PH607lec11-4gal2
... Disks: metal rich stars and ISM, nearly circular orbits with little random motion, spiral patterns Bulge: metal poor to super-rich stars, high stellar densities, mostly random motion – similar to ellipticals Bar: present in 50 % of disk galaxies, long lived, flat, linear distribution of stars ...
... Disks: metal rich stars and ISM, nearly circular orbits with little random motion, spiral patterns Bulge: metal poor to super-rich stars, high stellar densities, mostly random motion – similar to ellipticals Bar: present in 50 % of disk galaxies, long lived, flat, linear distribution of stars ...
14. The Milky Way Galaxy: A Spiral in Space
... • These objects are very close to the Galactic center. The orbit on the right of star S2 is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of about 4 million solar masses. ...
... • These objects are very close to the Galactic center. The orbit on the right of star S2 is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of about 4 million solar masses. ...
The Great Debate - The Story Behind The Science
... but actually in the process of forming stars. Following the 1885 nova, astronomers looked more closely at the spiral nebulae. By 1900, over 100,000 nebulae had been detected. These twisted, whirlpool-like objects seemed as if they would condense into stars or planetary systems over time. If nebulae ...
... but actually in the process of forming stars. Following the 1885 nova, astronomers looked more closely at the spiral nebulae. By 1900, over 100,000 nebulae had been detected. These twisted, whirlpool-like objects seemed as if they would condense into stars or planetary systems over time. If nebulae ...
Our Local Group of Galaxies
... How complete is the list of Milky Way dSph companions? • Grey area shows region of the sky covered in Data Release 6 of the SDSS. Previously known MW satellites are marked in blue, new discoveries in red. Solid black line and middle grey stripe are at declination zero - inside is the region to be s ...
... How complete is the list of Milky Way dSph companions? • Grey area shows region of the sky covered in Data Release 6 of the SDSS. Previously known MW satellites are marked in blue, new discoveries in red. Solid black line and middle grey stripe are at declination zero - inside is the region to be s ...
How do stars orbit in our galaxy?
... • Active star-forming regions, marked by the presence of hot, massive stars and ionization nebulae, are found preferentially in spiral arms. The spiral arms represent regions where a spiral density wave has caused gas clouds to crash into each other, thereby compressing them and making star formatio ...
... • Active star-forming regions, marked by the presence of hot, massive stars and ionization nebulae, are found preferentially in spiral arms. The spiral arms represent regions where a spiral density wave has caused gas clouds to crash into each other, thereby compressing them and making star formatio ...
Absolute magnitude of type Ia supernovae
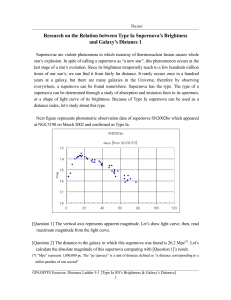
... Research on the Relation between Type Ia Supernova’s Brightness and Galaxy’s Distance 1 Supernovae are violent phenomena in which runaway of thermonuclear fusion causes whole star’s explosion. In spite of calling a supernova as “a new star”, this phenomenon occurs at the last stage of a star’s evolu ...
... Research on the Relation between Type Ia Supernova’s Brightness and Galaxy’s Distance 1 Supernovae are violent phenomena in which runaway of thermonuclear fusion causes whole star’s explosion. In spite of calling a supernova as “a new star”, this phenomenon occurs at the last stage of a star’s evolu ...
the printable Observing Olympics Object Info Sheet in pdf
... stars to produce this gas is ∿5.5 million years. NGC5846 was discovered by Willian Herschel on Feb. 24, 1786. NGC5907 – This edge-on spiral galaxy is located approximately 50 million light years from Earth and is also known as the “Knife Edge” or “Splinter” Galaxy. Visually it appears as a very thin ...
... stars to produce this gas is ∿5.5 million years. NGC5846 was discovered by Willian Herschel on Feb. 24, 1786. NGC5907 – This edge-on spiral galaxy is located approximately 50 million light years from Earth and is also known as the “Knife Edge” or “Splinter” Galaxy. Visually it appears as a very thin ...
Galaxy Structure
... structural components are the disk including the barred bulge with a central cusp, and most likely four spiral arms, a halo as well as a more extended corona including the Magellanic clouds and at least seven nearby dwarf galaxies and a large number of globular star clusters (see figure 1). The tota ...
... structural components are the disk including the barred bulge with a central cusp, and most likely four spiral arms, a halo as well as a more extended corona including the Magellanic clouds and at least seven nearby dwarf galaxies and a large number of globular star clusters (see figure 1). The tota ...
L6-Diskproperties
... Gas measured from Hα – ionized gas from disk HII regions HI (21cm) – atomic gas – allows us to “see” beyond disk stellar edge CO (2.6mm) – molecular gas (CO used to estimate H2) HI in disks is optically thin – little absorption so mass ≈ intensity *though in MW HI distribution can be hindered by dus ...
... Gas measured from Hα – ionized gas from disk HII regions HI (21cm) – atomic gas – allows us to “see” beyond disk stellar edge CO (2.6mm) – molecular gas (CO used to estimate H2) HI in disks is optically thin – little absorption so mass ≈ intensity *though in MW HI distribution can be hindered by dus ...
v = H o χ d “Hubble`s Law”
... • Milky Way forms about 1 new star per year • Starburst galaxies form 100’s of stars per year ...
... • Milky Way forms about 1 new star per year • Starburst galaxies form 100’s of stars per year ...
Characteristics of Our Galaxy
... variables (useful for judging distances), pre-main sequence stars, T-Tauri stars, Herbigharo objects, and even some A stars can be found in the arms. These stars are very metal rich and have highly circular orbits, although they comprise likely less than one percent of Milky Way stars. Young thin d ...
... variables (useful for judging distances), pre-main sequence stars, T-Tauri stars, Herbigharo objects, and even some A stars can be found in the arms. These stars are very metal rich and have highly circular orbits, although they comprise likely less than one percent of Milky Way stars. Young thin d ...
The first billion years of galaxy formation and evolution
... For the first time it will be possible to do a detailed characterization of the ISM in primeval galaxies during the epoch of reionization This will revolutionize our understanding of galaxy formation and evolution at all cosmic epochs ...
... For the first time it will be possible to do a detailed characterization of the ISM in primeval galaxies during the epoch of reionization This will revolutionize our understanding of galaxy formation and evolution at all cosmic epochs ...
CONSTELLATION CEPHEUS, KING OF ETHIOPIA Cepheus is a
... NGC 6946 (The Fireworks Galaxy) is a spiral galaxy in which nine supernovae have been observed, more than in any other galaxy. IC 469 is another spiral galaxy, characterized by a compact nucleus, of oval shape, with perceptible side arms. NGC 7538 nebula is home to the largest yet discovered protost ...
... NGC 6946 (The Fireworks Galaxy) is a spiral galaxy in which nine supernovae have been observed, more than in any other galaxy. IC 469 is another spiral galaxy, characterized by a compact nucleus, of oval shape, with perceptible side arms. NGC 7538 nebula is home to the largest yet discovered protost ...
File - Mr. Pelton Science
... • Galaxy clusters larger than the Local Group may have hundreds or thousands of members with diameters up to 30 million ly across. • Galaxies close together often collide to form strangely shaped galaxies or galaxies with more than one nucleus (Andromeda) ...
... • Galaxy clusters larger than the Local Group may have hundreds or thousands of members with diameters up to 30 million ly across. • Galaxies close together often collide to form strangely shaped galaxies or galaxies with more than one nucleus (Andromeda) ...
Andromeda Galaxy
.jpg?width=300)
The Andromeda Galaxy (/ænˈdrɒmɨdə/), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy approximately 780 kiloparsecs (2.5 million light-years) from Earth. It is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way and was often referred to as the Great Andromeda Nebula in older texts. It received its name from the area of the sky in which it appears, the constellation of Andromeda, which was named after the mythological princess Andromeda. Being approximately 220,000 light years across, it is the largest galaxy of the Local Group, which also contains the Milky Way, the Triangulum Galaxy, and about 44 other smaller galaxies.The Andromeda Galaxy is the most massive galaxy in the Local Group as well. Despite earlier findings that suggested that the Milky Way contains more dark matter and could be the most massive in the grouping, the 2006 observations by the Spitzer Space Telescope revealed that Andromeda contains one trillion (1012) stars: at least twice the number of stars in the Milky Way, which is estimated to be 200–400 billion.The Andromeda Galaxy is estimated to be 1.5×1012 solar masses, while the mass of the Milky Way is estimated to be 8.5×1011 solar masses. In comparison, a 2009 study estimated that the Milky Way and M31 are about equal in mass, while a 2006 study put the mass of the Milky Way at ~80% of the mass of the Andromeda Galaxy. The Milky Way and Andromeda are expected to collide in 3.75 billion years, eventually merging to form a giant elliptical galaxy or perhaps a large disk galaxy.At 3.4, the apparent magnitude of the Andromeda Galaxy is one of the brightest of any of the Messier objects, making it visible to the naked eye on moonless nights even when viewed from areas with moderate light pollution. Although it appears more than six times as wide as the full Moon when photographed through a larger telescope, only the brighter central region is visible to the naked eye or when viewed using binoculars or a small telescope and would it hence appear to be but another star.