Clusters
... ICM in the centres of galaxy clusters should be rapidly cooling at the rate of tens to thousands of solar masses per year this should happen as the ICM is quickly losing its energy by the emission of X-rays X-ray brightness of the ICM is proportional to the square of its density, which rises steeply ...
... ICM in the centres of galaxy clusters should be rapidly cooling at the rate of tens to thousands of solar masses per year this should happen as the ICM is quickly losing its energy by the emission of X-rays X-ray brightness of the ICM is proportional to the square of its density, which rises steeply ...
Milky Way
... •When a low mass object orbits a high mass object, there is a simple relationship between the distance and the velocity: ...
... •When a low mass object orbits a high mass object, there is a simple relationship between the distance and the velocity: ...
PH607lec12-5gal3
... Disks: metal rich stars and ISM, nearly circular orbits with little random motion, spiral patterns Bulge: metal poor to super-rich stars, high stellar densities, mostly random motion – similar to ellipticals Bar: present in 50 % of disk galaxies, long lived, flat, linear distribution of stars ...
... Disks: metal rich stars and ISM, nearly circular orbits with little random motion, spiral patterns Bulge: metal poor to super-rich stars, high stellar densities, mostly random motion – similar to ellipticals Bar: present in 50 % of disk galaxies, long lived, flat, linear distribution of stars ...
chapter19MilkyWay
... Why do orbits of bulge stars bob up and down? A. They’re stuck to interstellar medium B. Gravity of disk stars pulls toward disk C. Halo stars knock them back into disk ...
... Why do orbits of bulge stars bob up and down? A. They’re stuck to interstellar medium B. Gravity of disk stars pulls toward disk C. Halo stars knock them back into disk ...
3D Tour of the Universe Template
... regions, resulting in the formation of new young stars. As is common in these kinds of encounters, spiral structure was induced in the more massive galaxy. M51 is an easily found astronomical showpiece if the sky is dark, where suggestions of its spiral arms may be visible. As is also common with th ...
... regions, resulting in the formation of new young stars. As is common in these kinds of encounters, spiral structure was induced in the more massive galaxy. M51 is an easily found astronomical showpiece if the sky is dark, where suggestions of its spiral arms may be visible. As is also common with th ...
PDF format
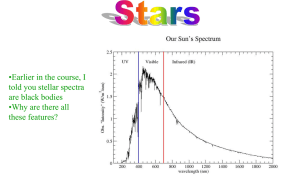
... d) It depends on the standard candle: if they are Cepheid variables, they will still pulsate at the same rate no matter what distance they are from you. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... d) It depends on the standard candle: if they are Cepheid variables, they will still pulsate at the same rate no matter what distance they are from you. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
슬라이드 1
... that there are 2,201 barred galaxies (fbar = 12.6%) by visual inspection and by ellipse fitting, and that fraction of barred galaxy rise to 17.6% when consider only moderately inclined systems with b/a≥ 0.65. The fraction of barred galaxy can be described as functions of several physical properties ...
... that there are 2,201 barred galaxies (fbar = 12.6%) by visual inspection and by ellipse fitting, and that fraction of barred galaxy rise to 17.6% when consider only moderately inclined systems with b/a≥ 0.65. The fraction of barred galaxy can be described as functions of several physical properties ...
US - Real Science
... Around one quarter of all large stars are born in starburst galaxies such as this. They spawn stars up to a thousand times faster than the Milky Way. In most starbursts the surge in starbirth is triggered when two galaxies come too close together. Mutual attraction between the galaxies causes immens ...
... Around one quarter of all large stars are born in starburst galaxies such as this. They spawn stars up to a thousand times faster than the Milky Way. In most starbursts the surge in starbirth is triggered when two galaxies come too close together. Mutual attraction between the galaxies causes immens ...
Galaxies
... • Astronomers now have decided that the morphology classification should consist of only two types of galaxies: the spiral and the elliptical. • Barred spirals are a subclass of spirals. Irregulars may be either spiral or barred spiral. ...
... • Astronomers now have decided that the morphology classification should consist of only two types of galaxies: the spiral and the elliptical. • Barred spirals are a subclass of spirals. Irregulars may be either spiral or barred spiral. ...
Chapter 14
... 14.7 The Galactic Center These objects are very close to the galactic center. The orbit on the right is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of 3.7 million solar masses. ...
... 14.7 The Galactic Center These objects are very close to the galactic center. The orbit on the right is the best fit; it assumes a central black hole of 3.7 million solar masses. ...
margarita2007
... one • Surviving satellites are predominantly low-mass systems and have been accreted recently • The building blocks of the stellar halo were on average more massive and were accreted (and disrupted) earlier than de population of satellites that survive until the present • These results may help to e ...
... one • Surviving satellites are predominantly low-mass systems and have been accreted recently • The building blocks of the stellar halo were on average more massive and were accreted (and disrupted) earlier than de population of satellites that survive until the present • These results may help to e ...
Sec 30.1 - Highland High School
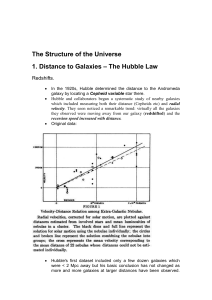
... What method did astronomers use to determine the shape of the Milky Way galaxy? a. measuring X-ray emissions b. observing Cepheid variables c. mapping the galaxy with radio waves d. sending out long-range space probes ...
... What method did astronomers use to determine the shape of the Milky Way galaxy? a. measuring X-ray emissions b. observing Cepheid variables c. mapping the galaxy with radio waves d. sending out long-range space probes ...
A Universe of Galaxies
... Quasars have enormous redshifts, indicating that they are moving away from us at more than 90% of the speed of light. Objects moving that fast wouldn’t remain near us for long, so quasars must be very far away. If they can be seen even at such large distances, their luminosities must be very high – ...
... Quasars have enormous redshifts, indicating that they are moving away from us at more than 90% of the speed of light. Objects moving that fast wouldn’t remain near us for long, so quasars must be very far away. If they can be seen even at such large distances, their luminosities must be very high – ...
Small galaxies are growing smaller
... 16–20 Mpc away. Studies of Virgo by Allan Sandage, Bruno Binggeli and Gustav Tammann, and of Fornax by Sandage and Harry Ferguson, revealed many low surface brightness objects looking just like Local Group dwarf ellipticals (though some contain central nuclei), dwarf irregulars and even dwarf sphero ...
... 16–20 Mpc away. Studies of Virgo by Allan Sandage, Bruno Binggeli and Gustav Tammann, and of Fornax by Sandage and Harry Ferguson, revealed many low surface brightness objects looking just like Local Group dwarf ellipticals (though some contain central nuclei), dwarf irregulars and even dwarf sphero ...
PH607lec08
... The formula z = v / c implies that you can't have redshifts greater than one because that would give you a velocity greater than the speed of light, something not permitted by the laws of physics. ...
... The formula z = v / c implies that you can't have redshifts greater than one because that would give you a velocity greater than the speed of light, something not permitted by the laws of physics. ...
Active Galaxies
... If we block out the light of luminous quasar, we can see evidence of an underlying host galaxy. Quasar hosts appear to be a mixed bag of galaxy types from disturbed galaxies to normal E’s and early type spirals. ...
... If we block out the light of luminous quasar, we can see evidence of an underlying host galaxy. Quasar hosts appear to be a mixed bag of galaxy types from disturbed galaxies to normal E’s and early type spirals. ...
Chapter 20. Galaxies
... – spirals, ellipticals and irregulars. As the name suggests, spirals show evidence of spiral structure if viewed face on or show a clear disk if seen edge on. Ellipticals have a much more uniform distribution of star light and look either spherical or elliptical, depending on their structure and vie ...
... – spirals, ellipticals and irregulars. As the name suggests, spirals show evidence of spiral structure if viewed face on or show a clear disk if seen edge on. Ellipticals have a much more uniform distribution of star light and look either spherical or elliptical, depending on their structure and vie ...
Introduction to Galaxies - West Jefferson Local Schools
... As predicted by Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, a compact intervening object is bending and distorting light from individual members of this cluster so that we see a halo effect. ...
... As predicted by Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, a compact intervening object is bending and distorting light from individual members of this cluster so that we see a halo effect. ...
Estudio de Cúmulos de Galaxias en el Sloan Digital Sky Survey
... A Milky Way mass galaxy is predicted to have a 50% of prob. of having a faint LBG progenitor. & to have a 6% (at z=3) and a 2% (at z=6) of probability of having a bright LBG progenitor. ...
... A Milky Way mass galaxy is predicted to have a 50% of prob. of having a faint LBG progenitor. & to have a 6% (at z=3) and a 2% (at z=6) of probability of having a bright LBG progenitor. ...
RNA-seq Analysis in Galaxy
... Trapnell et al. (2012) Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nature Protocols 7, 562–578 Tophat Manual: http://tophat.cbcb.umd.edu/manual.html Cufflinks Manual: http://cufflinks.cbcb.umd.edu/manual.html ...
... Trapnell et al. (2012) Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nature Protocols 7, 562–578 Tophat Manual: http://tophat.cbcb.umd.edu/manual.html Cufflinks Manual: http://cufflinks.cbcb.umd.edu/manual.html ...
Andromeda Galaxy
.jpg?width=300)
The Andromeda Galaxy (/ænˈdrɒmɨdə/), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy approximately 780 kiloparsecs (2.5 million light-years) from Earth. It is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way and was often referred to as the Great Andromeda Nebula in older texts. It received its name from the area of the sky in which it appears, the constellation of Andromeda, which was named after the mythological princess Andromeda. Being approximately 220,000 light years across, it is the largest galaxy of the Local Group, which also contains the Milky Way, the Triangulum Galaxy, and about 44 other smaller galaxies.The Andromeda Galaxy is the most massive galaxy in the Local Group as well. Despite earlier findings that suggested that the Milky Way contains more dark matter and could be the most massive in the grouping, the 2006 observations by the Spitzer Space Telescope revealed that Andromeda contains one trillion (1012) stars: at least twice the number of stars in the Milky Way, which is estimated to be 200–400 billion.The Andromeda Galaxy is estimated to be 1.5×1012 solar masses, while the mass of the Milky Way is estimated to be 8.5×1011 solar masses. In comparison, a 2009 study estimated that the Milky Way and M31 are about equal in mass, while a 2006 study put the mass of the Milky Way at ~80% of the mass of the Andromeda Galaxy. The Milky Way and Andromeda are expected to collide in 3.75 billion years, eventually merging to form a giant elliptical galaxy or perhaps a large disk galaxy.At 3.4, the apparent magnitude of the Andromeda Galaxy is one of the brightest of any of the Messier objects, making it visible to the naked eye on moonless nights even when viewed from areas with moderate light pollution. Although it appears more than six times as wide as the full Moon when photographed through a larger telescope, only the brighter central region is visible to the naked eye or when viewed using binoculars or a small telescope and would it hence appear to be but another star.