its shoulder – David Levy, p. 193 http://www.asod.info/?p=1699 (image asod – Dale Holt ...
Galaxies
... Often: result of galaxy collisions / mergers Often: Very active star formation (“Starburst galaxies”) Some: Small (“Dwarf galaxies”) satellites of larger galaxies ...
... Often: result of galaxy collisions / mergers Often: Very active star formation (“Starburst galaxies”) Some: Small (“Dwarf galaxies”) satellites of larger galaxies ...
Long Ago and Far Away
... of detail that HST provides in visible light. 1.The galaxy (or merging pair) on page 1 with recession velocity 0.058 LY/yr is a rare example of a fairly nearby “ultraluminous infrared galaxy,” which is experiencing a starburst as intense as those seen in young, distant galaxies. Using the ratio of t ...
... of detail that HST provides in visible light. 1.The galaxy (or merging pair) on page 1 with recession velocity 0.058 LY/yr is a rare example of a fairly nearby “ultraluminous infrared galaxy,” which is experiencing a starburst as intense as those seen in young, distant galaxies. Using the ratio of t ...
V: 0
... Using an electronic device, research one of the following galaxies: Andromeda, Messier 87 (M-87), Small Magellanic Cloud, Sombrero Galaxy, Tadpole Galaxy. On page 40 of your INB: 1. Name the galaxy you are researching and the type of galaxy it is (spiral, elliptical, irregular). 2. What is its dista ...
... Using an electronic device, research one of the following galaxies: Andromeda, Messier 87 (M-87), Small Magellanic Cloud, Sombrero Galaxy, Tadpole Galaxy. On page 40 of your INB: 1. Name the galaxy you are researching and the type of galaxy it is (spiral, elliptical, irregular). 2. What is its dista ...
Leo Powerpoint
... Hercules plugged one of the openings and entered the den empty-handed from the other. He strangled the lion to his death and using one of his claws tore away his skin, which he later used as an impermeable armor on his body for the remaining 11 tasks that he had to complete. As Hercules came out suc ...
... Hercules plugged one of the openings and entered the den empty-handed from the other. He strangled the lion to his death and using one of his claws tore away his skin, which he later used as an impermeable armor on his body for the remaining 11 tasks that he had to complete. As Hercules came out suc ...
Archaeology of the Milky Way - Max-Planck
... individual stars in detail, in large numbers and in three dimensions,” he says. Fortunately, our Milky Way is a typical galaxy, and what we learn about it can be generalized. Around half the stars in today’s universe are found in galaxies that are similar to our Milky Way in terms of size, mass and ...
... individual stars in detail, in large numbers and in three dimensions,” he says. Fortunately, our Milky Way is a typical galaxy, and what we learn about it can be generalized. Around half the stars in today’s universe are found in galaxies that are similar to our Milky Way in terms of size, mass and ...
Define luminosity - The Student Room
... 1. Define the absolute magnitude of a star 2. Explain how it is based on luminosity. 3. State the relation between apparent magnitude m, absolute magnitude M and distance r. 4. Derive the absolute magnitude equation using the inverse square law of radiation. 5. For Rigel, apparent magnitude m=+0.3 a ...
... 1. Define the absolute magnitude of a star 2. Explain how it is based on luminosity. 3. State the relation between apparent magnitude m, absolute magnitude M and distance r. 4. Derive the absolute magnitude equation using the inverse square law of radiation. 5. For Rigel, apparent magnitude m=+0.3 a ...
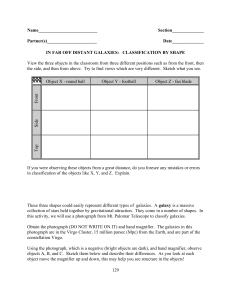
In Far Off Distant Galaxies: Classification by Shape
... Object A is a star in the fore ground (located between observer and Virgo Cluster). They are bright Milky Way Galaxy stars showing diffraction spikes (an artifact of the telescope). Object B is a spiral galaxy in the Virgo Cluster. It is disk shaped with arms. The two or more arms are visible due to ...
... Object A is a star in the fore ground (located between observer and Virgo Cluster). They are bright Milky Way Galaxy stars showing diffraction spikes (an artifact of the telescope). Object B is a spiral galaxy in the Virgo Cluster. It is disk shaped with arms. The two or more arms are visible due to ...
Andromeda Galaxy
.jpg?width=300)
The Andromeda Galaxy (/ænˈdrɒmɨdə/), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy approximately 780 kiloparsecs (2.5 million light-years) from Earth. It is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way and was often referred to as the Great Andromeda Nebula in older texts. It received its name from the area of the sky in which it appears, the constellation of Andromeda, which was named after the mythological princess Andromeda. Being approximately 220,000 light years across, it is the largest galaxy of the Local Group, which also contains the Milky Way, the Triangulum Galaxy, and about 44 other smaller galaxies.The Andromeda Galaxy is the most massive galaxy in the Local Group as well. Despite earlier findings that suggested that the Milky Way contains more dark matter and could be the most massive in the grouping, the 2006 observations by the Spitzer Space Telescope revealed that Andromeda contains one trillion (1012) stars: at least twice the number of stars in the Milky Way, which is estimated to be 200–400 billion.The Andromeda Galaxy is estimated to be 1.5×1012 solar masses, while the mass of the Milky Way is estimated to be 8.5×1011 solar masses. In comparison, a 2009 study estimated that the Milky Way and M31 are about equal in mass, while a 2006 study put the mass of the Milky Way at ~80% of the mass of the Andromeda Galaxy. The Milky Way and Andromeda are expected to collide in 3.75 billion years, eventually merging to form a giant elliptical galaxy or perhaps a large disk galaxy.At 3.4, the apparent magnitude of the Andromeda Galaxy is one of the brightest of any of the Messier objects, making it visible to the naked eye on moonless nights even when viewed from areas with moderate light pollution. Although it appears more than six times as wide as the full Moon when photographed through a larger telescope, only the brighter central region is visible to the naked eye or when viewed using binoculars or a small telescope and would it hence appear to be but another star.













![Dust Mapping Our Galaxy 1 [12.1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008843408_1-27426dc8e4663be1f32bca5fc2999474-300x300.png)