Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... and Matt Weisner. see their theses at www.physics.niu.edu/physics/academic/grad/theses1.shtml) ...
... and Matt Weisner. see their theses at www.physics.niu.edu/physics/academic/grad/theses1.shtml) ...
Dark Matter -24-------------------------------~-----------R-E-S-O-N-A-N-C
... (i) It doesn't exist; the law of gravitation must be modified so that the stars are all there is to a galaxy. (ii) Dark matter exists, but consists entirely of ord~nary matter - Jupiter-like objects called broum dwarfs that are not massive enough to start the stellar energy-generating process of nuc ...
... (i) It doesn't exist; the law of gravitation must be modified so that the stars are all there is to a galaxy. (ii) Dark matter exists, but consists entirely of ord~nary matter - Jupiter-like objects called broum dwarfs that are not massive enough to start the stellar energy-generating process of nuc ...
observing the universe
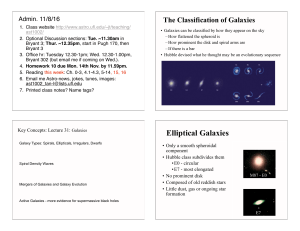
... A galaxy is an assembly of between a billion (109) and a hundred billion (1011) stars. There is often a large amount of dust and gas intermingled, all held together by gravity. The Sun and Earth are in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies have many different characteristics, but the easiest way to classif ...
... A galaxy is an assembly of between a billion (109) and a hundred billion (1011) stars. There is often a large amount of dust and gas intermingled, all held together by gravity. The Sun and Earth are in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies have many different characteristics, but the easiest way to classif ...
Our Place in Space
... International Space Station, Moon, Mars, Sun, Saturn, Pleiades, Orion Nebula, M13 Globular Cluster, Large Magellanic Cloud, Andromeda Galaxy, one of the Galaxy Clusters (Stephan’s Quintet or Virgo Supercluster; Although Stephan’s Quintet is further from Earth it is impossible for a student to kno ...
... International Space Station, Moon, Mars, Sun, Saturn, Pleiades, Orion Nebula, M13 Globular Cluster, Large Magellanic Cloud, Andromeda Galaxy, one of the Galaxy Clusters (Stephan’s Quintet or Virgo Supercluster; Although Stephan’s Quintet is further from Earth it is impossible for a student to kno ...
Stars and the Milky Way
... • It is called the Milky Way because when astronomers looked up at the sky, they saw a line of light that looked like some milk had been spilt. • Stars in our Milky Way can be white, yellow or red. White stars are the hottest and red are the coolest. • It takes light over 100,000 years to travel fro ...
... • It is called the Milky Way because when astronomers looked up at the sky, they saw a line of light that looked like some milk had been spilt. • Stars in our Milky Way can be white, yellow or red. White stars are the hottest and red are the coolest. • It takes light over 100,000 years to travel fro ...
What Globular Clusters Teach Us About Oleg Gnedin
... begin with cosmological simulations of halo formation supplement halos with cold gas mass based on observations use MGC - Mgas relation from hydro simulations metallicity from observed M* - Z relation for host galaxies, including evolution with time ...
... begin with cosmological simulations of halo formation supplement halos with cold gas mass based on observations use MGC - Mgas relation from hydro simulations metallicity from observed M* - Z relation for host galaxies, including evolution with time ...
Hoag`s Object
... In the initial announcement of his discovery, Art Hoag proposed the hypothesis that the visible ring was a product of gravitational lensing. This idea was later discarded because the nucleus and the ring have the same redshift, and because more advanced telescopes revealed the knotty structure of th ...
... In the initial announcement of his discovery, Art Hoag proposed the hypothesis that the visible ring was a product of gravitational lensing. This idea was later discarded because the nucleus and the ring have the same redshift, and because more advanced telescopes revealed the knotty structure of th ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... - contains globular clusters, old stars, little gas and dust, much "dark matter" - roughly spherical ...
... - contains globular clusters, old stars, little gas and dust, much "dark matter" - roughly spherical ...
CHP 15
... ____ 31. Astronomers before Shapely underestimated the size of the Milky Way galaxy because they lacked large enough telescopes. ____ 32. Shapley found the distance to the center of the galaxy by studying the distance to open clusters. ____ 33. The disk of the Milky Way is approximately 20,000 ly in ...
... ____ 31. Astronomers before Shapely underestimated the size of the Milky Way galaxy because they lacked large enough telescopes. ____ 32. Shapley found the distance to the center of the galaxy by studying the distance to open clusters. ____ 33. The disk of the Milky Way is approximately 20,000 ly in ...
The Life Cycle of Spiral Arm Galaxies
... “B” stars using the Yerkes classification system. O-‐type stars are very hot and luminous, and appear in the visible spectrum as bluish-‐white. These stars are commonly called giants, and supergiants. ...
... “B” stars using the Yerkes classification system. O-‐type stars are very hot and luminous, and appear in the visible spectrum as bluish-‐white. These stars are commonly called giants, and supergiants. ...
powerpoint
... • In the centers of clusters you tend to find Giant Elliptical Galaxies that can be 10-100 times more massive than our galaxy. • Spirals tend to hang on their own – but often have small satellite galaxies. • The smallest galaxies are dwarf ellipticals. • Elliptical galaxies don’t have much dust or g ...
... • In the centers of clusters you tend to find Giant Elliptical Galaxies that can be 10-100 times more massive than our galaxy. • Spirals tend to hang on their own – but often have small satellite galaxies. • The smallest galaxies are dwarf ellipticals. • Elliptical galaxies don’t have much dust or g ...
20 pm - Starmap
... A faint spiral galaxy in the Virgo Cluster. Nice bluish color with a bright yellow core. ...
... A faint spiral galaxy in the Virgo Cluster. Nice bluish color with a bright yellow core. ...
D109: A Spectactularly Forgotten Galaxy Aggregate
... Introduction and Background: Often times identifying the characteristics of extreme examples of galaxy morphology and properties (e.g. Perseus A, Malin 1, NGC 1569) provides very important constraints on our overall understanding of galaxy evolution. Since these extreme galaxies exist, then there ar ...
... Introduction and Background: Often times identifying the characteristics of extreme examples of galaxy morphology and properties (e.g. Perseus A, Malin 1, NGC 1569) provides very important constraints on our overall understanding of galaxy evolution. Since these extreme galaxies exist, then there ar ...
Chapter 5 Galaxies and Star Systems
... Spiral galaxies are those that appear to have a bulge in the middle and arms that spiral outward, like pinwheels. The spiral arms contain many bright, young stars as well as gas and dust. Most new stars in the spiral galaxies form in theses spiral arms. Relatively few new stars form in the central b ...
... Spiral galaxies are those that appear to have a bulge in the middle and arms that spiral outward, like pinwheels. The spiral arms contain many bright, young stars as well as gas and dust. Most new stars in the spiral galaxies form in theses spiral arms. Relatively few new stars form in the central b ...
Milky Way Galaxy
... The Universe is filled with these star systems which themselves cluster together into larger systems. ...
... The Universe is filled with these star systems which themselves cluster together into larger systems. ...
Andromeda Galaxy
.jpg?width=300)
The Andromeda Galaxy (/ænˈdrɒmɨdə/), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy approximately 780 kiloparsecs (2.5 million light-years) from Earth. It is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way and was often referred to as the Great Andromeda Nebula in older texts. It received its name from the area of the sky in which it appears, the constellation of Andromeda, which was named after the mythological princess Andromeda. Being approximately 220,000 light years across, it is the largest galaxy of the Local Group, which also contains the Milky Way, the Triangulum Galaxy, and about 44 other smaller galaxies.The Andromeda Galaxy is the most massive galaxy in the Local Group as well. Despite earlier findings that suggested that the Milky Way contains more dark matter and could be the most massive in the grouping, the 2006 observations by the Spitzer Space Telescope revealed that Andromeda contains one trillion (1012) stars: at least twice the number of stars in the Milky Way, which is estimated to be 200–400 billion.The Andromeda Galaxy is estimated to be 1.5×1012 solar masses, while the mass of the Milky Way is estimated to be 8.5×1011 solar masses. In comparison, a 2009 study estimated that the Milky Way and M31 are about equal in mass, while a 2006 study put the mass of the Milky Way at ~80% of the mass of the Andromeda Galaxy. The Milky Way and Andromeda are expected to collide in 3.75 billion years, eventually merging to form a giant elliptical galaxy or perhaps a large disk galaxy.At 3.4, the apparent magnitude of the Andromeda Galaxy is one of the brightest of any of the Messier objects, making it visible to the naked eye on moonless nights even when viewed from areas with moderate light pollution. Although it appears more than six times as wide as the full Moon when photographed through a larger telescope, only the brighter central region is visible to the naked eye or when viewed using binoculars or a small telescope and would it hence appear to be but another star.