Overview of the Earth`s Atmosphere
... Overview of the Earth’s Atmosphere • when the earth is scaled to the size of an apple, 99% of atmosphere is no thicker than the skin on an apple • Water vapor molecules are invisible: clouds; ...
... Overview of the Earth’s Atmosphere • when the earth is scaled to the size of an apple, 99% of atmosphere is no thicker than the skin on an apple • Water vapor molecules are invisible: clouds; ...
Eyewitness
... 4. What keeps our air warm after dark? 5. Who invented Meteorology? 6. What is one way nature can provide a sign of upcoming weather & what does that sign mean? ...
... 4. What keeps our air warm after dark? 5. Who invented Meteorology? 6. What is one way nature can provide a sign of upcoming weather & what does that sign mean? ...
Norwegian Cyclone Model
... • The front is often stationary. • Can be just about any boundary. – Differential heating ...
... • The front is often stationary. • Can be just about any boundary. – Differential heating ...
Norwegian Cyclone model (pdf format)
... – Cause of most of the stormy weather in U.S., especially during the winter season. ...
... – Cause of most of the stormy weather in U.S., especially during the winter season. ...
File - geography and history 1eso social studies
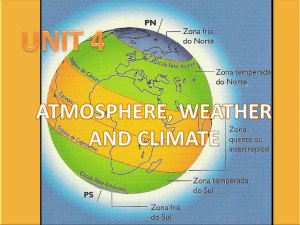
... Temperatures decrease as we There is less precipitation as LATITUDE move away from the equator. we move further away from the equator. The temperature falls 0.64oC for Precipitation is more Pressure decreases the ALTITUDE every 100 metre increase in frequent the higher the higher the altitude height ...
... Temperatures decrease as we There is less precipitation as LATITUDE move away from the equator. we move further away from the equator. The temperature falls 0.64oC for Precipitation is more Pressure decreases the ALTITUDE every 100 metre increase in frequent the higher the higher the altitude height ...
Meteorology 3/2/2016 Which gas comprises a maximum of 4% of the
... For the following questions match the letter with the Question 15) Visible minute water particles at the earths surface that reduce visibility to less the 5/8 mile 16) Visible minute water particles suspended in the atmosphere that reduce visibility to < 7mi ...
... For the following questions match the letter with the Question 15) Visible minute water particles at the earths surface that reduce visibility to less the 5/8 mile 16) Visible minute water particles suspended in the atmosphere that reduce visibility to < 7mi ...
Help for Test
... b. identify the distance between isobars on a weather map indicates the relative change in atmospheric pressure in an area. If the isobars are close together, this means that places that are not far apart experience a large difference in air pressure. As a result, the winds in this region will be ...
... b. identify the distance between isobars on a weather map indicates the relative change in atmospheric pressure in an area. If the isobars are close together, this means that places that are not far apart experience a large difference in air pressure. As a result, the winds in this region will be ...
Chapter01c
... above that level, and atmospheric pressure always decreases with increasing height above the surface. ...
... above that level, and atmospheric pressure always decreases with increasing height above the surface. ...
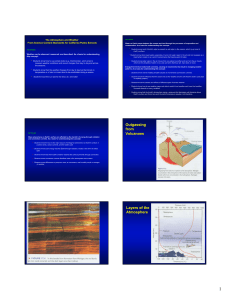
Outgassing from Volcanoes Layers of the Atmosphere
... measure weather conditions and record changes from day to day and across the seasons. ...
... measure weather conditions and record changes from day to day and across the seasons. ...
Weather Unit Notes - Lindbergh School District
... Evaporation: Water turns from liquid to gas. Condensation: Water turns from gas to liquid Dew: moisture condensed from the atmosphere, esp. at night, and deposited in the form of small drops upon any cool surface. Dew Point: The temperature to which air must be cooled for saturation to occur. Sling ...
... Evaporation: Water turns from liquid to gas. Condensation: Water turns from gas to liquid Dew: moisture condensed from the atmosphere, esp. at night, and deposited in the form of small drops upon any cool surface. Dew Point: The temperature to which air must be cooled for saturation to occur. Sling ...
Weather & Climate Chapter 1
... The Sun rises, and the Sun goes down, And hastens to the place where it rises. The wind blows to the south, and goes around to the north. Round and round goes the wind, and on its circuits the wind returns. ...
... The Sun rises, and the Sun goes down, And hastens to the place where it rises. The wind blows to the south, and goes around to the north. Round and round goes the wind, and on its circuits the wind returns. ...
chapter 4 - Maritime Safety Queensland
... breezes may be vigorous by late afternoon, particularly in the summer months. The rising air along coastal hinterlands, particularly where the higher land reinforces the uplift of air, may produce heavy cloud build-ups and possible storms that are likely to drift seaward during the late afternoon. T ...
... breezes may be vigorous by late afternoon, particularly in the summer months. The rising air along coastal hinterlands, particularly where the higher land reinforces the uplift of air, may produce heavy cloud build-ups and possible storms that are likely to drift seaward during the late afternoon. T ...
1. The atmosphere is a layer of gases that surround the earth_
... 2. The 2 most abundant gases in the Earth’s atmosphere are Oxygen and Nitrogen. 3. Instruments that is used to measure air pressure is called a Barometer. 4. As you rise farther in the atmosphere, air pressure decreases ...
... 2. The 2 most abundant gases in the Earth’s atmosphere are Oxygen and Nitrogen. 3. Instruments that is used to measure air pressure is called a Barometer. 4. As you rise farther in the atmosphere, air pressure decreases ...
Atmosphere and Weather Unit notes
... Condensation – Water vapor (gas) turns back to a liquid. (energy required / cold) -cloud formation. ...
... Condensation – Water vapor (gas) turns back to a liquid. (energy required / cold) -cloud formation. ...
Meteorology
... Differences in heating (land vs. water, light vs. dark, rough vs. smooth) cause differences in air pressure which creates winds. ...
... Differences in heating (land vs. water, light vs. dark, rough vs. smooth) cause differences in air pressure which creates winds. ...
Difficult Quiz on Meteorology
... The air flowing around the low pressure center of a large storm rotates a) cyclonically in both hemispheres. b) anti-cyclonically in both hemispheres. c) cyclonically in the northern hemispheres and anti-cyclonically in the southern hemisphere. d) anti-cyclonically in the northern hemisphere and cyc ...
... The air flowing around the low pressure center of a large storm rotates a) cyclonically in both hemispheres. b) anti-cyclonically in both hemispheres. c) cyclonically in the northern hemispheres and anti-cyclonically in the southern hemisphere. d) anti-cyclonically in the northern hemisphere and cyc ...
what to know about meteorology list
... cools as it rises; temperature falls to the dew point; condensation (onto condensation nuclei) of clouds occurs. **Making air rise will almost always make clouds; air rises along fronts, in a low pressure system, up a mountain or just because it is heated so ALL these things are associated with prec ...
... cools as it rises; temperature falls to the dew point; condensation (onto condensation nuclei) of clouds occurs. **Making air rise will almost always make clouds; air rises along fronts, in a low pressure system, up a mountain or just because it is heated so ALL these things are associated with prec ...
notes for meteorofe - pams
... Dew: moisture condensed from the atmosphere, esp. at night, and deposited in the form of small drops upon any cool surface. Dew Point: The temperature to which air must be cooled for saturation to occur. ...
... Dew: moisture condensed from the atmosphere, esp. at night, and deposited in the form of small drops upon any cool surface. Dew Point: The temperature to which air must be cooled for saturation to occur. ...
Earth Science SOL Review Power Point (Oceanography and
... 23. These are the major winds that affect the continental United States ________________________________ 24. How do hurricanes differ from tornadoes? ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ...
... 23. These are the major winds that affect the continental United States ________________________________ 24. How do hurricanes differ from tornadoes? ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ...
Weather Satellite Weather Stations around Fiji
... staff of the Fiji Meteorological Service and others are staff of other government departments, or other organizations. 3. The Automatic Weather Station (AWS) is defined a station which automatically transmits or records observations obtained by measuring instruments. The data derived from AWS includ ...
... staff of the Fiji Meteorological Service and others are staff of other government departments, or other organizations. 3. The Automatic Weather Station (AWS) is defined a station which automatically transmits or records observations obtained by measuring instruments. The data derived from AWS includ ...
Hurricane! - Event
... clouds bring rain? What's a hygrometer? Weather Watch teaches you all about the science of meteorology and the job of weather forecasting. You'll also learn sky-watching techniques, how to read a weather map, and how to build your own weather instruments. Storm Warning: Tornadoes and Hurricanes, Kah ...
... clouds bring rain? What's a hygrometer? Weather Watch teaches you all about the science of meteorology and the job of weather forecasting. You'll also learn sky-watching techniques, how to read a weather map, and how to build your own weather instruments. Storm Warning: Tornadoes and Hurricanes, Kah ...
Unit 8 Day 5
... hemisphere. Meteorology now provides an understanding of the reasons for these reliable winds ...
... hemisphere. Meteorology now provides an understanding of the reasons for these reliable winds ...
Study Guide Unit Meteorology Test
... weather and associate trends to pressure. 30. List three phenomenon associated with a thunderstorm 31. At what water temp do hurricanes form? 32. What type of clouds form in thunderstorms? 33. What causes most hurricane deaths/damage? 34. What is the relationship between pressure gradient and winds? ...
... weather and associate trends to pressure. 30. List three phenomenon associated with a thunderstorm 31. At what water temp do hurricanes form? 32. What type of clouds form in thunderstorms? 33. What causes most hurricane deaths/damage? 34. What is the relationship between pressure gradient and winds? ...
Your Weather Knowledge Study Guide
... Humidity is the amount of water vapor in a certain amount of air; it is compared to the maximum amount of water vapor the air can have at a given temperature. ...
... Humidity is the amount of water vapor in a certain amount of air; it is compared to the maximum amount of water vapor the air can have at a given temperature. ...
Storm

A storm is any disturbed state of an environment or astronomical body's atmosphere especially affecting its surface, and strongly implying severe weather. It may be marked by significant disruptions to normal conditions such as strong wind, hail, thunder and lightning (a thunderstorm), heavy precipitation (snowstorm, rainstorm), heavy freezing rain (ice storm), strong winds (tropical cyclone, windstorm), or wind transporting some substance through the atmosphere as in a dust storm, blizzard, sandstorm, etc.Storms generally lead to negative impacts on lives and property such as storm surge, heavy rain or snow (causing flooding or road impassibility), lightning, wildfires, and vertical wind shear; however, systems with significant rainfall can alleviate drought in places they move through. Heavy snowfall can allow special recreational activities to take place which would not be possible otherwise, such as skiing and snowmobiling.The English word comes from Proto-Germanic *sturmaz meaning ""noise, tumult"".