UNIT 1, Chapter 1, Lesson 2
... into liquid to form Earth’s first oceans. This was made possible as Earth’s surface cooled to form a solid surface. 13. The early atmosphere did not have ____________________ to protect Earth from ultraviolet radiation. This radiation helped break apart molecules of methane and ammonia in our atmosp ...
... into liquid to form Earth’s first oceans. This was made possible as Earth’s surface cooled to form a solid surface. 13. The early atmosphere did not have ____________________ to protect Earth from ultraviolet radiation. This radiation helped break apart molecules of methane and ammonia in our atmosp ...
Meteorology – Atmosphere and Sky
... Rising temperature with altitude due to ozone (30 miles). Mesosphere - cooling with height, very thin air, virtually no air pressure, includes the coldest part of the atmosphere (50 miles). Thermosphere – virtually no air, but extreme heating of solid objects, caused by being first line of contact w ...
... Rising temperature with altitude due to ozone (30 miles). Mesosphere - cooling with height, very thin air, virtually no air pressure, includes the coldest part of the atmosphere (50 miles). Thermosphere – virtually no air, but extreme heating of solid objects, caused by being first line of contact w ...
Earth, Sun, Moon Christmas Squares 5.8D
... Meteors burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere before they can strike the Home surface. ...
... Meteors burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere before they can strike the Home surface. ...
Warm ocean current that develops off of the western coast of South
... Areas on Earth where solar radiation strikes at a low angle, resulting in temperatures that are nearly always cold; extends from 66.5 degrees north and south of the equator to the poles ...
... Areas on Earth where solar radiation strikes at a low angle, resulting in temperatures that are nearly always cold; extends from 66.5 degrees north and south of the equator to the poles ...
Earth and atmosphere Topic Checklist
... Metamorphic rocks are formed when rocks are changed by heat and/or pressure Metamorphic rocks include marble (from limestone) and slate (from mudstone) In the rock cycle, rocks are recycled over millions of years Know how individuals can help reduce air pollution Know the meaning of global warming. ...
... Metamorphic rocks are formed when rocks are changed by heat and/or pressure Metamorphic rocks include marble (from limestone) and slate (from mudstone) In the rock cycle, rocks are recycled over millions of years Know how individuals can help reduce air pollution Know the meaning of global warming. ...
Answer Sheet
... Most of the heat energy in the atmosphere is transferred by ____________. A. B. C. D. ...
... Most of the heat energy in the atmosphere is transferred by ____________. A. B. C. D. ...
91 Important Earth Science Facts
... 33. Conduction: molecule to molecule through collisions. 34. Convection: through fluids (gases, liquids) due to density differences. 35. Radiation: through space (vacuum) ex. light. 36. Energy moves source to sink, high to low. 37. Kinetic energy: energy of motion, increases with velocity. 38. Poten ...
... 33. Conduction: molecule to molecule through collisions. 34. Convection: through fluids (gases, liquids) due to density differences. 35. Radiation: through space (vacuum) ex. light. 36. Energy moves source to sink, high to low. 37. Kinetic energy: energy of motion, increases with velocity. 38. Poten ...
The Living Earth
... •Eventually, O2 level stabilized at 21% •N2 are produced by bacteria that extract energy from nitrate minerals ...
... •Eventually, O2 level stabilized at 21% •N2 are produced by bacteria that extract energy from nitrate minerals ...
Earth`s Interior Structure
... •Eventually, O2 level stabilized at 21% •N2 are produced by bacteria that extract energy from nitrate minerals ...
... •Eventually, O2 level stabilized at 21% •N2 are produced by bacteria that extract energy from nitrate minerals ...
Weather/Climate Vocabulary Matching
... Process by which water molecules in liquid water escape into the air as water vapor. The measure of the amount of water vapor in the air. ...
... Process by which water molecules in liquid water escape into the air as water vapor. The measure of the amount of water vapor in the air. ...
Astronomy 211 EXAM 3 2010 April 20 Answer TRUE or FALSE (not
... 7. The lava that comes out of Earth’s volcanoes, wells up from the liquid core. 8. Generally, felsic rocks are found in the core and ultra mafic rocks rocks are found in the mantle. 9. We expect that smaller “planets” are less geologically active, but Io is an exception. 10. The heavily cratered lun ...
... 7. The lava that comes out of Earth’s volcanoes, wells up from the liquid core. 8. Generally, felsic rocks are found in the core and ultra mafic rocks rocks are found in the mantle. 9. We expect that smaller “planets” are less geologically active, but Io is an exception. 10. The heavily cratered lun ...
Cornell Chap 2,5 - Santa Rosa Home
... Chapter 2 Earth’s Physical Systems: Matter, Energy, and Geology Case Study: The Tohoku Earthquake (Summarize) Essential Questions 1. What are the parts of an atom? 2. What are the macromolecules and their function? 3. How do the 2 laws of thermodynamics affect available energy? 4. How do the 3 types ...
... Chapter 2 Earth’s Physical Systems: Matter, Energy, and Geology Case Study: The Tohoku Earthquake (Summarize) Essential Questions 1. What are the parts of an atom? 2. What are the macromolecules and their function? 3. How do the 2 laws of thermodynamics affect available energy? 4. How do the 3 types ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... • Atmosphere is pulled to Earth’s surface by __________________. – Air closes to surface is more ____________ than air found at higher altitudes • ________________ of Atmosphere – The atmosphere is divided into ___ layers based on changes in temp that take place at different altitudes. – ___________ ...
... • Atmosphere is pulled to Earth’s surface by __________________. – Air closes to surface is more ____________ than air found at higher altitudes • ________________ of Atmosphere – The atmosphere is divided into ___ layers based on changes in temp that take place at different altitudes. – ___________ ...
Meteorology 3/2/2016 Which gas comprises a maximum of 4% of the
... 48) Form around mature low pressure areas, with one air mass overtaking another 49) Usually devolves into a shear line from two weak fronts ...
... 48) Form around mature low pressure areas, with one air mass overtaking another 49) Usually devolves into a shear line from two weak fronts ...
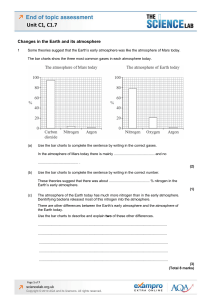
End of topic assessment Unit C1, C1.7
... Why were people living in Kent not warned about this earthquake? ...
... Why were people living in Kent not warned about this earthquake? ...
Changes to the Earth`s rocks and atmosphere
... organisms live in deepish water to avoid ultra-violet rays - photosynthesis begins! ...
... organisms live in deepish water to avoid ultra-violet rays - photosynthesis begins! ...
Chapter 4
... atmosphere in a local area. These include temperature, humidity, clouds, precipitation, wind speed and atmospheric pressure. • Climate- The average weather that occurs in a given region over a long periodtypically several decades. ...
... atmosphere in a local area. These include temperature, humidity, clouds, precipitation, wind speed and atmospheric pressure. • Climate- The average weather that occurs in a given region over a long periodtypically several decades. ...
Solubility of Carbon Dioxide
... and listen to the fizzing noise made by each. SEPERATELY listen to the fizzing The solubility and of the carbon dioxide in water noise made by each. The solubility of So the increases as the temperature decreases. the carbon dioxide inin water decreases water in the bottle put the freezer will have ...
... and listen to the fizzing noise made by each. SEPERATELY listen to the fizzing The solubility and of the carbon dioxide in water noise made by each. The solubility of So the increases as the temperature decreases. the carbon dioxide inin water decreases water in the bottle put the freezer will have ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 1
... 3. If an atmosphere exists and one or more greenhouse gases are present then some of the radiation given off by the planet will be absorbed by the molecules in the gas. In the process the gas heats up and emits infrared radiation itself. However this radiation is in all directions so much of the rad ...
... 3. If an atmosphere exists and one or more greenhouse gases are present then some of the radiation given off by the planet will be absorbed by the molecules in the gas. In the process the gas heats up and emits infrared radiation itself. However this radiation is in all directions so much of the rad ...
ppt
... orbits are typically less than 1000 km above the surface of Earth orbits are usually “sun synchronous” - pass over the same location at the same local time each day have the advantage of viewing Earth directly beneath them ...
... orbits are typically less than 1000 km above the surface of Earth orbits are usually “sun synchronous” - pass over the same location at the same local time each day have the advantage of viewing Earth directly beneath them ...
Earth Science and Climate Change - Brad Hubbard
... • An incompressible fluid – nearly uniform density, depending slightly on salt content and temperature • Large heat capacity – 1000x that of the atmosphere – strong but slow effect on climate • Salty : typically 3.4% concentration by weight • Acidity: pH of 8.1, about 0.1 lower (25% higher acidi ...
... • An incompressible fluid – nearly uniform density, depending slightly on salt content and temperature • Large heat capacity – 1000x that of the atmosphere – strong but slow effect on climate • Salty : typically 3.4% concentration by weight • Acidity: pH of 8.1, about 0.1 lower (25% higher acidi ...
Chapter 15
... • Gases are layered and do not mix much • Air is very thin and contains little moisture • Lower part of stratosphere is -60°C and rises as altitude increases due to the ozone absorbing ultraviolet radiation from the sun ...
... • Gases are layered and do not mix much • Air is very thin and contains little moisture • Lower part of stratosphere is -60°C and rises as altitude increases due to the ozone absorbing ultraviolet radiation from the sun ...
Layers of the Earth
... • The Earth's interior is made of _____________ and ____________. It has ________main layers: 1) the inner core: a _______________ __________________ core 2) the outer core: a _______________ __________________ core 3) the mantle: dense and mostly ______________ _____________ 4) the crust: _________ ...
... • The Earth's interior is made of _____________ and ____________. It has ________main layers: 1) the inner core: a _______________ __________________ core 2) the outer core: a _______________ __________________ core 3) the mantle: dense and mostly ______________ _____________ 4) the crust: _________ ...
Atmosphere of Earth

The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation).The common name air is given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis. By volume, dry air contains 78.09% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.039% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air content and atmospheric pressure vary at different layers, and air suitable for the survival of terrestrial plants and terrestrial animals is found only in Earth's troposphere and artificial atmospheres.The atmosphere has a mass of about 5.15×1018 kg, three quarters of which is within about 11 km (6.8 mi; 36,000 ft) of the surface. The atmosphere becomes thinner and thinner with increasing altitude, with no definite boundary between the atmosphere and outer space. The Kármán line, at 100 km (62 mi), or 1.57% of Earth's radius, is often used as the border between the atmosphere and outer space. Atmospheric effects become noticeable during atmospheric reentry of spacecraft at an altitude of around 120 km (75 mi). Several layers can be distinguished in the atmosphere, based on characteristics such as temperature and composition.The study of Earth's atmosphere and its processes is called atmospheric science (aerology). Early pioneers in the field include Léon Teisserenc de Bort and Richard Assmann.