Chapter 19 Test Review Notes
... balancing the weight of the air column that stretches from your head to the top of the atmosphere. Air exerts pressure in all directions. A barograph records and measures air pressure on a chart. ...
... balancing the weight of the air column that stretches from your head to the top of the atmosphere. Air exerts pressure in all directions. A barograph records and measures air pressure on a chart. ...
Weather 101 Water - Sports Turf Managers Association
... compared to amount air can hold at a given ...
... compared to amount air can hold at a given ...
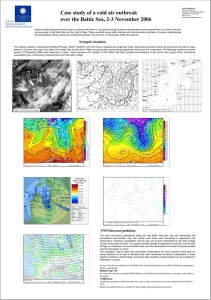
Case study of a cold air outbreak over the Baltic Sea, 2-3
... The weather situation is illustrated by NOAA IR image 2006-11-02/20:51 UTC and a set of analysis and prognostic maps. Mesoscale convection bands forming within the cold air mass behind a cold front over warm sea water of the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Riga were particularly strong along trajectories ...
... The weather situation is illustrated by NOAA IR image 2006-11-02/20:51 UTC and a set of analysis and prognostic maps. Mesoscale convection bands forming within the cold air mass behind a cold front over warm sea water of the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Riga were particularly strong along trajectories ...
Climate and Weather
... As this air cools down, it falls as rain or snow. The windward sides of a mountain tend to be wetter than the leeward sides (the sides sheltered from the wind). Rain Shadow – the area on the leeward side of a mountain that receives little precipitation. ...
... As this air cools down, it falls as rain or snow. The windward sides of a mountain tend to be wetter than the leeward sides (the sides sheltered from the wind). Rain Shadow – the area on the leeward side of a mountain that receives little precipitation. ...
Weather/Climate Study Guide KEY Know the following vocabulary
... 2. What is an air mass? Large body of air that takes on the characteristics of the area over which it forms 3. Do air masses move? Yes and they transfer heat as they go. 4. How are air masses classified? According to their source regions; ex. Continental polar, maritime tropical 5. Which direction d ...
... 2. What is an air mass? Large body of air that takes on the characteristics of the area over which it forms 3. Do air masses move? Yes and they transfer heat as they go. 4. How are air masses classified? According to their source regions; ex. Continental polar, maritime tropical 5. Which direction d ...
Weather Tools
... • Wind speed is an important part of weather. • An anemometer is a weather tool that measures wind speed. ...
... • Wind speed is an important part of weather. • An anemometer is a weather tool that measures wind speed. ...
The Day After Tomorrow
... What process could most likely change the climate? More moisture in the air ...
... What process could most likely change the climate? More moisture in the air ...
Weather
... • We have applied some of the basic principles of atmospheric air movements to gain an understanding of Tasmania’s ...
... • We have applied some of the basic principles of atmospheric air movements to gain an understanding of Tasmania’s ...
8 - Meteorology - Simone Damiano
... A local effect is the breeze. Daytime heating along a beach area warms the land and water at different rates. The land heats up much faster than the water does. The land then heats up the air above it. The air becomes less dense and rises. The cooler air over the water moves in to take its place. Th ...
... A local effect is the breeze. Daytime heating along a beach area warms the land and water at different rates. The land heats up much faster than the water does. The land then heats up the air above it. The air becomes less dense and rises. The cooler air over the water moves in to take its place. Th ...
weather test study guide
... 8. How do clouds form? Water vapor condenses and droplets form on tiny dust particles in the air. When many droplets come together a cloud is formed. 9. What are the four forms of precipitation? Rain, hail, sleet, and snow 10. What causes different types of precipitation? The temperature of the air ...
... 8. How do clouds form? Water vapor condenses and droplets form on tiny dust particles in the air. When many droplets come together a cloud is formed. 9. What are the four forms of precipitation? Rain, hail, sleet, and snow 10. What causes different types of precipitation? The temperature of the air ...
metIstudyguide F14
... 11. What is dew point? 12. The hot seat belt against skin is what form of heat transfer? 13. Earth receives energy from sun through which method? 14. Heat flow that cycles (heat rises & cold sinks) is which form of heat transfer? 15. **Which cloud is… cotton-like & puffy=_____________________ Low & ...
... 11. What is dew point? 12. The hot seat belt against skin is what form of heat transfer? 13. Earth receives energy from sun through which method? 14. Heat flow that cycles (heat rises & cold sinks) is which form of heat transfer? 15. **Which cloud is… cotton-like & puffy=_____________________ Low & ...
Weather and Climate - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets
... 11. The state of the earth's atmosphere at a certain time and place is called http://www.helpteaching.com/tests/159771/weather-and-climate ...
... 11. The state of the earth's atmosphere at a certain time and place is called http://www.helpteaching.com/tests/159771/weather-and-climate ...
Weather and Water Cycle Study Guide
... 2. air mass: large body of air with same temperature and humidity. 3.weather: condition of atmosphere at particular time. 4.climate: pattern of weather in an area over time. 5.current: stream of water that flows like a river in the ocean. 6.meteorology: study of weather. 7.freezing point: the temper ...
... 2. air mass: large body of air with same temperature and humidity. 3.weather: condition of atmosphere at particular time. 4.climate: pattern of weather in an area over time. 5.current: stream of water that flows like a river in the ocean. 6.meteorology: study of weather. 7.freezing point: the temper ...
Atmosphere. Clouds.
... Dew forms due to the ground temperature drop at night. Fog forms when large areas of cool land or water come in contact with air. Clouds form due to air cooling by expansion as it rises. A normal cooling rate of air is 0.65oC for each 100 m of rise. There are several cloud types which form at differ ...
... Dew forms due to the ground temperature drop at night. Fog forms when large areas of cool land or water come in contact with air. Clouds form due to air cooling by expansion as it rises. A normal cooling rate of air is 0.65oC for each 100 m of rise. There are several cloud types which form at differ ...
Warm Spring Night
... 1. Insolation: amount of solar radiation a place receives (amount of daylight & angle of suns rays - Latitude) 2. Elevation: Altitude (air pressure/heat released) 3. Proximity of water bodies: (moderates, continental areas with large lakes) 4. Ocean currents: movement of heat from the equator toward ...
... 1. Insolation: amount of solar radiation a place receives (amount of daylight & angle of suns rays - Latitude) 2. Elevation: Altitude (air pressure/heat released) 3. Proximity of water bodies: (moderates, continental areas with large lakes) 4. Ocean currents: movement of heat from the equator toward ...
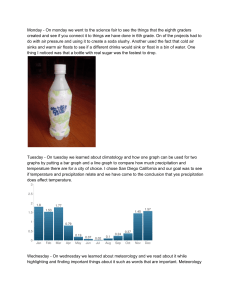
Monday On monday we went to the science fair to see the things that
... created and see if you connect it to things we have done in 6th grade. On of the projects had to do with air pressure and using it to create a soda slushy. Another used the fact that cold air sinks and warm air floats to see if a different drinks would sink or float in a bin of water. One thing I ...
... created and see if you connect it to things we have done in 6th grade. On of the projects had to do with air pressure and using it to create a soda slushy. Another used the fact that cold air sinks and warm air floats to see if a different drinks would sink or float in a bin of water. One thing I ...
“Meteorology”? - U. S. Naval Sea Cadet Corps Resources Page
... • The condensation of water in the atmosphere • Rising air mass cools causing the water vapor to condense into minute ...
... • The condensation of water in the atmosphere • Rising air mass cools causing the water vapor to condense into minute ...
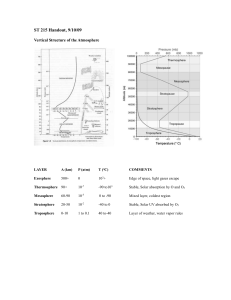
910 Handout, Structure and Composition
... Ancient meaning (Aristotle) was much broader. Climate: Aggregate of regional weather conditions over time. Usually a 30-year average over a region plus a statement about frequency of extreme conditions, such as lightning strikes, tornadoes, hurricanes or drought. Climatology: Scientific study of cli ...
... Ancient meaning (Aristotle) was much broader. Climate: Aggregate of regional weather conditions over time. Usually a 30-year average over a region plus a statement about frequency of extreme conditions, such as lightning strikes, tornadoes, hurricanes or drought. Climatology: Scientific study of cli ...
File
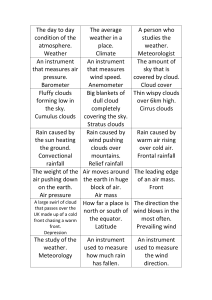
... A large swirl of cloud How far a place is that passes over the north or south of UK made up of a cold the equator. front chasing a warm front. Latitude ...
... A large swirl of cloud How far a place is that passes over the north or south of UK made up of a cold the equator. front chasing a warm front. Latitude ...
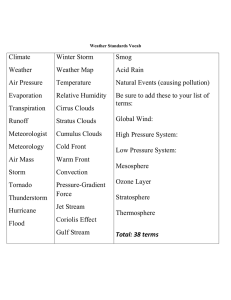
Weather Vocabulary
... Global Wind: heated air rises near the equator and moves toward Earth's poles, while cooler air at the poles falls and moves toward the equator; move in a particular direction across Earth over long distances; often steer weather in different directions. High Pressure System: Formed when an air mass ...
... Global Wind: heated air rises near the equator and moves toward Earth's poles, while cooler air at the poles falls and moves toward the equator; move in a particular direction across Earth over long distances; often steer weather in different directions. High Pressure System: Formed when an air mass ...
The Difference Between Weather and Climate
... *Condensation: occurs when water vapor condenses *Precipitation: rain, sleet, hail, or snow due to gravity *Ground Water: liquid water collected on the surface of earth *Transpiration: the process of releasing water from plants ...
... *Condensation: occurs when water vapor condenses *Precipitation: rain, sleet, hail, or snow due to gravity *Ground Water: liquid water collected on the surface of earth *Transpiration: the process of releasing water from plants ...
Meteorology Study Guide
... 10. ___________________ help us predict the weather by observing the atmosphere and Earth. 11. A summary of the weather conditions over a long period of time is called _______________. 12. ________________ air rises and _______________ air falls. 13. The study of the atmosphere and weather is called ...
... 10. ___________________ help us predict the weather by observing the atmosphere and Earth. 11. A summary of the weather conditions over a long period of time is called _______________. 12. ________________ air rises and _______________ air falls. 13. The study of the atmosphere and weather is called ...
Storm

A storm is any disturbed state of an environment or astronomical body's atmosphere especially affecting its surface, and strongly implying severe weather. It may be marked by significant disruptions to normal conditions such as strong wind, hail, thunder and lightning (a thunderstorm), heavy precipitation (snowstorm, rainstorm), heavy freezing rain (ice storm), strong winds (tropical cyclone, windstorm), or wind transporting some substance through the atmosphere as in a dust storm, blizzard, sandstorm, etc.Storms generally lead to negative impacts on lives and property such as storm surge, heavy rain or snow (causing flooding or road impassibility), lightning, wildfires, and vertical wind shear; however, systems with significant rainfall can alleviate drought in places they move through. Heavy snowfall can allow special recreational activities to take place which would not be possible otherwise, such as skiing and snowmobiling.The English word comes from Proto-Germanic *sturmaz meaning ""noise, tumult"".