The Atmosphere
... • Above 80 Km the gases are stratified such that the heavier gases decrease much more rapidly than the lighter ones; this is the HETEROSPHERE • In addition, we can identify four layers in the atmosphere that have distinct characteristics. • The four layers of the atmosphere, in order from lowest to ...
... • Above 80 Km the gases are stratified such that the heavier gases decrease much more rapidly than the lighter ones; this is the HETEROSPHERE • In addition, we can identify four layers in the atmosphere that have distinct characteristics. • The four layers of the atmosphere, in order from lowest to ...
Meteorology Powerpoint
... that reaches Earth is either reflected or absorbed How much is reflected or absorbed depends on surface The fraction that is reflected is called albedo ...
... that reaches Earth is either reflected or absorbed How much is reflected or absorbed depends on surface The fraction that is reflected is called albedo ...
11 Test Review - The Planet Earth
... Multiple Choice/True or false/Fill in the blanks 1. Without proper water and carbon, the earth would be _________. 2. _________ play a significant role in creating a stable temperature through releasing water vapor oxygen by the processes of photosynthesis and transpiration. 3. _______ is the metabo ...
... Multiple Choice/True or false/Fill in the blanks 1. Without proper water and carbon, the earth would be _________. 2. _________ play a significant role in creating a stable temperature through releasing water vapor oxygen by the processes of photosynthesis and transpiration. 3. _______ is the metabo ...
Meteorology_Study_Guide
... ______ 9. The outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere ______ 10. Approximately 21% of Earth's atmosphere is this gas ______ 12. Burning of these have increased CO2 levels in the atmosphere ______ 13. Rise of global temperatures due to increase in CO2 ______ 14. CFCs are destroying this molecule in the ...
... ______ 9. The outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere ______ 10. Approximately 21% of Earth's atmosphere is this gas ______ 12. Burning of these have increased CO2 levels in the atmosphere ______ 13. Rise of global temperatures due to increase in CO2 ______ 14. CFCs are destroying this molecule in the ...
Meteorology Test
... 2) Water Vapor, Carbon Dioxide, Ozone 3) These gases are considered variable because they are not always present in a constant proportion. 4) Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, and Thermosphere 5) An inversion occurs in the stratosphere and thermosphere. 6) Orographic clouds are formed by air be ...
... 2) Water Vapor, Carbon Dioxide, Ozone 3) These gases are considered variable because they are not always present in a constant proportion. 4) Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, and Thermosphere 5) An inversion occurs in the stratosphere and thermosphere. 6) Orographic clouds are formed by air be ...
The Dynamic Earth
... • Almost all ozone (made of 3 oxygen atoms) is located here • Ozone absorbs UV radiation ...
... • Almost all ozone (made of 3 oxygen atoms) is located here • Ozone absorbs UV radiation ...
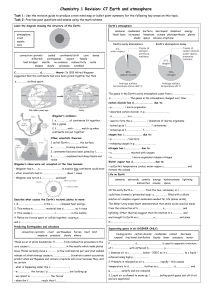
C7 Revision Earth and atmosphere[1].
... • w…………..……… the forces / p……………………………….. are building up ...
... • w…………..……… the forces / p……………………………….. are building up ...
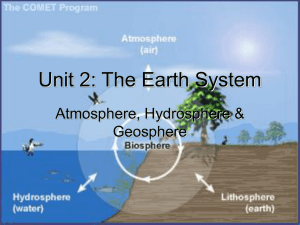
Earth System PP slides
... • Air we breath, plants use in photosynthesis • Filters solar energy, blocking much of harmful UV wavelengths • Protects us from “space junk” • Allows for a natural greenhouse effect keeping earth warm enough for liquid water and life • Cycles moisture and heat throughout earth in moving air systems ...
... • Air we breath, plants use in photosynthesis • Filters solar energy, blocking much of harmful UV wavelengths • Protects us from “space junk” • Allows for a natural greenhouse effect keeping earth warm enough for liquid water and life • Cycles moisture and heat throughout earth in moving air systems ...
The Earth Inside Outside and Above
... • The stratosphere begins six miles above the earth’s surface. The stratosphere is nearly cloudless and really dry except there are ice clouds during the winter. This layer of the atmosphere is still. ...
... • The stratosphere begins six miles above the earth’s surface. The stratosphere is nearly cloudless and really dry except there are ice clouds during the winter. This layer of the atmosphere is still. ...
UNIT 5_THE ATMOSPHERE
... this from escaping back up into space. This is called the greenhouse effect. Without the atmosphere our planet would be much colder. Finally, the atmosphere is a very important filter. There is a layer of a gas called ozone which protects us from some dangerous radiation. ...
... this from escaping back up into space. This is called the greenhouse effect. Without the atmosphere our planet would be much colder. Finally, the atmosphere is a very important filter. There is a layer of a gas called ozone which protects us from some dangerous radiation. ...
Earth`s Systems Study Guide 1. Name the four parts of Earth`s
... 13. What are the tectonic plates? What do they have to do with earthquakes? Formation of mountains? ...
... 13. What are the tectonic plates? What do they have to do with earthquakes? Formation of mountains? ...
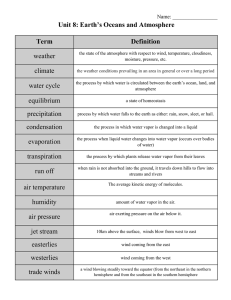
Unit 8: Earth`s Oceans and Atmosphere
... 30 degrees N and S of equator calm winds occurring in both the northern and southern hemispheres between the trade winds and the westerlies. ...
... 30 degrees N and S of equator calm winds occurring in both the northern and southern hemispheres between the trade winds and the westerlies. ...
Colorado State Science Content Standards
... 10. there are interrelationships between the circulation of oceans and weather and climate 11. there are factors that may influence weather patterns and climate and their effects within ecosystems (for example: elevation, proximity to oceans, prevailing winds, fossil fuel burning, volcanic eruption ...
... 10. there are interrelationships between the circulation of oceans and weather and climate 11. there are factors that may influence weather patterns and climate and their effects within ecosystems (for example: elevation, proximity to oceans, prevailing winds, fossil fuel burning, volcanic eruption ...
Presentation
... Includes all life and Concentrated near the surface in a zone that extends from the ocean floor upward for several kilometers into the atmosphere ...
... Includes all life and Concentrated near the surface in a zone that extends from the ocean floor upward for several kilometers into the atmosphere ...
NS2-M3C7_-_Our_Atmosphere_Exam
... The phenomenon whereby the Earth's atmosphere traps solar radiation, caused by the presence in the atmosphere of gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane that allows incoming sunlight to pass through but absorb heat radiated back from the Earth's surface. A B C D ...
... The phenomenon whereby the Earth's atmosphere traps solar radiation, caused by the presence in the atmosphere of gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane that allows incoming sunlight to pass through but absorb heat radiated back from the Earth's surface. A B C D ...
The Origin of Earth
... The remaining 1% is mostly other gases, such as Ar, CO2, He, and H2O The original atmosphere is thought to have come from volcanoes, much like the gases now emitted, which contains no O2 The atmosphere first free O2 likely came from the breakup of water molecules by sunlight in the upper atmosphere ...
... The remaining 1% is mostly other gases, such as Ar, CO2, He, and H2O The original atmosphere is thought to have come from volcanoes, much like the gases now emitted, which contains no O2 The atmosphere first free O2 likely came from the breakup of water molecules by sunlight in the upper atmosphere ...
Chapter 5
... 2nd atmosphere from volcanic activity Mostly carbon dioxide (CO2) l Most CO2 absorbed into oceans → limestone l Early plant life absorbed most of the rest CO2 l Oxygen produced from early plant life l First formed minerals then built up in atmosphere l ...
... 2nd atmosphere from volcanic activity Mostly carbon dioxide (CO2) l Most CO2 absorbed into oceans → limestone l Early plant life absorbed most of the rest CO2 l Oxygen produced from early plant life l First formed minerals then built up in atmosphere l ...
The Human Body and Health
... continental drift. This suggested that the outer layers of the Earth are composed of a number of large pieces called tectonic plates which are moving very slowly. ...
... continental drift. This suggested that the outer layers of the Earth are composed of a number of large pieces called tectonic plates which are moving very slowly. ...
Study Island
... increasing. Many scientists hypothesize that this increase has led to an imbalance in the carbon cycle and a climatic trend known as global warming. In which of the following ways could humans help the carbon cycle return to normal? A. reduce the amount of fossil fuels they combust B. cut down trees ...
... increasing. Many scientists hypothesize that this increase has led to an imbalance in the carbon cycle and a climatic trend known as global warming. In which of the following ways could humans help the carbon cycle return to normal? A. reduce the amount of fossil fuels they combust B. cut down trees ...
Q2 Environmental Science Study Guide
... 8. Tectonic plates move as a result of ________________________ in the magma below. 9. The fault that runs along the center of California and is the site of numbers earthquakes is called the __________________________________. 10. What type of boundary causes each of the following: ...
... 8. Tectonic plates move as a result of ________________________ in the magma below. 9. The fault that runs along the center of California and is the site of numbers earthquakes is called the __________________________________. 10. What type of boundary causes each of the following: ...
Atmosphere of Earth

The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation).The common name air is given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis. By volume, dry air contains 78.09% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.039% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air content and atmospheric pressure vary at different layers, and air suitable for the survival of terrestrial plants and terrestrial animals is found only in Earth's troposphere and artificial atmospheres.The atmosphere has a mass of about 5.15×1018 kg, three quarters of which is within about 11 km (6.8 mi; 36,000 ft) of the surface. The atmosphere becomes thinner and thinner with increasing altitude, with no definite boundary between the atmosphere and outer space. The Kármán line, at 100 km (62 mi), or 1.57% of Earth's radius, is often used as the border between the atmosphere and outer space. Atmospheric effects become noticeable during atmospheric reentry of spacecraft at an altitude of around 120 km (75 mi). Several layers can be distinguished in the atmosphere, based on characteristics such as temperature and composition.The study of Earth's atmosphere and its processes is called atmospheric science (aerology). Early pioneers in the field include Léon Teisserenc de Bort and Richard Assmann.






![C7 Revision Earth and atmosphere[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001217671_1-b9cc347117db8dff9935614904a55b09-300x300.png)